Posts filed under ‘economy’
The New Abnormal: Living with Negative Rates

Pimco, the $1.5 trillion fixed-income manager located a stone’s throw distance from my office in Newport Beach, famously (or infamously) coined the phrase, “New Normal”. As former Pimco CEO (Mohamed El-Erian) described years ago, around the time of the Great Recession, the New Normal “reflects a growing realization that some of the recent abrupt changes to markets, households, institutions, and government policies are unlikely to be reversed in the next few years. Global growth will be subdued for a while and unemployment high.”
As it turns out, El-Erian was completely wrong in some respects and shrewdly prescient in others. For instance, although the job recovery has been one of the slowest in a generation, 14.5 million private sector jobs have been added since 2010, and the unemployment rate has been more than halved from 10% in early 2009, to below 5% today. However, the pace of global growth has been relatively weak since the 2008-2009 financial crisis, which has forced central banks all over the world to lower interest rates in hope of stimulating growth. Monetary policies around the globe have been cut so much that almost 25% of global GDP is tied to countries with negative interest rates (see chart below).
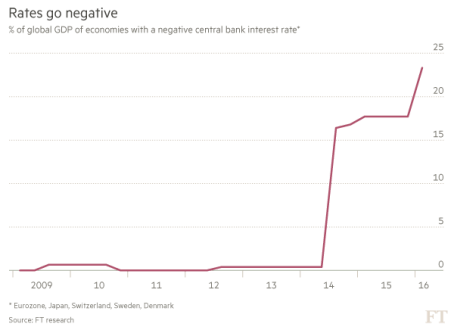
Source: Financial Times
The European central banks started the sub-zero trend in 2014, and the Bank of Japan recently joined the central banks of Denmark, Sweden and Switzerland in negative territory. The negative short-term rate virus has spread further to long-term bonds as well, as evidenced by the 10-Year German Bund (sovereign bond) yield, which crossed into negative territory last week (see chart below).
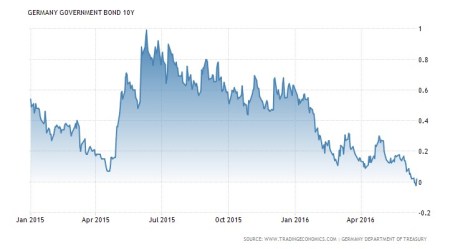
Source: TradingEconomics.com
The New Abnormal
The unprecedented post-crisis move to a 0% Fed Funds rate target, along with the implementation of Quantitative Easing (QE) by former Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke, was already pushing the envelope of “normal” stimulative monetary policy. Nevertheless, central banks pushing rates to a negative threshold takes the whole stimulus discussion to another level because investors are guaranteed to lose money if they hold these bonds until maturity.
As we enter this new submerged rate phase, this activity can only be described as abnormal…not normal. Preserving money at a 0% level and losing value to inflation (i.e., essentially stuffing money under the proverbial mattress) is a bitter enough pill to swallow. Paying somebody to lend them money gives “insanity” a good name.
The stimulative objectives of negative interest policies established by central bankers may be purely intentioned, however there can be plenty of unintentional consequences. For starters, negative rates can produce too much of a good thing, in the form of excess borrowing or leverage. In addition, retirees and savers across a broad spectrum of ages are getting crushed by the paltry rates, and bank profit margins (net interest margins) are getting squeezed to boot.
Another unintended consequence of negative rate policies could be a polar opposite outcome to the envisioned stimulative design. Scott Mather, a co-portfolio manager of the $86 billion PIMCO Total Return Fund (PTTRX) is making the case that these policies could be creating more economic contractionary effects than invigorating expansion. More specifically, Mather notes, “It seems that financial markets increasingly view these experimental moves as desperate and consequently damaging to financial and economic stability.”
Eventually, the cheap money deliberately created by central banks will result in a glut of risk-taking and defaults. However, despite all the cries from hawks protesting money printing policies, cautious bank lending behavior coupled with regulatory handcuffs have yet to create widespread debt bubbles. Certainly, oceans of cheap money can create pockets of problems, as I have identified and discussed in the private equity market (see also Dying Unicorns), but supply and demand rule the day at some point.
In the end, as I have repeatedly documented, money goes where it is treated best. Realizing guaranteed losses while trapped in negative rate bonds is no way to treat your investment portfolio over the long-run. In the short-run, the safety and stability of short duration bonds may sound appealing, but ultimately rational and efficient behavior prevails. Why settle for 0% or negative rates when yields of 2%, 4%, and 6% can be found in plenty of other responsible investment alternatives?
Arguably, in this post financial crisis world we live in, we have transitioned from the New Normal to a New Abnormal environment of negative rates. Pundits and prognosticators will continue spewing fear-filled cautionary advice, but experienced, long-term investors will continue taking advantage of these risk averse markets by investing in a quality, diversified portfolio of superior yielding investments. For now, there are plenty of opportunities to choose from, until the next phase of this economic cycle… when the New Abnormal transitions to the New Normalized.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds , but at the time of publishing had no direct position in PTTRX, or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Cleaning Out Your Investment Fridge

This article is an excerpt from a previously released Sidoxia Capital Management complimentary newsletter (June 1, 2016). Subscribe on the right side of the page for the complete text.
Summer is quickly approaching, but it’s not too late to do some spring cleaning. This principle not only applies to your cluttered refrigerator with stale foods but also your investment portfolio with moldy investments. In both cases, you want to get rid of the spoiled goods. It’s never fun discovering a science experiment growing in your fridge.
Over the last three months, the stock market has been replenished after a rotten first two months of the year (S&P 500 index was down -5.5% January through February). The +1.5% increase in May added to a +6.6% and +0.3% increase in March and April (respectively), resulting in a three month total advance in stock prices of +8.5%. Not surprisingly, the advance in the stock market is mirroring the recovery we have seen in recent economic data.
After digesting a foul 1st quarter economic Gross Domestic Product (GDP) reading of only +0.8%, activity has been smelling better in the 2nd quarter. A recent wholesome +3.4% increase in April durable goods orders, among other data points, has caused the Atlanta Federal Reserve Bank to raise its 2nd quarter GDP estimate to a healthier +2.9% growth rate (from its prior +2.5% forecast).
Consumer spending, which accounts for roughly 70% of our country’s economic activity, has been on the rise as well. The improving employment picture (5.0% unemployment rate last month) means consumers are increasingly opening their wallets and purses. In addition to spending more on cars, clothing, movies, and vacations, consumers are also doling out a growing portion of their income on housing. Housing developers have cautiously kept a lid on expansion, which has translated into limited supply and higher home prices, as evidenced by the Case-Shiller indices charted below.
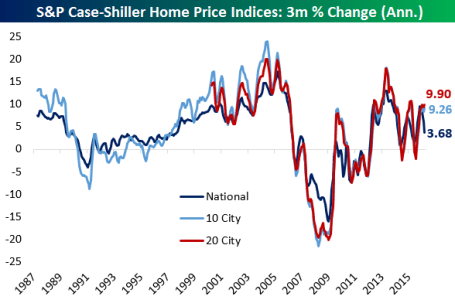
Source: Bespoke
Spoiling the Fun?
While the fridge may look like it’s fully stocked with fresh produce, meat, and dairy, it doesn’t take long for the strawberries to get moldy and the milk to sour. Investor moods can sour quickly too, especially as they fret over the impending “Brexit” (British Exit) referendum on June 23rd when British voters will decide whether they want to leave the European Union. A “yes” exit vote has the potential of roiling the financial markets and causing lots of upset stomachs.
Another financial area to monitor relates to the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy and its decision when to further increase the Federal Funds interest rate target at its June 14th – 15th meeting. With the target currently set at an almost insignificantly small level of 0.25% – 0.50%, it really should not matter whether Chair Janet Yellen decides to increase rates in June, July, September and/or November. Considering interest rates are at/near generational lows (see chart below), a ¼ point or ½ point percentage increase in short-term interest rates should have no meaningfully negative impact on the economy. If your fridge was at record freezing levels, increasing the temperature by a ¼ or ½ degree wouldn’t have a major effect either. If and when short-term interest rates increase by 2.0%, 3.0%, or 4.0% in a relatively short period will be the time to be concerned.
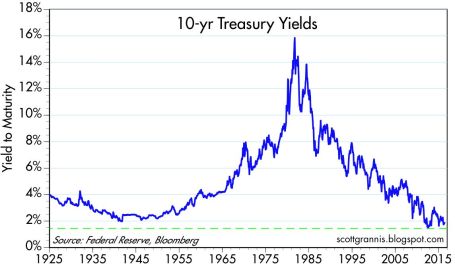
Source: Scott Grannis
Keep a Fresh Financial Plan
As mentioned earlier, your investments can get stale too. Excess cash sitting idly earning next-to-nothing in checking, savings, CDs, or in traditional low-yielding bonds is only going to spoil rapidly to inflation as your savings get eaten away. In the short-run, stock prices will move up and down based on frightening but insignificant headlines. However, in the long-run, the more important issues are determining how you are going to reach your retirement goals and whether you are going to outlive your savings. This mindset requires you to properly assess your time horizon, risk tolerance, income needs, tax situation, estate plan, and other unique circumstances. Like a balanced diet of various food groups in your refrigerator, your key personal financial planning factors are dependent upon you maintaining a properly diversified asset allocation that is periodically rebalanced to meet your long-term financial goals.
Whether you are managing your life savings, or your life-sustaining food supply, it’s always best to act now and not be a couch potato. The consequences of sitting idle and letting your investments spoil away are a lot worse than letting the food in your refrigerator rot away.

Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Market Inefficiencies Give Black-Eyes to Classic Economists
Markets are efficient. Individuals behave rationally. All information is reflected in prices. Huh…are you kidding me? These are the beliefs held by traditional free market economists (“rationalists”) like Eugene Fama (Economist at the University of Chicago and a.k.a. the “Father of the Efficient Market Hypothesis”). Striking blows to the rationalists are being thrown by “behavioralists” like Richard Thaler (Professor of Behavioral Science and Economics at the University of Chicago), who believes emotions often lead to suboptimal decisions and also thinks efficient market economics is a bunch of hogwash.
Individual investors, pensions, endowments, institutional investors, governments, were left sifting through the rubble in the aftermath of the 2008-2009 financial crisis because common beliefs were thrown out the window. Experts and non-experts are still attempting to figure out how this mass destruction occurred and how it can be prevented in the future. Economists, as always, are happy to throw in their two cents. Right now traditional free market economists like Fama have received a black eye and are on the defensive – forced to explain to the behavioral finance economists (Thaler et. al.) how efficient markets could lead to such a disastrous outcome.
Religion and Economics
Like religious debates, economic rhetoric can get heated too. Religion can be divided up in into various categories (e.g., Christianity, Islam, Judaism, Hinduism, Buddhism, and other), or more simply, religion can be divided into those who believe in a god (theism) and those who do not (atheism). There are multiple economic categorizations or schools as well (e.g., Keynsians, monetarists, libertarians, behavioral finance economists, etc.). Debates and disagreements across the rainbow of religions and economic schools have been going on for centuries, and the arrival and departure of the 2008-09 financial crisis further ignited the battle between the “behavioralists” (behavioral finance economists) and the “rationalists” (traditional free market economists).
Behavioral Finance on the Offensive
In the efficient market world of the “rationalists,” market prices reflect all available information and cannot be wrong at any moment in time. Effectively, individuals are considered human calculators that optimize everything from interest rates and costs to benefits and inflation expectations in every decision. What classic economists fail to account for are the emotional and behavioral flaws made by individuals.
Claiming financial market decisions are not impacted by emotions becomes more challenging to defend, if you consider the countless irrational anomalies occurring throughout history. Consider the following:
- Tulip Mania: Bubbles are nothing new – they have persisted for hundreds of years. Let’s reflect on the tulip bulb mania of the 1600s. For starters, I’m not sure how classic economists can explain the irrational exchanging of homes or a thousand pounds of cheese for a tulip bulb? Or how peak prices of $60,000+ in inflation-adjusted dollars were paid for a bulb at the time (C-Cynical)? These are tough questions to answer for the rationalists.
- Flash Crash: Seeing multiple stocks and Exchange Traded Funds (ETFs) temporarily plummet -99% in minutes is not exactly the sign of an efficient market. Stalwarts like Procter & Gamble also collapsed -37%, only to rebound minutes later near pre-collapse levels. All this volatility doesn’t exactly ooze with efficiency (see Making Millions in Minutes).
- Negative Interest Rates: Plenty of so-called pundits are arguing that equity markets are expensive, but what about the $8 trillion in negative interest rate bonds? Prices for many of these bonds are astronomical. Paying someone to take my money doesn’t make a lot of sense, but trillions in speculative investments are still being made today.
- Technology and Real Estate Bubbles: Both of these asset classes were considered “can’t lose” investments in the late 1990s and mid-2000s, respectively. Many tech stocks were trading at unfathomable values (more than 100 x’s annual profits) and homebuyers were inflating real estate prices because little-to-no money was required for the purchases.
- ’87 Crash: October 19, 1987 became infamously known as “Black Monday” since the Dow Jones Industrial Average plunged over -22% in one day (-508 points), the largest one-day percentage decline ever.
The ever-growing list of nonsensical anomalies only makes the rationalists’ jobs that much tougher in refuting the illogical behavior. Risk aversion has been alive and well in the post financial crisis environment as wild swings have resulted from a wide range of concerns, including: the U.S. debt downgrade; Arab Spring; potential Greek exit from the EU; Sequestration; Fed Taper Tantrum; Obamacare implementation; Russian invasion of Ukraine; Gaza conflict; Fukashima disaster; Ebola outbreak; Ferguson tensions; Paris/San Bernardino/Brussels terrorist attacks; China recessionary fears; oil price volatility; Mideast turmoil – ISIS expansion; Federal Reserve rate increases; and many other worries. Often, the human lizard brain is what leads to sub-optimal decision making. Maybe the rationalists can use the same efficient market framework to help explain to my wife why I ate a whole box of Twinkies in one sitting?
Rationalist Rebuttal
The growing list of market inefficiencies has given the rationalists a black eye, but they are not going down without a fight. Here are some quotes from Fama and fellow Chicago rationalist pals:
On the Crash-Related Attacks from Behavioralists: Behavioralists say traditional economics has failed in explaining the irrational decisions and actions leading up to the 2008-09 crash. Fama states, “I don’t see this as a failure of economics, but we need a whipping boy, and economists have always, kind of, been whipping boys, so they’re used to it. It’s fine.”
Rationalist Explanation of Behavioral Finance: Fama doesn’t deny the existence of irrational behavior, but rather believes rational and irrational behaviors can coexist. “Efficient markets can exist side by side with irrational behavior, as long as you have enough rational people to keep prices in line,” notes Fama. John Cochrane treats behavioral finance as a pseudo-science by replying, “The observation that people feel emotions means nothing. And if you’re going to just say markets went up because there was a wave of emotion, you’ve got nothing. That doesn’t tell us what circumstances are likely to make markets go up or down. That would not be a scientific theory.”
Description of Panics: “Panic” is not a term included in the dictionary of traditional economists. Fama retorts, “You can give it the charged word ‘panic,’ if you’d like, but in my view it’s just a change in tastes.” Calling these anomalous historic collapses a “change in tastes” is like calling American Idol judge Simon Cowell, “diplomatic.” More likely, what’s really happening is these severe panics are driving investors’ changes in preferences.
Throwing in White Towel Regarding Crash: Not all classic economists are completely digging in their heels like Fama and Cochrane. Gary Becker, a rationalist disciple, acknowledged the blind-siding of the 2008-2009 financial crisis when he admitted, “Economists as a whole didn’t see it coming. So that’s a black mark on economics, and it’s not a very good mark for markets.”
Settling Dispute with Lab Rats
The boxing match continues, and the way the behavioralists would like to settle the score is through laboratory tests. In the documentary Mind Over Money, numerous laboratory experiments are run using human subjects to tease out emotional behaviors. Here are a few examples used by behavioralists to bolster their arguments:
- The $20 Bill Auction: Zach Burns, a professor at the University of Chicago, conducted an auction among his students for a $20 bill. Under the rules of the game, as expected, the highest bidder wins the $20 bill, but as an added wrinkle, Burns added the stipulation that the second highest bidder receives nothing but must still pay the amount of the losing bid. Traditional economists would conclude nobody would bid higher than $20. See the not-so rational auction results here at minute 1:45.
- $100 Today or $102 Tomorrow? This was the question posed to a group of shoppers in Chicago, but under two different scenarios. Under the first scenario, the individuals were asked whether they would prefer receiving $100 in a year from now (day 366) or $102 in a year and one additional day (day 367)? Under the second scenario, the individuals were asked whether they would prefer receiving $100 today or $102 tomorrow? The rational response to both scenarios would be to select $102 under both scenarios. See how the participants responded to the questions here at minute 4:30.
Rationalist John Cochrane is not fully convinced. “These experiments are very interesting, and I find them interesting, too. The next question is, to what extent does what we find in the lab translate into how people…understanding how people behave in the real world…and then make that transition to, ‘Does this explain market-wide phenomenon?,’” he asks.
As I alluded to earlier, religion, politics, and economics will never fall under one universal consensus view. The classic rationalist economists, like Eugene Fama, have in aggregate been on the defensive and taken a left-hook in the eye for failing to predict and cohesively explain recurring market inefficiencies, including the financial crash of 2008-09. On the other hand, Richard Thaler and his behavioral finance buds will continue on the offensive, consistently swinging at the classic economists over this key economic mind versus money dispute.
See Complete Mind Over Money Program
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in PG and certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Pulling the Band-Aid Off Slowly
Federal Reserve monetary policy once again came to the forefront as the Fed released its April minutes this week. After living through years of a ZIRP (Zero Interest Rate Policy) coupled with QE (Quantitative Easing), many market participants and commentators are begging for a swifter move back to “normalization” (a Federal Funds Rate target set closer to historical averages). The economic wounds from the financial crisis may be healing, as seen in the improving employment data, but rather than ripping off the interest rate Band-Aid quickly and putting the pain behind investors, the dovish Fed Chair Janet Yellen has been signaling for months the Fed will increase rates at a “gradual” pace.
Despite the more hawkish tone regarding the possibility of an additional rate hike in June, Fed interest rate futures are currently still only factoring in about a 26% probability of a rate increase in June. As I have been saying for years (see “Fed Fatigue”), there has, and will likely continue to be, an overly, hyper-sensitive focus on monetary policy and language disseminated by members of the Feral Reserve Open Market Committee.
For example, in 1994, despite the Fed increasing target rates by +2.5% in a single year (from 3.0% to 5.5%), stock prices finished roughly flat for the year, and the market resumed its decade-long bull market run the subsequent year. Today, the higher bound of Fed Funds sits at a mere 0.5%, and the Fed has announced only one target increase this cycle (equaling a fraction of the ’94 pace). Even if investors are panicking over another potential quarter point in June or July, can you say, “overkill?”
While the Fed is approaching the lower-end of the range for its employment mandate (unemployment currently sitting at 5%), despite the recent bounce in oil prices, core inflation remains in check (see Calafia Pundit chart below). This long-term benign pricing trend gives the Fed a longer leash as it relates to the pace of future rate hikes.
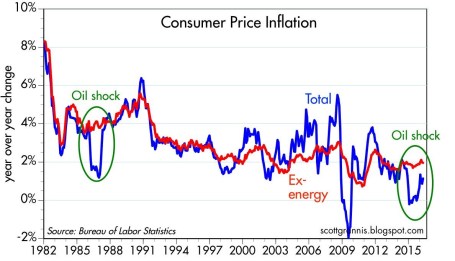
Source: Calafia Beach Pundit
Sure, ripping off the Fed Band-Aid with a small handful of +0.5% (50 bps) hikes might appease hawkish investors, but Janet Yellen, the “Fed Fairy Godmother,” has made it abundantly clear she is in no hurry to raise rates. Whether there is zero, one, or two additional rate hikes this year is much less important than other fundamental factors. Adding fuel to the Fed-speak fire in the short-run will be Yellen speeches on May 27th at Harvard University and on June 6th at the World Affairs Council of Philadelphia. And then following that, we will have the “Brexit” referendum (i.e., the vote on whether Britain should exit the EU); a steady stream of election noise; and many other unanticipated economic/geopolitical headlines.
As I continually state, the key factors driving the direction of long-term stock prices are profits, interest rates, valuations, and sentiment (see Follow the Stool). Profits (ex-energy) are growing near record levels; interest rates are near record lows (even with potential 2016 hikes); valuations remain near historical averages; and sentiment regarding stock ownership is firing strongly as a positive contrarian indicator.
While many pundits have been calling for and predicting the Fed to rip the Band-Aid off with a swift string of rate increases, persistently low inflation, coupled with a consistently dovish Fed Chair are likely to lead to a slow peeling of the monetary policy Band-Aid. Unfortunately, the endless flow of irrelevant monetary policy guesswork regarding the timing of future rate hikes will be more painful than the actual hikes themselves. In the end, any future hikes should be justified with a stronger economic foundation, which should represent future strength, rather than future weakness.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Yield Starving Foreigners Go Muni Hunting

In the current cold, barren, negative interest rate environment, foreign investors are getting hungry and desperate as they hunt for yield. In the hopes of kick-starting economic activity around the globe, central bankers are taking the drastic measure of establishing negative interest rate policies. This unusual endeavor is pressing international investors to chase yield, no matter how small, wherever they can find it.
One of those areas in which foreigners are hunting for yield is the U.S. municipal bond market (see FT article). On the surface, this sounds ludicrous. Why would an outsider living in Germany or Japan invest in a U.S. municipal bond that yields a paltry rate that’s less than 1.7%, especially considering those investors will not benefit from the tax-free income advantages offered to Americans?
As strange as it sounds, Natalie Cohen, Wells Fargo’s head of municipal research correctly pointed out this pursuit for municipal bond yield across continents boils down to simple math. “Even if [foreign investors] are not subject to the US tax code, a plus two is better than a minus one,” Cohen notes.
Although foreign investment in the $3.7 trillion municipal bond market is relatively small, the rapidly rising appetite for munis is clearly evident, as shown in the chart below.
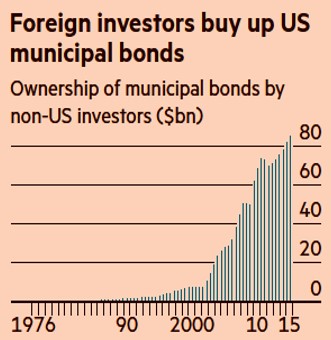
Source: The Financial Times
With our country’s crumbling roads and bridges, these ever-increasing piles of foreign cash pouring into our municipal bonds are helping fund a broad array of U.S. infrastructure projects. Given the election season is upon us, this issue may gain heightened attention. Both likely-presidential candidates are highlighting the need for infrastructure investment as part of their platforms, and the NIRP (negative interest rate policies) agenda of international central banks may make these municipal infrastructure dreams a reality.
We Americans are no stranger to the idea of borrowing money from foreigners. In fact, the Chinese own about $1.3 trillion of our Treasury bonds. This is all fine and dandy as long as the international appetite for lending us money remains healthy. If our city, state, and federal governments become too addicted to the Chinese, Europeans, and Japanese loans, financial risks can/will grow to unmanageable levels. Guess what happens once our borrowings swell to a level that forces foreigners to question our ability of repaying their debt? Interest rates will accelerate upwards, our interest payments will balloon, and our deficits will widen. The consequences of these unfavorable outcomes will be devastating budget cuts and/or tax increases.
For the time being, we will gladly accept the charitable donations of foreign investors to help lower funding costs for our sorely needed infrastructure projects. Fortunately, for now fiscal sanity is prevailing. The post financial crisis political environment has scared municipalities from borrowing too much, as explained here by the FT:
“For local and state politicians grappling with pension reforms, new healthcare programs and — in Alaska, Texas and Oklahoma — a drag on finances from lower energy prices, the looming presidential election is also diminishing the appeal of [municipal debt] issuance.”
In a near-zero/negative rate environment, there certainly will be incentives for irresponsible governments and corporations to extend themselves too far with cheap debt. However, in the short-run, as starving foreigners hunt for yield in the U.S. municipal bond market, Americans have the opportunity of exploiting this foreign generosity for the benefit our country’s long-term infrastructure.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Want to Retire at Age 90?

Do you love working 40-50+ hour weeks? Do you want to be a Wal-Mart (WMT) greeter after you get laid off from your longstanding corporate job? Do you love relying on underfunded government entitlements that you hope won’t be insolvent 10, 20, or 30 years from now? Are you banking on winning the lottery to fund your retirement? Do you enjoy eating cat food?
If you answered “Yes” to one or all of these questions, then do I have a sure-fire investment program for you that will make your dreams of retiring at age 90 a reality! Just follow these three simple rules:
- Buy Low Yielding, Long-Term Bonds: There are approximately $7 trillion in negative yielding government bonds outstanding (see chart below), which as you may understand means investors are paying to give someone else money – insanity. Bank of America recently completed a study showing about two-thirds of the $26 trillion government bond market was yielding less than 1%. Not only are investors opening themselves up to interest rate risk and credit risk, if they sell before maturity, but they are also susceptible to the evil forces of inflation, which will destroy the paltry yield. If you don’t like this strategy of investing near 0% securities, getting a match and gasoline to burn your money has about the same effect.
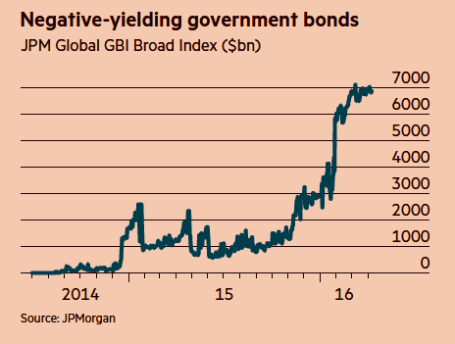
Source: Financial Times
- Speculate on the Timing of Future Fed Rate Hikes/Cuts: When the economy is improving, talking heads and so-called pundits try to guess the precise timing of the next rate hike. When the economy is deteriorating, aimless speculation swirls around the timing of interest rate cuts. Unfortunately, the smartest economists, strategists, and media mavens have no consistent predicting abilities. For example, in 1998 Nobel Prize winning economists Robert Merton and Myron Scholes toppled Long Term Capital Management. Similarly, in 1996 Federal Reserve Chairman Alan Greenspan noted the presence of “irrational exuberance” in the stock market when the NASDAQ was trading at 1,350. The tech bubble eventually burst, but not before the NASDAQ tripled to over 5,000. More recently, during 2005-2007, Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke whiffed on the housing bubble – he repeatedly denied the existence of a housing problem until it was too late. These examples, and many others show that if the smartest financial minds in the room (or planet) miserably fail at predicting the direction of financial markets, then you too should not attempt this speculative feat.
- Trade on Rumors, Headlines & Opinions: Wall Street analysts, proprietary software with squiggly lines, and your hot shot day-trader neighbor (see Thank You Volatility) all promise the Holy Grail of outsized financial returns, but regrettably there is no easy path to consistent, long-term outperformance. The recipe for success requires patience, discipline, and the emotional wherewithal to filter out the endless streams of financial noise. Continually chasing or reacting to opinions, headlines, or guaranteed software trading programs will only earn you taxes, transaction costs, bid-ask spread costs, impact costs, high frequency trading manipulation and underperformance.
Saving for your future is no easy task, but there are plenty of easy ways to destroy your savings. If you want to retire at age 90, just follow my three simple rules.

Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing had no direct position in WMT or any security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Spring Has Sprung: Market Weather Turning

This article is an excerpt from a previously released Sidoxia Capital Management complimentary newsletter (April 1, 2016). Subscribe on the right side of the page for the complete text.
It was a cold winter for stocks, but as we approached the spring season in March, the flowers have begun to bloom. More specifically, during the month of March, the Dow Jones Industrial index catapulted +7.1% and the S&P 500 index jumped +6.6%. While this roughly +80% annualized rate is unlikely to sustain itself, this flurry of strong performance could be the sign of warmer weather conditions in the economic forecast.
What started out as a cold and blustery January, with stocks posting one of the worst beginning months in history (S&P 500 down -5.1%), quickly thawed out in February and March. Fears over deteriorating economic conditions in the U.S., China along with plummeting oil prices proved fleeting. In fact, as Scott Grannis at Calafia Beach Pundit pointed out, there is no sign of recession in the U.S. as evidenced by a 43-year low in unemployment claims and a 4.9% unemployment rate (see chart below).
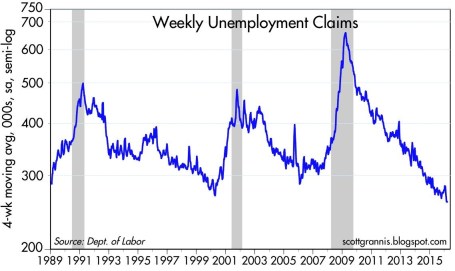
As I’ve stated for many years, focusing on the never-ending hurricane of pessimistic headlines is a wasteful use of time and destructive force on performance, if acted upon. Offsetting the downpour of negative news stories are the record low interest rates (now incomprehensibly negative in parts of the globe), which serve as a protective umbrella against the short-term stormy volatility. When investors face the soggy reality of earning a near-0% return on their bank savings and a sub-2% Treasury bond market for 10-year maturities, suddenly a 6-7% earnings yield on stocks certainly looks pretty sunny. There have been very few times in history when dividends earned on stocks have exceeded the payments received on a 10 year Treasury bond, but that is exactly the extreme environment we are living in today. No doubt, if the interest rate climate changes, and rates spike higher, stocks will face a more thunderous environment.
However, fortunately for stock market investors (and unfortunately for savers), this week Federal Reserve Chair Janet Yellen reiterated her forceful view of maintaining interest rates at a low, stimulative level for an extended period of time.
If It Bleeds It Leads – At the Expense of Your Portfolio
Even in the face of European terrorist attacks in Brussels and a turbulent (but entertaining) political presidential election season, the four pillars of earnings, interest rates, valuations, and sentiment are still protecting stock investors from an economic flood (see also Don’t Be a Fool, Follow the Stool). Scary news headlines may sell newspapers and attract advertising dollars, but the real money is made by following the four investing pillars.
Also contributing to a clearer outlook this spring is the steadying value of the U.S. dollar and stabilizing trend realized in oil prices.
For most of 2015, multinational corporations saw their profits squeezed due to a 20-25% spike in the dollar. For example, an auto manufacturer selling a car for $20,000 in the U.S. could suddenly see the price of the same car changed to $25,000 in Europe. Meanwhile, a different German competitor could price a similar car manufactured in their country at the lower $20,000. This all translates into diminished sales and profits for American companies. Mercifully, we are beginning to see these currency headwinds abate, and even begin to shift into a slight tailwind (see 5-year chart below).
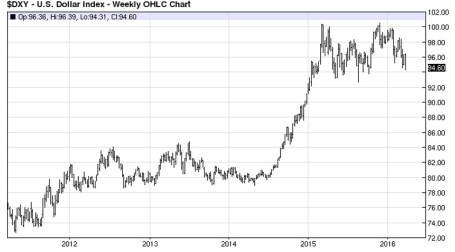
Source: barchart.com
From copper and corn to silver and soy beans, commodity prices have been in a downward death spiral over the last five years. And crude oil hasn’t escaped the commodity collapse either…until recently. The supply glut, created by factors like the U.S. shale revolution and new added Iranian post-sanction reserves, led to price declines from a 2009 high of $147 per barrel to a 2016 low of $26. With China and U.S. dollar fears abating, oil prices have bounced about +45% from the 2016 lows to about $38 per barrel.
While the weather has been improving on our shores, not everyone appreciates the fact the U.S. has been the “best house in a bad global neighborhood.” As the chart below shows (February 2016), international stock markets have gone into a bear market (down > -20%) since the 2011 and 2014 peaks, while the U.S. has performed about 100% better. Even in the U.S. market, small-midcap stocks (small & midsize companies) fell about -22% from their 2015 peak before recouping much of the losses.
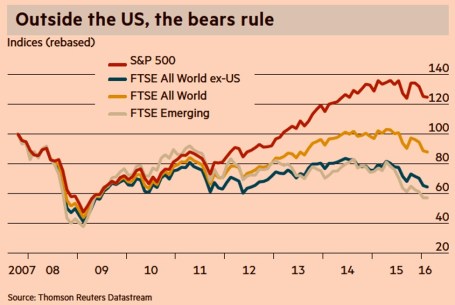
Source: Financial Times
Whether large companies, as measured by the S&P 500 index, which fell about -15% from the peak, suffer a true, technical -20% “bear market” or continue the current seven-year bull market is debatable. Regardless, what we do know is investors survived another cold winter and spring has produced a weather forecast that is currently predicting warmer weather and sunnier economic skies.

Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing had no direct position in any security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Shoot Now, Ask Later
![940614_83408820[1]](https://investingcaffeine.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/08/940614_834088201.jpg?w=311&h=230)
Since the start of 2016, investor sentiment has led to a shoot now, ask questions later mentality. In the court of economic justice, all stocks have been convicted guilty of recession despite the evidence and defense that proves the economy innocent. Even the Federal Reserve Chair Janet Yellen did not prove to be a great public defender of the economy with her comments that negative interest rates are on the table.
With large cap stocks down -13% and small cap stocks losing -25% from 2015, there are a mixture of indicators suggesting a looming recession could be coming. For example, banking stocks, the beating heart of the U.S. economy, saw prices collapse almost -30% from the 2015 highs this week. As CNBC pointed out, “American Airlines (AAL), United Continental (UAL), General Motors (GM) and Ford (F) all sell for five times 2016 earnings” – about a 70% discount to the average S&P 500 stock. As a group, these economically sensitive cyclical stocks grew earnings per share greater than 50%, while their stock prices are down by more than -30% from their 52-week highs. In general, the cyclicals are serving jail time, even though growth has been gangbusters and the current valuations massively discounted.
On the flip side, defensive stocks with little-to-no revenue growth like “Campbell Soup (CPB) trade at 20 times earnings, Kimberly-Clark (KMB) is at 21 times earnings, Procter & Gamble (PG) is at 22 times earnings and Clorox (CLX) is at 25 times earnings. All of these stocks are near 52-week highs.”
Confused? Well, if we are indeed going into recession, than this valuation dichotomy between cyclicals and staples makes sense. Stocks can be a leading indicator (i.e., predictor) of future recessions, but as the famed Nobel Prize winner in economics Paul Samuelson noted, “The stock market has forecast nine of the last five recessions.”
On the other hand, if this current correction is a false recession scare, then now would be a tremendous buying opportunity. In fact, over the last five years, there have been plenty of tremendous buying opportunities for those courageous long-term investors willing to put capital to work during these panic periods (see also Groundhog Day All Over Again):
- 2011: Debt Downgrade/Debt Ceiling Debate/European PIIGS Crisis (-22% correction)
- 2012:Arab Spring/Greek “Gr-Exit” Fears (-11% correction)
- 2013: Fed Taper Tantrum (-8% correction)
- 2014: Ebola Outbreak (-10% correction)
- 2015: China Slowdown Fears (-13% correction in August)
- 2016 (1st Six Weeks): Strong Dollar, Collapsing Oil, interest Rate Hikes/Negative Rates, Weakening China (-15% correction)
- 2016 (Next 46 Weeks): ??????????
Today’s threats rearing their ugly heads have definite recession credibility, but if you think about the strong dollar, collapsing oil prices, Fed monetary policies, weakening Chinese economy, and negative global interest rates, all of these threats existed well before stock prices nose-dived during the last six weeks. If the economic court is judging the current data for potential recession evidence, making a case and proving the economy guilty is challenging. It’s tough to find a recession when we witness a low unemployment rate (4.9%); record corporate profits (ex-energy); record car sales (17.5 million); an improving housing market; a positively sloped yield curve; healthy banking and consumer balance sheets; sub-$2/gallon gasoline; and a flattening U.S. dollar, among other factors.
Could stock prices be clairvoyantly predicting Armageddon? Sure, anything is possible…but this scenario is unlikely now. Even if the U.S. economy is headed towards a recession, the -20% plunge in stock prices is already factoring in most, if not all, of a mild-to-moderate recession. If the economic data does actually get worse, there is still room for stock prices to go down. Under a recession scenario, the tremendous buying opportunities will only get better. While weak hands may be shooting (selling) first and asking questions later, now is the time for you to use patience and discipline. These characteristics will serve as bullet proof vest for your investment portfolio and lead to economic justice over the long-term.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs) and non-discretionary positions in PG, and KMB, but at the time of publishing had no direct position in AAL, CLX, CPB, F, GM, UAL, or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Invest with a Telescope…Not a Microscope

It was another bloody week in the stock market (S&P 500 index dropped -3.1%), and any half-glass full data was interpreted as half-empty. The week was epitomized by a Citigroup report entitled “World Economy Trapped in a Death Spiral.” A sluggish monthly jobs report on Friday, which registered a less than anticipated addition of 151,000 jobs, painted a weakening employment picture. Professional social media site LinkedIn Corp. (LNKD) added fuel to the fire with a soft profit forecast, which resulted in the stock getting almost chopped in half (-44%)…in a single day (ouch).
It’s funny how quickly the headlines can change – just one week ago, the Dow Jones Industrial index catapulted higher by almost +400 points in a single day and we were reading about soaring stocks.
Coherently digesting the avalanche of diverging and schizophrenic headlines is like attempting to analyze a windstorm through a microscope. A microscope is perfect for looking at a single static item up close, but a telescope is much better suited for analyzing a broader set of data. With a telescope, you are better equipped to look farther out on the horizon, to anticipate what trends are coming next. The same principle applies to investing. Short-term traders and speculators are great at using a short-term microscope to evaluate one shiny, attention-grabbing sample every day. The investment conclusion, however, changes the following day, when a different attention-grabbing headline is analyzed to a different conclusion. As Mark Twain noted, “If you don’t read the newspaper, you are uninformed. If you do read the newspaper, you are misinformed.”
Short-termism is an insidious disease that will slowly erode short-run performance and if not controlled will destroy long-run results as well. This is not a heretic concept. Some very successful investors have preached this idea in many ways. Here are a few of them:
‘‘We will continue to ignore political and economic forecasts which are an expensive distraction for many investors and businessmen.” –Warren Buffett (Annual Newsletter 1994)
‘‘If you spend more than 14 minutes a year worrying about the market, you’ve wasted 12 minutes’’ –Peter Lynch
“Excessive short-termism results in permanent destruction of wealth, or at least permanent transfer of wealth” -Jack Gray Grantham
On the flip side, those resilient investors who have succeeded through investment cycles understand the importance of taking a long-term view.
“Whatever method you use to pick stocks or stock mutual funds, your ultimate success or failure will depend on your ability to ignore the worries of the world long enough to allow your investments to succeed.” –Peter Lynch
“The farther you can lengthen your time horizon in the investment process, the better off you will be.” – David Nelson (Legg Mason)
“Long term owners are more relaxed, more informed, more patient, less emotional.” –John Templeton
“If you are really a long-term investor, you will view a bear market as an opportunity to make money.” –John Templeton
“Long term is not a popular time-horizon for today’s hedge fund short-term mentality. Every wiggle is interpreted as a new secular trend.” –Don Hays
“In the long run, one of the greatest risk to your net worth is not owning stocks. Bonds do not grow. They can only return their face value at maturity…Inflation is a silent, insidious tax that erodes your net worth…Fortunately, there is an easy way to keep pace with and even beat inflation, and this is stocks.” – John Spears
“In the short-term, the stock market is a voting machine; in the long-term a weighing machine.” -Benjamin Graham
There has been a lot of pain experienced so far in 2016, and there may be more to come. However, trying to time the market and call a bottom is a fruitless effort. Great companies and investments do not disappear in a bear market. At times like these, it is important to stick to a systematic, disciplined approach that integrates valuation and risk controls based on where we are in an economic cycle. Despite all the recent volatility, as I’ve repeated many times, the key factors driving the direction of the stock market are the following: 1) Corporate profits; 2) Interest rates; 3) Valuations; and 4) Sentiment (see also Don’t Be a Fool, Follow the Stool). Doom and gloom “Death Spiral” headlines may currently rule the day, but the four key stock-driving factors on balance remain skewed towards the positive…if you have the ability to put away your microscope and take out your telescope.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing had no direct position in LNKD or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Financial Markets Recharge with a Nap…Zzzzzz

This article is an excerpt from a previously released Sidoxia Capital Management complimentary newsletter (January 4, 2016). Subscribe on the right side of the page for the complete text.
Did you enjoy your New Year’s festivities? If you were like me and ate excessively and drank too much egg nog, you may have decided along the line to take a nap. It’s not a bad idea to recharge those batteries before implementing those New Year’s resolutions and jumping on the treadmill. That’s exactly what happened in the financial markets this year. After six consecutive years of positive returns in the Dow Jones Industrial Average (2009 – 2014), stock markets took a snooze in 2015, as measured by the S&P 500 and Dow, which were each down -0.7% and -2.2%, respectively. And bonds didn’t fare any better, evidenced by the -1.9% decline in the Aggregate Bond ETF (AGG), over the same time period. Given the deep-seated fears about the Federal Reserve potentially catapulting interest rates higher in 2015, investors effectively took a big yawn by barely nudging the 10-year Treasury Note yield higher by +0.1% from 2.2% to 2.3%.
Even though 2015 ended up being a quiet year overall, there were plenty of sweet dreams mixed in with scary nightmares during the year-long nap:
INVESTMENT SWEET DREAMS
Diamonds in the Rough: While 2015 stock prices were generally flat to down around the globe (Vanguard Total Word -4.2%), there was some sunshine and rainbows gleaming for a number of segments in the market. For example, handsome gains were achieved in the NASDAQ index (+5.7%); Biotech Index – BTK (+10.9%); Consumer Discretionary ETF – XLY (+8.3%); Health Care ETF – VHT (+5.8%); Information Technology ETF – VGT (+4.6%); along with numerous other investment areas.
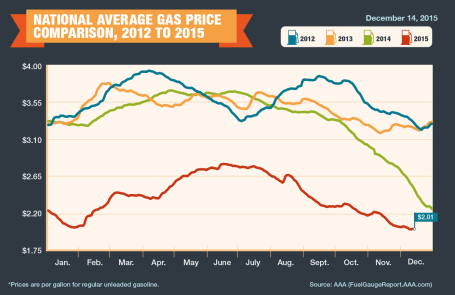
Fuel Fantasy Driven by Low Gas Prices: Gas prices averaged $2.01 per gallon nationally in December (see chart below), marking the lowest prices seen since 2009. Each penny in lower gas prices roughly equates to $1 billion in savings, which has strengthened consumers’ balance sheets and contributed to the multi-year economic expansion. Although these savings have partially gone to pay down personal debt, these gas reserves have also provided a financial tailwind for record auto sales (estimated 17.5million in 2015) and a slow but steady recovery in the housing market. The outlook for “lower-for-longer” oil prices is further supported by an expanding oil glut from new, upcoming Iranian supplies. Due to the lifting of economic sanctions related to the global nuclear deal, Iran is expected to deliver crude oil to an already over-supplied world energy market during the first quarter of 2016. Additionally, the removal of the 40-year ban on U.S. oil exports -could provide a near-term ceiling on energy prices as well.
Counting Cash Cows
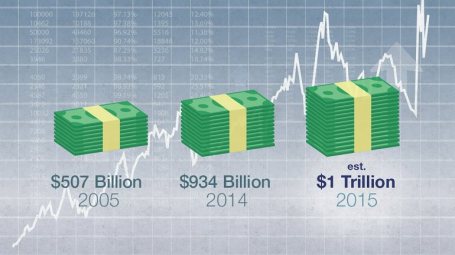
Catching some shut-eye after reading frightening 2015 headlines on the China slowdown, $96 billion Greek bailout/elections, and Paris/San Bernardino terrorist attacks forced some nervous investors to count sheep to fall asleep. However, long-term investors understand that underpinning this long-lived bull market are record revenues, profits, and cash flows. The record $4.7 trillion dollars in 2015 estimated mergers along with approximately $1 trillion in dividends and share buybacks (see chart below) is strong confirmation that investors should be concentrating on counting more cash cows than sheep, if they want to sleep comfortably.
INVESTMENT NIGHTMARES
Creepy Commodities: Putting aside the -30% collapse in WTI crude oil prices last year, commodity investors overall were exhausted in 2015. The -24% decline in the CRB Commodity Index and the -11% weakening in the Gold Index (GLD) was further proof that a strong U.S. dollar, coupled with stagnant global growth, caused investors a lot of tossing and turning. While bad for commodity exporting countries, the collapse in commodity prices will ultimately keep a lid on inflation and eventually become stimulative for those consumers suffering from lower standards of living.
Dollar Dread: The +25% spike in the value of the U.S. dollar over the last 18 months has made life tough for multinational companies. If your business received approximately 35-40% of their profits overseas and suddenly your goods cost 25% more than international competitors, you might grind your teeth in your sleep too. Monetary policies around the globe, including the European Union, will have an impact on the direction of future foreign exchange rates, but after a spike in the value of the dollar in early 2015, there are signs this scary move may now be stabilizing. Although multinationals are getting squeezed, now is the time for consumers to load up on cheap imports and take that bargain foreign vacation they have long been waiting for.
January has been a challenging month the last couple years, and inevitably there will be additional unknown turbulence ahead – the opening day of 2016 not being an exception (i.e., China slowdown concerns and Mideast tensions). However, given near record-low interest rates, record corporate profits, and accommodative central bank policies, the 2015 nap taken by global stock markets should supply the necessary energy to provide a lift to financial markets in the year ahead.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions VHT, AGG, and in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing had no direct position VT, BTK, XLY, VGT, GLD, or in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.