Posts tagged ‘Warren Buffett’
Eggs or Oatmeal: Binging on Over-Analysis
I about chuckled my way out of my chair when ESPN reminded me of the absurd over-analysis that takes place in the sports world (I can’t wait for the 8 hour pre-game show before the upcoming Super Bowl) through a 30-second, football commercial. Typically when sports analysts get together, the most irrelevant issues are scrutinized under a microscope. After endless wasted amounts of time, the viewer is generally left with lots of worthless information about an immaterial topic. In this particular video, San Diego NFL quarterback Phillip Rivers innocently asks Sunday Countdown football analysts Chris Berman, Mike Ditka, Keyshawn Johnson, Tom Jackson, and Cris Carter whether they would like some eggs or oatmeal for breakfast?
Mayhem ensues while the analysts breakdown everything from the pros of frittatas and brats to the cons of cholesterol and sauerkraut. After listening to all the jaw flapping, Phillip Rivers is left dejected, banging his head against the kitchen refrigerator. It is funny, I feel much the same way as Phillip Rivers does when I’m presented with same overkill analysis found plastered over the financial media and blogosphere.
Analysis of Over-Analysis
Just as I mock the excess analysis occurring in the financial world, I will move ahead and assess this same over-thinking (that’s what we bloggers do). If this much analysis takes place when examining simple options such as eggs vs. oatmeal, or AFC vs. NFC, just imagine the endless debate that arises when discussing the merits of investing in a simple, diversified domestic equity mutual fund. Sounds simple on paper, but if I want to be intellectually honest, I first need to compare this one fund versus the thousands of other equity fund offerings, not to mention the thousands of other ETFs (Exchange Traded Funds), bond funds, lifecycle funds, annuities, index funds, private equity funds, hedge funds, and other basket-related investment vehicles.
Mutual funds are only part of the investment game. We haven’t even scratched the surface of individual securities, futures, options, currencies, CDs, real estate, mortgage backed securities, or other derivatives.
The investment menu is virtually endless (see TMI – Too Much Information), and new options are created every day – many of which are indecipherable to large swaths of investors (including professionals).
Sidoxia’s Questions of Engagement
Not all analysis is psychobabble, but separating the wheat from the manure can be difficult. Before engaging in the never-ending over-analysis taking place in the financial world, answer these three questions:
1.) “Do I Care?” If the latest advance-decline statistics on the NYSE don’t tickle your fancy, or the latest “breaking news” headline on monthly pending home sales doesn’t float your boat, then maybe it’s time to do something more important like…absolutely anything else.
2.) “Do I Understand?” If conversation drifts towards complex currency swaptions comparing the Thai Baht against the Brazilian Real, then perhaps it’s time to leave the room.
3.) “Is This New News?” Not sure if you heard, but there’s this new shiny metal called gold, and it’s the cure-all for inflation, deflation, and any-flation (hyperbole for those not able to translate my written word sarcasm). The point being, ask yourself if the information you receive is valuable and actionable. Typically the best investment ideas are not discussed 24/7 over every media venue, but rather in the boring footnotes of an unread annual report.
Investing in the Stock Market
For individual securities it’s best to stick to your circle of competence with companies and industries you understand – masters like Peter Lynch and Warren Buffett appreciate this philosophy. Once you find an investment opportunity you understand, you need a way of appraising the value and gauging a company’s growth trajectory. As Charlie Munger and Warren Buffett have described, “value and growth are two sides of the same coin.” Cigar-butt investing solely using value-based metrics is not enough. Even value jock Warren Buffet appreciates the merit of a good business with sustainable expansion prospects. As a matter of fact, some of Buffett’s best performing stocks are considered the greatest growth stocks of all-time. If you cannot assign a price (or range), then you are merely playing the speculation game. Speculation often comes in the form of stock tips (i.e.,stock broker or Jim Cramer) and day trading (see Momentum Investing and Technical Analysis).
We live in a world of endless information, and the analysis can often become overkill. So when overwhelmed with data, do yourself a favor by asking yourself the three questions of engagement – that way you will not miss the forest for the trees. As for stocks, stick with industries and companies you understand and develop a disciplined investment process by appraising both the growth and valuation components of the investment. If making these decisions are too difficult, perhaps you should stay in the kitchen and have Phillip Rivers whip you up some scrambled eggs or serve you a bowl of oatmeal.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in DIS, BRKA/B, or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
The Accomplished Mole – Seth Klarman
I do quite a bit of reading and in my spare time I came across something very interesting. Here are some of the characteristics that describe this unique living mammal: 1) You will rarely see this creature in the open; 2) It roams freely and digs in deep, dark areas where many do not bother looking; and 3) This active being has challenged eyesight.
If you thought I was talking about a furry, burrowing mole (Soricomorpha Talpidae) you were on the right track, but what I actually was describing was legendary value investor Seth Klarman. He shares many of the same features as a mole, but has made a lot more money than his very distant evolutionary cousin.
The Making of a Legend
Before becoming the President of The Baupost Group, a Boston-based private investment partnership which manages about $22 billion in assets on behalf of wealthy private families and institutions, he worked for famed value investors Max Heine and Michael Price of the Mutual Shares (purchased by Franklin Templeton Investments). Klarman also published a classic book on investing, Margin of Safety, Risk Averse Investing Strategies for the Thoughtful Investor, which is now out of print and has fetched upwards of $1,000-2,000 per copy in used markets like Amazon.com (AMZN).
Klarman chooses to keep a low public profile, but recently his negative views on stock market and inflation risk have filtered out into the public domain. Nonetheless, he is still optimistic about certain distressed opportunities and believes the financial crisis has cultivated a more favorable, less competitive environment for investment managers due to the attrition of weaker investors.
Philosophy
Klarman despises narrow mandates – they are like shackles on potential returns. Opportunities do not lay dormant in one segment of the financial markets. Investors are fickle and fundamentals change. He believes superior results are achieved through a broadening of mandates. He prefers to invest in areas off the proverbial beaten path – the messier and more complicated the situation, the better. Currently his funds have significant investments in distressed debt instruments, many of which were capitulated forced sales by funds that are unable to hold non-investment grade debt.
In order to make his wide net point to investing, Klarman uses real estate as an illustration device. For example, investors do not need to limit themselves to publicly traded REITs (Real Estate Investment Trusts) – they can also invest in the debt of a REIT, convertible real estate debt, equity of property (such as own building), bank loan on a building, municipal bond that’s backed by real estate, or commercial/residential mortgage backed securities.
Klarman summarizes his thoughts by saying:
“If you have a broader mandate, they let you own all kinds of debt, all kinds of equity. Perhaps some private assets, like real estate. Perhaps hold cash when you can’t find anything great to do. You now have more weapons at your disposal to take advantage of conditions in the market.”
Klarman’s 3 Underlying Investment Pillars
Besides mentors Heine and Price, Klarman is quick to highlight his investment philosophy has been shaped by the likes of Warren Buffett and Benjamin Graham, among others. In addition to many of the basic tenets espoused by these investment greats, Klarman adds these three main investment pillars to his repertoire:
1) Focus on risk first (the probability of loss) before return. Determine how much capital you can lose and what the probability of that loss is. Also, do not confuse volatility with risk. Volatility creates opportunities.
2) Absolute performance, not relative performance, is paramount. The world is geared towards relative performance because of asset gathering incentives. Wealthy investors and institutions are more focused on absolute returns. Focus on benchmarks will insure mediocrity.
3) Concentrate on bottom-up research, not top down. Accurately forecasting macroeconomic trends and also profiting from those predictions is nearly impossible to do over longer periods of time.
These are great, but represent just a few of his instructional nuggets.
Performance
I did some digging regarding Klarman’s performance, and given the range of markets experienced over the last 25+ years, the results are nothing short of spectacular. Here is what I dug up from the Outstanding Investor Digest:
“Since its February 1, 1983 [2008] inception through December 31st, his Baupost Limited Partnership Class A-1 has provided its limited partners an average annual return of 16.5% net of fees and incentives, versus 10.1% for the S&P 500. During the “lost decade”, Baupost obliterated the averages, returning 14.8% and 15.9% for the 5 and 10-year periods ending December 31st versus -2.2% and -1.4%, respectively, for the S&P.”
Here is some additional color from Market Folly on Klarman’s incredible feats:
“Despite Klarman’s typically high levels of cash [sometimes in excess of 50%], Baupost has still generated astonishing performance. It was up 22% in 2006, 54% in 2007, and around 27% in 2009. During the crisis in 2008, Klarman’s funds lost “between 7% and the low teens.” Still though, he certainly outperformed the market indices and much of his investment management brethren in a time of panic.”
Although Seth Klarman has plowed over the competition and remained underground from the mass media, it’s still extremely difficult to ignore the long-term record of success of this accomplished mole. In the short-run, volatility may hurt his performance – especially if holding 20-30% cash. But as I was told at a young age by my grandmother, it is not prudent to make mountains out of molehills. Apparently, Klarman’s grandma taught her mole-like grandson how to make mountains of money from hills of opportunities. Klarman’s investors certainly stand to benefit as he continues to dig for value-based gems.
Watch interesting but lengthy presentation video given by Seth Klarman
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
*DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, and AMZN, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct positions in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Margin Surplus Retake
Like a B-rated horror movie using the same old cliques (i.e., girl home alone with serial killer on the loose or a concealed intruder hidden in the back seat of a car), one of the financial cliques that persists today is the belief that the United States trade deficit will result in financial ruin for our economy. The recent widening of the trade deficit to $40.3 billion makes this economic issue a topical discussion. Enter Andy Kessler, former hedge fund manager and author of Running Money. He believes the stale, exploding trade deficit arguments are hogwash, primarily due to his “margin surplus” theory articulated in his book and Wall Street Journal article entitled, We Think, They Sweat.
Profiting from Trade Deficits
The absolute numbers used by Kessler in his Toshiba laptop example might have changed since his book was first published in 2004, but this margin surplus theory example is just as relevant today as it was back then. Here is an excerpt from his book:
“Let’s open up that Toshiba laptop. With a $300 Intel chip (which has at least $250 in profit for Intel) and a $50 Windows license ($49.95 margin to Microsoft), the laptop is then sold by Toshiba back into the U.S. for $1,000. Toshiba and every other supplier are lucky if they make $50 profit, combined, on the deal.”
In this illustration, government statistics would recognize a $1,000 contribution to our bloating trade deficit figures, even though nearly 90% of the laptop profits would be flowing (“surplus-ing”) back to the U.S. Hmmm, maybe this trade deficit thing isn’t as evil as it is portrayed in the popular media, or perhaps we are measuring it incorrectly? Kessler makes the case that Gross Domestic Product (GDP) is not the most important economic gauge, but rather the real crucial GDP metric is actually Gross Domestic PROFIT. He adds the best indicator for economic profits is the stock market, and as foreigners seek more productive returns on their cash beyond the 3% Treasury yields, they will eventually filter back their dollar currency reserves into stocks and other more productive asset classes.
Brain Driven Economy
You don’t have to be a brain surgeon to realize our roots as an industrial economy have shifted to an intellectual property economy. So while we may be exporting low-skilled labor jobs to China and other low-cost regions, our country is also creating higher-skilled, higher-paying jobs at innovative growing companies such as Google Inc. (GOOG) and Apple Inc. (AAPL). Case in point, flip an Apple iPod over and read the fine print on the back – it reads, “Assembled in China…Designed by Apple in California.” Once again, the commoditized aspects of slapping together a widget have been outsourced to workers in far-off lands for a small fraction of what American workers earn. If improving the standard of living is our goal, then transferring low paying jobs to foreigners should not be a concern. According to Kessler, $70 in iPod profits (versus $4 for the Chinese assemblers) from this unique, differentiated device has generated millions in profits, which in turn can be used for the creation of desirable, high-paying jobs here in the U.S.
Selling the Farm
Warren Buffets has a different view about our trade deficits and the directional value of the U.S. dollar. He perceives our economy as a fixed size farm that is selling $2 billion pieces of the farm to foreigners on a daily basis. Buffet adds:
“We’re like a very rich family; we own a farm the size of Texas but want to consume more. If you force-feed $2 billion a day to the rest of the world, they get somewhat less enthusiastic over time – and the dollar is worth less.”
Over time, Buffett believes future generations will resent paying for the gluttony of consumption by prior generations and foreigners will demand a higher interest rate for their loans. What I believe Buffet fails to consider is that the farm is not static. As we sell off $2 billion chunks of the farm, portions of those proceeds are being used to adjoin additions, buy new farms, build adjacent wind turbines, and/or incorporate other productive uses. Now if the proceeds were used to solely purchase bon-bons and doughnuts, then indeed we would be in trouble. Ultimately, the financial markets will be the true arbiter of how efficiently the foreign capital is being invested and will dictate the level of rates paid on the loans. From a pure cash management standpoint, stretching out payables (net imports) is a sound practice (i.e., it’s desirable to collect early and pay late).
The flip side of the argument explains how the farm sale proceeds from our asset sales to foreigners (such as our real estate, our Treasuries, and our stocks) can be employed in a productive manner. The Buffett argument states that our farm will eventually be completely sold to foreigners or they will hold a gun to our head asking for higher interest rates to fund our deficits. The problem with that argument is that the money received from the farm sales (Treasuries, stocks, real estate, etc.) can be (and is) used to build new farms. And that is the key question…are all these deficit building dollars being used to create new, innovative, job creating companies like Google and Apple, or are these dollars being redeployed into unproductive uses (e.g., worthless t-shirts and lead-filled toys from China, or funding of bailouts and cash-for-clunkers waste) ?
At the end of the day, money goes where it is treated best – meaning global capital seeks the royal treatment in markets where profits reign supreme. So rather than relying on rusty, obsolete statistics measuring the balance of trade (i.e., trade deficits and GDP), investors would be better served by taking a page from Andy Kessler’s book. Following the principles of “margin surplus” will increase the probabilities of profiting from global capital flows.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
*DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, Treasury securities, GOOG, and AAPL, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct positions in Toshiba, INTC, BRKA/B or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Inside the Brain of an Investing Genius
Those readers who have frequented my Investing Caffeine site are familiar with the numerous profiles on professional investors of both current and prior periods (See Profiles). Many of the individuals described have a tremendous track record of success, while others have a tremendous ability of making outrageous forecasts. I have covered both. Regardless, much can be learned from the successes and failures by mirroring the behavior of the greats – like modeling your golf swing after Tiger Woods (O.K., since Tiger is out of favor right now, let’s say Phil Mickelson). My investment swing borrows techniques and tips from many great investors, but Peter Lynch (ex-Fidelity fund manager), probably more than any icon, has had the most influence on my investing philosophy and career as any investor. His breadth of knowledge and versatility across styles has allowed him to compile a record that few, if any, could match – outside perhaps the great Warren Buffett.
Consider that Lynch’s Magellan fund averaged +29% per year from 1977 – 1990 (almost doubling the return of the S&P 500 index for that period). In 1977, the obscure Magellan Fund started with about $20 million, and by his retirement the fund grew to approximately $14 billion (700x’s larger). Cynics believed that Magellan was too big to adequately perform at $1, $2, $3, $5 and then $10 billion, but Lynch ultimately silenced the critics. Despite the fund’s gargantuan size, over the final five years of Lynch’s tenure, Magellan outperformed 99.5% of all other funds, according to Barron’s. How did Magellan investors fare in the period under Lynch’s watch? A $10,000 investment initiated when he took the helm would have grown to roughly $280,000 (+2,700%) by the day he retired. Not too shabby.
Background
Lynch graduated from Boston College in 1965 and earned a Master of Business Administration from the Wharton School of the University of Pennsylvania in 1968. Like the previously mentioned Warren Buffett, Peter Lynch shared his knowledge with the investing masses through his writings, including his two seminal books One Up on Wall Street and Beating the Street. Subsequently, Lynch authored Learn to Earn, a book targeted at younger, novice investors. Regardless, the ideas and lessons from his writings, including contributing author to Worth magazine, are still transferrable to investors across a broad spectrum of skill levels, even today.
The Lessons of Lynch
Although Lynch has left me with enough financially rich content to write a full-blown textbook, I will limit the meat of this article to lessons and quotations coming directly from the horse’s mouth. Here is a selective list of gems Lynch has shared with investors over the years:
Buy within Your Comfort Zone: Lynch simply urges investors to “Buy what you know.” In similar fashion to Warren Buffett, who stuck to investing in stocks within his “circle of competence,” Lynch focused on investments he understood or on industries he felt he had an edge over others. Perhaps if investors would have heeded this advice, the leveraged, toxic derivative debacle occurring over previous years could have been avoided.
Do Your Homework: Building the conviction to ride through equity market volatility requires rigorous homework. Lynch adds, “A company does not tell you to buy it, there is always something to worry about. There are always respected investors that say you are wrong. You have to know the story better than they do, and have faith in what you know.”
Price Follows Earnings: Investing is often unnecessarily made complicated. Lynch fundamentally believes stock prices will follow the long-term trajectory of earnings growth. He makes the point that “People may bet on hourly wiggles of the market, but it’s the earnings that waggle the wiggle long term.” In a publicly attended group meeting, Michael Dell, CEO of Dell Inc. (DELL), asked Peter Lynch about the direction of Dell’s future stock price. Lynch’s answer: “If your earnings are higher in 5 years, your stock will be higher.” Maybe Dell’s price decline over the last five years can be attributed to its earnings decline over the same period? It’s no surprise that Hewlett-Packard’s dramatic stock price outperformance (relative to DELL) has something to do with the more than doubling of HP’s earnings over the same time frame.
Valuation & Price Declines: “People Concentrate too much on the P (Price), but the E (Earnings) really makes the difference.” In a nutshell, Lynch believes valuation metrics play an important role, but long-term earnings growth will have a larger impact on future stock price appreciation.
Two Key Stock Questions: 1) “Is the stock still attractively priced relative to earnings?” and 2) “What is happening in the company to make the earnings go up?” Improving fundamentals at an attractive price are key components to Lynch’s investing strategy.
Lynch on Buffett: Lynch was given an opportunity to write the foreword in Buffett’s biography, The Warren Buffett Way. Lynch did not believe in “pulling out flowers and watering the weeds,” or in other words, selling winners and buying losers. In highlighting this weed-flower concept, Lynch said this about Buffett: “He purchased over $1 billion of Coca-Cola in 1988 and 1989 after the stock had risen over fivefold the prior six years and over five-hundredfold the previous sixty years. He made four times his money in three years and plans to make a lot more the next five, ten, and twenty years with Coke.” Hammering home the idea that a few good stocks a decade can make an investment career, Lynch had this to say about Buffett: “Warren states that twelve investments decisions in his forty year career have made all the difference.”
You Don’t Need Perfect Batting Average: In order to significantly outperform the market, investors need not generate near perfect results. According to Lynch, “If you’re terrific in this business, you’re right six times out of 10 – I’ve had stocks go from $11 to 7 cents (American Intl Airways).” Here is one recipe Lynch shares with others on how to beat the market: “All you have to do really is find the best hundred stocks in the S&P 500 and find another few hundred outside the S&P 500 to beat the market.”
The Critical Element of Patience: With the explosion of information, expansion of the internet age, and the reduction of trading costs has come the itchy trading finger. This hasty investment principle runs contrary to Lynch’s core beliefs. Here’s what he had to say regarding the importance of a steady investment hand:
- “In my investing career, the best gains usually have come in the third or fourth year, not in the third or fourth week or the third or fourth month.”
- “Whatever method you use to pick stocks or stock mutual funds, your ultimate success or failure will depend on your ability to ignore the worries of the world long enough to allow your investments to succeed.”
- “Often, there is no correlation between the success of a company’s operations and the success of its stock over a few months or even a few years. In the long term, there is a 100% correlation between the success of a company and the success of its stock. It pays to be patient, and to own successful companies.”
- “The key to making money in stocks is not to get scared out of them.”
Bear Market Beliefs: “I’m always more depressed by an overpriced market in which many stocks are hitting new highs every day than by a beaten-down market in a recession,” says Lynch. The media responds in exactly the opposite manner – bear markets lead to an inundation of headlines driven by panic-based fear. Lynch shares a similar sentiment to Warren Buffett when it comes to the media holding a glass half full view in bear markets.
Market Worries: Is worrying about market concerns worth the stress? Not according to Lynch. His belief: “I’ve always said if you spend 13 minutes a year on economics, you’ve wasted 10 minutes.” Just this last March, Lynch used history to drive home his views: “We’ve had 11 recessions since World War II and we’ve had a perfect score — 11 recoveries. There are a lot of natural cushions in the economy now that weren’t there in the 1930s. They keep things from getting out of control. We have the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation [which insures bank deposits]. We have social security. We have pensions. We have two-person, working families. We have unemployment payments. And we have a Federal Reserve with a brain.”
Thoughts on Cyclicals: Lynch divided his portfolio into several buckets, and cyclical stocks occupied one of the buckets. “Cyclicals are like blackjack: stay in the game too long and it’s bound to take all your profit,” Lynch emphasized.
Selling Discipline: The rationale behind Lynch’s selling discipline is straightforward – here are some of his thoughts on the subject:
- “When the fundamentals change, sell your mistakes.”
- “Write down why you own a stock and sell it if the reason isn’t true anymore.”
- “Sell a stock because the company’s fundamentals deteriorate, not because the sky is falling.”
Distilling the genius of an investing legend like Peter Lynch down to a single article is not only a grueling challenge, but it also cannot bring complete justice to the vast accomplishments of this incredible investment legend. Nonetheless, his record should be meticulously studied in hopes of adding jewels of investment knowledge to the repertoires of all investors. If delving into the head of this investing mastermind can provide access to even a fraction of his vast knowledge pool, then we can all benefit by adding a slice of this greatness to our investment portfolios.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at time of publishing had no direct positions in DELL, KO, HPQ or any other security mentioned. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Getting off the Market Timing Treadmill
Most investors have been stuck on the financial treadmill of the 2000s and have nothing to show for it, other than battle scars from the 2008-2009 financial crisis. A lot of running, sweating, and jumping has produced effectively no results. Most media outlets continue to focus on the “lost decade” (see other Lost Decade story) in which investors have earned nothing in the equity markets. After a decade of excess in the 1990s should the majority of investors be surprised? Investing is no different than dieting and exercise – those topics are easy to understand but difficult to execute.
Where are the Billionaire Market Timers?
The financial industry oversimplifies investing and sells market timing as an effortless path to riches – even in tough times. In the search of the financial Holy Grail, the industry constantly crams new software bells and whistles and so-called “can’t lose” strategies down the throats of individual investors. Sadly, there is no miracle system, wonder algorithm, or get rich scheme that can sustainably last the test of time. Sure, a minority of speculators can get lucky and make money by following a risky strategy in the short-run, but as the global economic disaster caused by LTCM (Long Term Capital Management) taught us, even certain successful trading strategies or computer algorithms can stop working in a heartbeat and lead to a widespread bloodbath.
Are you still a believer in market timing? If so, then where are all the billionaire market timers? Famed growth manager, Peter Lynch astutely noted:
“I can’t recall ever once having seen the name of a market timer on Forbes‘ annual list of the richest people in the world. If it were truly possible to predict corrections, you’d think somebody would have made billions by doing it.”
Certainly, there are some hedge fund managers that have hit home runs with amazing market calls, but time will be the arbiter in determining whether they can stay on top.
Sage Speak on Market Timing
If you don’t believe me about market timing, then listen to what knowledgeable investors and thought leaders have to say on the subject. Larry Swedroe, a principal at Buckingham Asset Management, compiled a list including the following quotes:
- Warren Buffett (Investor extraordinaire): “We continue to make more money when snoring than when active.” He adds, “The only value of stock forecasters is to make fortune-tellers look good.”
- Jason Zweig (Columnist): “Whenever some analyst seems to know what he’s talking about, remember that pigs will fly before he’ll ever release a full list of his past forecasts, including the bloopers.” (See also Peter Schiff and Meredith Whitney stories)
- Bernard Baruch (Financier): “Only liars manage to always be out during bad times and in during good times.”
- Jonathan Clements (Columnist): “What to do when the market goes down? Read the opinions of the investment gurus who are quoted in the WSJ. And, as you read, laugh. We all know that the pundits can’t predict short-term market movements. Yet there they are, desperately trying to sound intelligent when they really haven’t got a clue.”
- David L. Babson (Investment Manager): “It must be apparent to intelligent investors that if anyone possessed the ability to do so [forecast the immediate trend of stock prices] consistently and accurately he would become a billionaire so quickly he would not find it necessary to sell his stock market guesses to the general public.”
- Peter Lynch (Retired Growth Manager): “Far more money has been lost by investors preparing for corrections, or trying to anticipate corrections, than has been lost in corrections themselves.”
Market Timing Road Rules
Rather than make guesses regarding the direction of the market, here are some investment rules to follow:
- Rule #1: Do not attempt to market time. Statistically it is a certainty that a minority of the millions of investors can time the market in the short-run – the problem is that very few, if any, can time the market for sustainable periods of time. Don’t try to be the hero, because often you will become the goat.
- Rule #2: Patiently make good investments, regardless of the economic conditions. It is best to assume the market will go nowhere and invest accordingly. Paying attention to a hot or cold economy leads to investors chasing their tails. Good investments should outperform in the long-run, regardless of the macroeconomic environment.
- Rule #3: Diversify. In the midst of the crisis, diversification didn’t cure simultaneous drops in most asset classes, however ownership of government Treasuries, cash, and certain commodities provided a cushion from the economic blows. Longer-term, the benefits of diversification become more apparent – it makes absolute sense to spread your risk around.
In some respects, there is always an aspect of timing to investing, but as referenced by some of the intelligent professionals previously, the driving force behind an investment decision should not be, “I think the market is going up,” or “I think the market is going down” – those thought processes are recipes for disaster. I strongly believe an investment process that includes patience, discipline, diversification, valuation sensitivity, and low-cost/ tax-efficient products and strategies will get you off the financial treadmill and move you closer to reaching your financial goals.
Read the Full Larry Swedroe Story
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at time of publishing had no direct positions in BRKA or any other security mentioned. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Balance Sheet: The Foundation for Value
Let’s talk balance sheets… how exciting! Most people would rather hear nails scratching against a chalkboard or pour lemon juice on a fresh paper-cut, rather than slice and dice a balance sheet. However, the balance sheet plays a critical role in establishing the foundational value of a business. As part of my financial statement analysis series of articles, today we will explore the balance sheet in more detail.
It’s not just legendary value investors like Warren Buffett and Benjamin Graham who vitally rely on a page filled with assets and liabilities. Modern day masters like Bill Ackman (CEO of Pershing Square Capital Management LP – read more about Bill Ackman) and Eddie Lampert (CEO of Sears Holdings – SHLD) have in recent years relied crucially on the balance sheet, and specifically on real estate values, when it came to defining investments in Target Corporation (TGT) and Sears, respectively.
Balance Sheet Description
What is the balance sheet? For starters, it is one of the three major financial statements (in addition to the “Income Statement” and “Cash Flow Statement”), which provides a snapshot summary of a company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholders’ equity on a specific date. One of the main goals of the balance sheet is to provide an equity value of the corporation (also called “book value”).
Conceptually the balance sheet concept is no different than determining the value of your home. First, a homeowner must determine the price (asset value) of the house – usually as a function of the sales price (estimated or actual). Next, the mortgage value (debt) is subtracted from the home price to arrive at the value (equity) of the homeowner’s position. The same principle applies to valuing corporations, but as you can imagine, the complexity can increase dramatically once you account for the diverse and infinite number of potential assets and liabilities a company can hold.
Metrics
Many key financial analysis metrics are derived directly from the balance sheet, or as a result of using some of its components. Here are a few key examples:
- ROE (Return on Equity): Derived by dividing the income from the income statement by the average equity value on the balance sheet. This indicator measures the profitability of a business relative to shareholders’ investments. All else equal, a higher ROE is preferred.
- P/B (Price to Book): A ratio comparing the market capitalization (total market price of all shares outstanding) of a company to its book value (equity). All else equal, a lower P/B is preferred.
- Debt/Equity or Debt/Capitalization: These ratios explain the relation of debt to the capital structure, indicating the overall amount of financial leverage a company is assuming. All else equal, lower debt ratios are preferred, however some businesses and industries can afford higher levels of debt due to a company’s cash flow dynamics.
There are many different ratios to provide insight into a company, nonetheless, these indicators provide a flavor regarding a company’s financial positioning. In addition, these ratios serve a valuable purpose in comparing the financial status of one company relative to others (inside or outside a primary industry of operation).
Balance Sheet Shortcomings
The balance sheet is primarily built upon a historical cost basis due to defined accounting rules and guidelines, meaning the stated value of an asset or liability on a balance sheet is determined precisely when a transaction occurs in time. Over time, this accounting convention can serve to significantly understate or overstate the value of balance sheet items.
Here are a few examples of how balance sheet values can become distorted:
- Hidden Assets: Not all assets are visible on the balance sheet. Certain intangible assets have value, but cannot be touched and are not recognized by accounting rules on this particular financial statement. Examples include: human capital (employees), research & development, brands, trademarks, and patents. All these items can have substantial value, yet show up nowhere on the balance sheet.
- Lack of Comparability: Comparability of balance sheet data can become fuzzy when certain accounting rules and assumptions are exercised by one company and not another. For instance, if two different companies purchased the same property, plant, and equipment at the same time and price, the values on the balance sheets may vary significantly in the future due to the application of different depreciation schedules (e.g., 10 years versus 20 years). Share repurchase is another case in point that can alter the comparison of equity values – in some cases resulting in a negative equity value.
- Goodwill & Distorted M&A Values: Companies that are active with mergers and acquisitions are forced to reprice assets and liabilities upwards and downwards (inflation, or the lack thereof, can lead to large balance sheet adjustments). Goodwill (asset) is the excess value paid over fair market value in an acquisition. Goodwill can be quite substantial in certain transactions, especially when a high premium price is paid.
- Write-offs and Write-ups: In 2001, telecom component maker JDS Uniphase (JDSU) slashed the value of its goodwill by a massive $44.8 billion. This is an extreme illustration of how the accounting-based values on the financial statement can exhibit significant differences from a company’s market capitalization. Often, the market value (the cumulative value of all outstanding market-priced shares) is a better indicator of a company’s true value – conceptually considered the present value of all future cash flows.
Some balance sheets are built on shaky foundations. A risky, debt-laden balance sheet can resemble a shoddy home foundation built on sand, along an earthquake fault-line. In other words, a small shock can lead to financial collapse. In the credit-driven global bubble we are currently working through, many companies that were built on shaky foundations (i.e., a lot of debt) are struggling to survive. Survival may be dependent on a company restructuring, selling assets, paying down debt, merging, or other tactic with the aim of shoring up the balance sheet. Using the balance sheet value of a company in conjunction with the marketplace price of the same business can be a valuable approach in establishing a more reliable valuation. Before you make an investment or valuation conclusion about a company, do yourself a favor and dig into the balance sheet to verify the condition and soundness of a company’s financial foundation.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at time of publishing had no direct positions in TGT, SHLD, or JDSU. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Running with the Bulls
Guest Contributing Writer: Bruce Wimberly
No matter where you turn some “expert” is espousing his or her view on the direction of the market. The reality is none of them know. My advice to anyone is avoid the fallacy of experts. Those that purport to know, donʼt. It is a mere exercise in futility to justify charging higher fees. Letʼs be honest if anyone knew the future direction of asset prices they would be beyond rich (Iʼm talking John Paulson – Trade of the Century rich!). Nice job John who would have thought you could make that much money betting against mortgages.
As investors our best bet is to accept that fact that market timing is a losing strategy. Timing the market is similar to a coin flip. Pure and simple, the cost of getting it wrong wipes out the occasional gain of getting it right. Remember, every time you listen to the perma-bears and try to time the market, there is big time investment professional on the other side of that trade who is by definition taking the opposite view.
Good investors expand their timeframes. They do not get sucked into the news of the day. Let the perma-bears worry about Dubai, currency devaluation, or whatever else is todayʼs fear. Keep in mind there is always something to worry about. For long term investors the greatest fear is not being in the market. For example, if inflation were to average 3% and you are sitting in cash earning nothing your money will be cut in half by 2033. Grandmaʼs mattress is not an option for most people.
Now back to the question of bulls versus bears and the direction of the markets. Who is right? The simplest way to think about this comes from Oracle of Omaha himself, Warren Buffett. Buffett thinks of the market as a reflection of total market cap relative to US GNP (gross national product). After all, in the long run the market should approximate some measure of overall corporate profitability or in this case overall economic growth. If you accept Buffettʼs argument then the market is neither overly expensive or cheap. As of yesterday the total market index is at $11,296.2 billion which is about 79% of the last reported GDP. (I know the perma-bulls will find some reason to bash the reported GDP number). Nevertheless, this simple formula provides a good long term context on which to gage the relative attractiveness of the overall market. To put todayʼs number in context (79%) at the peak of the market bubble in 1999, the ratio of total market cap/GDP was 150% or almost double todayʼs reading. Yes, the market has made a major move from depressed levels earlier in the year but that is irrelevant. Donʼt anchor on that number or you will never get off the sidelines.
My advice is simple, ignore the perma-bears and avoid market timing like the plague for it is a suckers bet (see also article on passive vs. active investing). If the market does pull back (and it will at some point) this is great news for the long term investor. Anytime you can buy a stock on sale – this is a good thing! So enjoy the Christmas holidays, donʼt believe the hyped up bears and as always:
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds and equity securities in client and personal portfolios at the time of publishing, but had no direct position in BRKA/B. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
The Not So Good, Bad, and Ugly
There’s a new bounty hunter in town, and it’s not Clint Eastwood from the legendary western film The Good, the Bad and the Ugly. Rather, it’s John Carney from Clusterstock who is keeping the bold bears honest, even though they have received their heads handed to them in this supposed “sucker, bear-market rally.” Perhaps, the bears will ultimately be proven right, but in the mean time, these tape fighters are losing blood by the quart.
Music from what Quentin Tarantino calls the best-directed film of all-time.
I find the existence of accountability sheriffs in the business media world rejuvenating since these roles are sorely lacking. Too often, so-called pundits spout off bold assertive predictions and industry commentators make no effort to review the track records of those prognosticators. I commend many of the industry practitioners for putting their necks out on the line, but viewers need some sort of historical batting average to judge the odds of forecast reliability. The game of predictions is no science, but there can be some objective responsibility instituted by media researchers and commentators. Media outlets provide carte blanche to predictors without doing homework on the guests. Unfortunately, time-strapped viewers have little to no time to research commentator track records.
Typically how it works, especially in the massively fragmented media world (which I admittedly participate in on a relatively small scale), you have countless voices making extreme predictions across the broad economic and financial globe. Eventually, some forecasts will be right, including those correct for the wrong reasons – just think back to your statistics class where you learned about the “law of large numbers” or the family living room where the broken clock provides correct time twice a day (see my other article on bold predictions). Since any human likes to be associated with greatness, these future-seers are strolled into media studios, put on a pedestal and asked to share their brilliance, all without critically reviewing the past record of the purported expert.
Rather than make bold predictions about market direction, which is virtually impossible to predict with accuracy on a sustainable basis, I choose to look at the market with a perspective similar to the greats. For example, Peter Lynch who earned +29% per year from 1977 – 1990 (achieving about double the market return) says it’s best to “assume the market is going nowhere and invest accordingly.” Realizing your fallibility is important also. Even with Lynch’s incredible track record, he knows “you’re terrific in this business [if] you’re right six times out of 10.” According to Lynch fretting about the market direction is also useless: “If you spend more than 14 minutes a year worrying about the market, you’ve wasted 12 minutes.” Interestingly, even Warren Buffett, arguably the greatest investor of all-time, never comments on short-term directions of the market, despite being hailed as the “Oracle of Omaha.”
Predictions and forecasts will never go away, but I will sleep better at night knowing sheriffs like John Carney are keeping track of the good, the bad and the ugly. Who knows, maybe he’ll even take me on as a deputy.
View John Carney’s Full Article
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, and at the time of publishing had no direct positions in BRKA/B. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Action Dan (Poker King) and Professional Investing
As I write in my book (How I Managed $20,000,000,000.00 by Age 32), successful investing requires skillful use of both art and science. What I find so fascinating is that the same principles apply to poker playing. Like investing, poker is also a game of skill that rewards a player who adequately understands the mathematical probabilities (science) while still able to appropriately read the behavior of his or her opponents (art). Take for example professional poker player and 1995 WSOP champ Dan Harrington. In 2003 he finished 3rd at the World Series of Poker Main Event (the Super Bowl of poker) out of a pool of 839 players. In 2004, the following year, despite the pool more than tripling to 2,576 participants, Mr. Harrington managed to finish 4th and take home a cool $1.5 million in prize money. Did luck account for this success? I think not. Odds, if left to chance, would be 1 in 25,000 for repeating this feat, according to the Economist.
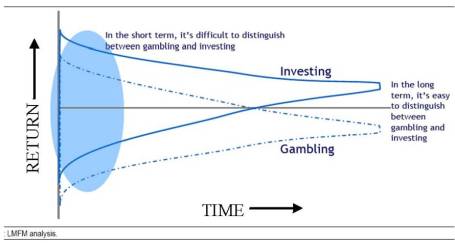
In the short-run, random volatility and luck can make the average investor look like Warren Buffett, but because of the efficiency of the market, that same average investor will look like a schmuck over the long-run. Legg Mason Funds Management put out an incredible chart that I believe so elegantly captures the incoherent and meaningless, short-term noise that the media attempts to interpret daily. What appears like outperformance in the short-run may merely be the lucky performance of a reckless speculator.
Dan Harrington, and so many other talented professionals know this fact all too well when an inexperienced “donkey” over-bets a clearly inferior hand, only to nail an inside-straight card on the “river” (last card of the round) out of pure luck – thereby knocking out a superior professional player. Over the long-run these out-of-control players end up losing all their money and professionals relish the opportunity of playing against them.
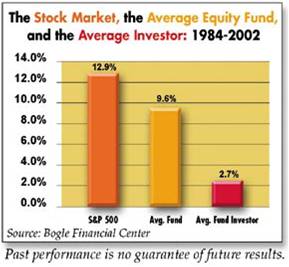
Talk to professionals and ask them what the biggest mistake new players make? The predominate answer: novices simply play too many hands. In the world of investing, the same can be said for excessive trading. Commissions, transactions costs, taxes and most importantly, ill-timed, emotionally driven trades lead the average investor to significantly underperform. I’ve referenced it before, and I’ll reference it again, John Bogle’s 1984-2002 study shows the significant drag the aforementioned costs have on professionals’ performance, and especially the average fund investor that underperformed the passive (a.k.a., “Do Nothing” strategy) S&P 500 return by more than a whopping 10% annually!
I consider myself an above average player, and I’ve won a few small tournaments, but match me up against a professional like “Action Dan” Harrington and I’ll get destroyed in the long-run. Investing, like professional poker, can lead to excess returns with the proper integration of patience and a disciplined systematic approach. I strongly believe that all great long-term investors successfully implement a strategy that marries the art and science aspects of investing. Don’t hold your breath if you expect to see me on ESPN, it may be a while before you see me at the Final Table with Dan Harrington at the World Series of Poker.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, and at the time of publishing had no direct positions in LM, DIS, or BRKA/B. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.