Posts tagged ‘stagflation’
Animal Spirits to Animal Hibernation

Investor mood or sentiment can change rather quickly. Immediately after the 2024 presidential elections, positive animal spirits catapulted the stock market higher due to hopes of stimulating tax cuts and deregulation legislation. However, those warm and fuzzy feelings soured last month, as investor focus shifted to on-again, off-again tariff talks, and stagflation concerns, which have converted animal spirits into gloomy feelings of hibernation.
As a result, the advancing bull market took a breather and transformed into a weary bear during March. For the month, the S&P 500 (-5.8%), NASDAQ (-8.2%), and the Dow Jones Industrial Average (-4.2%) all fell significantly in the wake of tariffs, inflation, and recession worries.
Lovely Liberation Day or Tariff Trouble?
Since the President took office in January, he has announced, reversed, and implemented tariffs across a wide range of countries and sectors, including China, Canada, Mexico, the EU, Colombia, Venezuela, steel, aluminum, oil, automobiles, digital services taxes, and more.
The day of reckoning begins on April 2nd, designated Liberation Day by the president. This is when the president and the White House officially announce global reciprocal tariffs on foreign countries in an attempt to reverse the nation’s large trade deficit (see chart below) and bring manufacturing back to the United States. For example, if Germany subsidizes BMW cars sold in the U.S. while simultaneously placing tariffs (i.e., additional taxes) on American Ford Explorers sold in Germany, the president wants to impose equivalent reciprocal tariffs on those same BMWs sold in the U.S. in an effort to level the trading playing field. On the surface, a $131 billion trade deficit sounds very significant, but when compared to a $30 trillion economy (Gross Domestic Product – GDP), this negative trade balance represents less than 0.5% of GDP – effectively a rounding error. I have previously written how tariffs represent more of a molehill than a mountain (see Tariff Sheriff), in part because consumer spending and services make up the vast majority of our country’s economic activity, whereas trade and manufacturing are relatively smaller segments.

Source: Trading Economics
Driving home the point that tariffs are more bark than bite, Senior White House trade and manufacturing counselor Peter Navarro recently stated the 2025 tariffs could add $700 billion annually to U.S. revenues, including $100 billion from the recently announced 25% auto tariffs. Many economists believe this collection estimate is too optimistic. However, even if this target is achievable, $700 billion only represents a measly 2% of overall GDP.
Tariffs = Recession or Stagflation?
With the recent stock market downdraft and growing concerns related to tariffs, some economists and pundits are raising the probability of a recession and the possibility of inflation accompanying an economic downturn (i.e., stagflation).
Economic data should clear some of the fog. Fresh employment numbers will be released this Friday, which should shine some light on the health of the economy. Irrespective of this month’s results, the most recent 4.1% unemployment rate (see chart below), though slightly higher over the last two years, does not strongly indicate a recession.

Source: Trading Economics
Other “hard” data, such as GDP, also suggest a slowing economy rather than a recession. For instance, a recent survey of 14 economists estimates the economy is growing at a paltry +0.3% rate in Q1 – 2025 versus +2.3% in Q4 – 2024. Data is continually changing, but if a looming recession were imminent, corporate earnings would likely be trending downward, not upwards, as evident in the chart below.

Source: Yardeni Research
Tariff Inflation Has Yet to Arrive
There is no doubt tariffs function as a tax hike on consumers because U.S. companies that pay the tariffs on imported goods are eventually forced to raise prices to maintain profit margins or limit margin degradation.
Nonetheless, inflation did not spike under President Trump’s first term. Even if the president’s new policies result in more aggressive tariff actions this go-around, inflation will likely remain in check due to the point mentioned earlier – imported goods represent a small percentage of overall consumer and business purchases.
Tariff implementation is just beginning, so only time will tell how pervasive inflation will become. However, what we do know now is that inflation has declined dramatically over the last couple of years and has not yet spiked (see Consumer Price Index chart below).

Source: Calafia Beach Pundit
Where Could I Be Wrong?
I have explained how some of the lagging “hard” data does not signal recession or stagflation, but what could I be missing? For starters, some of the leading “soft” data (e.g., surveys) indicate various cracks in the economic foundation are forming. Take the recent Consumer Confidence data (see chart below), which has weakened dramatically from pre-COVID and even post-COVID levels.

Source: Trading Economics
It’s not just consumers who are feeling uneasy about the economic environment; businesses are as well. Another soft data point flashing red is the NFIB Small Business Uncertainty index, which recently reported its second-highest reading in 48 years (see chart below). Even if my argument that tariffs are too small to materially impact the economy holds, if the psychological effects of tariff uncertainty paralyzes consumer and business economic activity to a standstill, then tariffs could indeed become a substantial factor.

Source: National Federation of Independent Business (NFIB)
What Comes Next After Liberation Day?
Liberation Day is unlikely to trigger an immediate and sustained V-shaped recovery in the stock market because international trading partners will be forced to announce retaliatory tariffs in response to President Trump’s reciprocal tariffs, potentially leading to additional reactionary tariffs by the U.S.
Additionally, the reciprocal tariffs announced on April 2nd will likely serve as a starting point for subsequent negotiations with trading partners. Without a comprehensive resolution, investor sentiment will likely remain somewhat unresolved and unsettled. Regardless of your views on the size and impact of tariffs, Liberation Day will at least bring some clarity and reduce the uncertainty surrounding the current murky and chaotic environment.
The multi-year bull market continued its charge after the presidential election, but investor sentiment has weakened the bull run due to tariff uncertainty. In response, the excited bull has temporarily turned into a sleepy bear. Depending on how these tariff events unfold, we will soon find out whether Liberation Day will awaken the bear to hunt for bulls or send it into deep hibernation.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
This article is an excerpt from a previously released Sidoxia Capital Management complimentary newsletter (April 1, 2025). Subscribe Here to view all monthly articles.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing had no direct position in F or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on the IC Contact page.
Air Bags Deployed to Cushion Bank Crashes
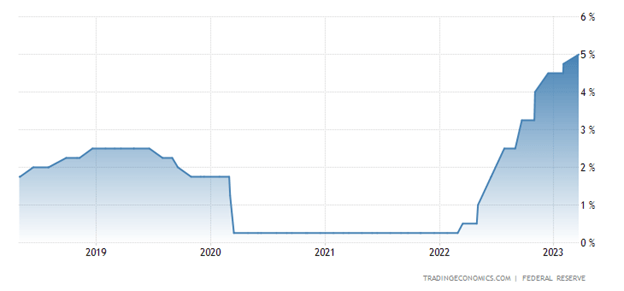
In recent years, COVID and a ZIRP (Zero Interest Rate Policy) caused out-of-control inflation to swerve the economy in the wrong direction. However, the Federal Reserve and its Chairman, Jerome Powell, slammed on the brakes last year by instituting the most aggressive interest rate hiking policy in over four decades.
At the beginning of last year, interest rates (Federal Funds Rate target) stood at 0% (at the low end of the target), and today the benchmark interest rate stands at 5.0% (at the upper-end of the target) – see chart below.
Source: Trading Economics
Unfortunately, this unparalleled spike in interest rates contributed to the 2nd and 3rd largest bank failures in American history, both occurring in March. The good news is the Federal Reserve and banking regulators (the Treasury and FDIC – Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation) deployed some safety airbags last month. Most notably, the Fed, FDIC, and Treasury jointly announced the guarantee of all deposits at SVB, shortly after the bank failure. Moreover, the Fed and Treasury also revealed a broader emergency-lending program to make more funds available for a large swath of banks to meet withdrawal demands, and ultimately prevent additional runs on other banks.
Investors were generally relieved by the government’s response, and the financial markets reacted accordingly. The S&P 500 rose +3.5% last month, and the technology-heavy NASDAQ index catapulted even more (+6.7%). But not everyone escaped unscathed. The KBW Bank Index got pummeled by -25.2%, which also injured the small-cap and mid-cap stock indexes, which declined -5.6% (IJR) and -3.5% (IJH), respectively.
Nevertheless, as mentioned earlier, slamming on the economic brakes too hard can lead to unintended consequences, for example, a bank failure or two. Well, that’s exactly what happened in the case of Silicon Valley Bank (SVB), the 2nd largest bank failure in history ($209 billion in assets), and cryptocurrency-heavy Signature Bank, the 3rd largest banking collapse in history – $110 billion in assets (see below).
Source: The Wall Street Journal
How did this Silicon Valley Bank failure happen? In short, SVB suffered a bank run, meaning bank customers pulled out money faster than the bank could meet withdrawal requests. Why did this happen? For starters, SVB had a concentrated customer base of financially frail technology start-ups. With a weak stock market last year, many of the start-ups were bleeding cash (i.e., shrinking their bank deposits) and were unable to raise additional funds from investors.
As bank customers began to lose confidence in the liquidity of SVB, depositors began to accelerate withdrawals. SVB executives added gasoline to the fire by making risky investments long-term dated government bonds. Essentially, SVB was making speculative bets on the direction of future interest rates and suffered dramatic losses when the Federal Reserve hiked interest rates last year at an unprecedented rate. This unexpected outcome meant SVB had to sell many of its government bond investments at steep losses in order to meet customer withdrawal requests.
It wasn’t only the large size of this bank failure that made it notable, but it was also the speed of its demise. It was only three and a half weeks ago that SVB announced a $1.8 billion loss on their risky investment portfolio and the subsequent necessity to raise $2.3 billion to fill the hole of withdrawals and losses. The capital raise announcement only heightened depositor and investor anxiety, which led to accelerated bank withdrawals. Within a mere 24-hour period, SVB depositors attempted to withdraw a whopping $42 billion.
Other banks, such as First Republic Bank (FRB), and a European investment bank, Credit Suisse Group (CS), also collapsed on the bank crashing fears potentially rippling through other financial institutions around the globe. Fortunately, a consortium of 11 banks provided a lifeline to First Republic with a $30 billion loan. And Credit Suisse was effectively bailed out by the Swiss central bank when Credit Suisse borrowed $53 billion to bolster its liquidity.
While stockholders and bondholders lost billions of dollars in this mini-banking crisis, financial vultures swirled around the remains of the banking sector. More specifically, First Citizens BancShares (FCNA) acquired the majority of Silicon Valley Bank’s assets with the assistance of the FDIC, and UBS Group (UBS) acquired Credit Suisse for more than $3 billion, thereby providing some stability to the banking sector during a volatile period.
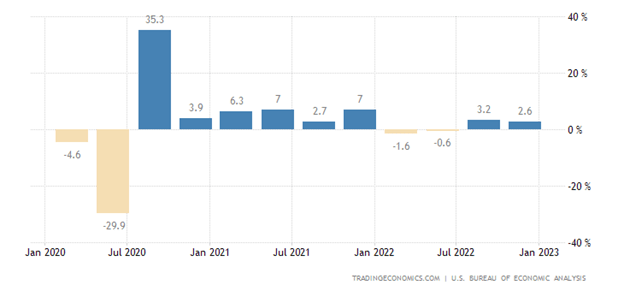
Many pundits have been predicting the U.S. economy to crash into a recession as a result of the aggressive, interest rate tightening policy of the Federal Reserve. So far, Mark Twain would probably agree that the death of the U.S. economy has been greatly exaggerated. Currently, the first quarter measurement of economic activity, GDP (Gross Domestic Product), is estimated to measure approximately +2.0% after closing 2022’s fourth quarter at +2.6% (see chart below). As you probably know, a definition of a recession is two consecutive quarters of negative GDP growth.
Source: Trading Economics
Regardless of the economic outcome, investors are now predicting the Federal Reserve to be at the end or near the end of its interest rate hiking cycle. Presently, there is roughly a 50/50 chance of one last 0.25% interest rate increase in May (see chart below), and then investors expect at least one interest rate cut by year-end.
Source: CME Group
Last year was a painful year for most investors, but stocks as measured by the S&P 500 have bounced approximately +18% since the October 2022 lows. Market participants are still worried about a possible recession crashing the economy later this year, but hopefully last year’s stock market collision and subsequent banking airbag protections put in place will protect against any further financial pain.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
This article is an excerpt from a previously released Sidoxia Capital Management complimentary newsletter (Apr. 3, 2023). Subscribe Here to view all monthly articles.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing had no direct position in SIVB, FCNA, UBS, FRB, CS, or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Fed Ripping Off the Inflation Band-Aid
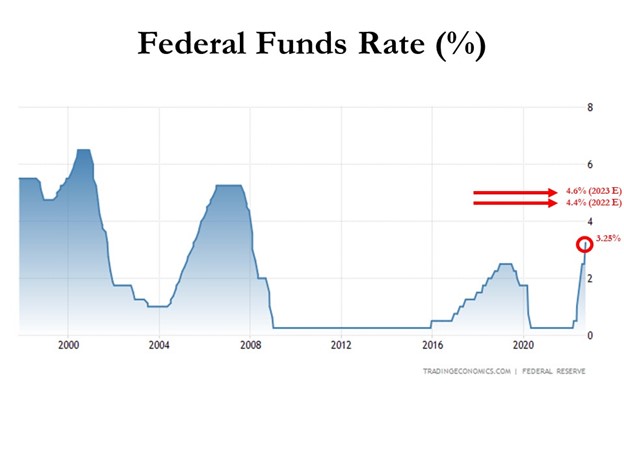
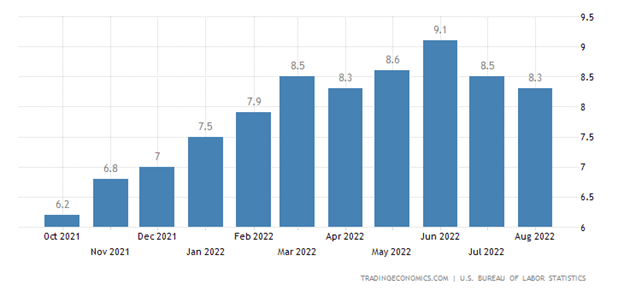
Inflation rates have been running near 40-year highs, and as a result, the Federal Reserve is doing everything in its power to rip off the Band-Aid of insidious high price levels in a swift manner. The Fed’s goal is to inflict quick, near-term pain on the economy in exchange for long-term price stability and future economic gains. How quickly has the Fed been hiking interest rates? The short answer is the rate of increases has been the fastest in decades (see chart below). Essentially, the Federal Reserve has pushed the targeted benchmark Federal Funds target rate from 0% at the beginning of this year to 3.25% today. Going forward, the goal is to lift rates to 4.4% by year-end, and then to 4.6% by next year (see Fed’s “dot plot” chart).
How should one interpret all of this? Well, if the Fed is right about their interest rate forecasts, the Band-Aid is being ripped off very quickly, and 95% of the pain should be felt by December. In other words, there should be a light at the end of the tunnel, soon.
The Good News on Inflation
When it comes to inflation, the good news is that it appears to be peaking (see chart below), and many economists see the declining inflation trend continuing in the coming months. Why do pundits see inflation peaking? For starters, a broad list of commodity prices have declined significantly in recent months, including gasoline, crude oil, steel, copper, and gold, among many others.
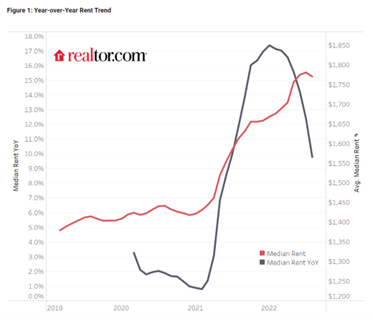
Outside of commodities, investors have seen prices drop in other areas of the economy as well, including housing prices, which recently experienced the fastest monthly price drop in 11 years, and rent prices as well (see chart below).
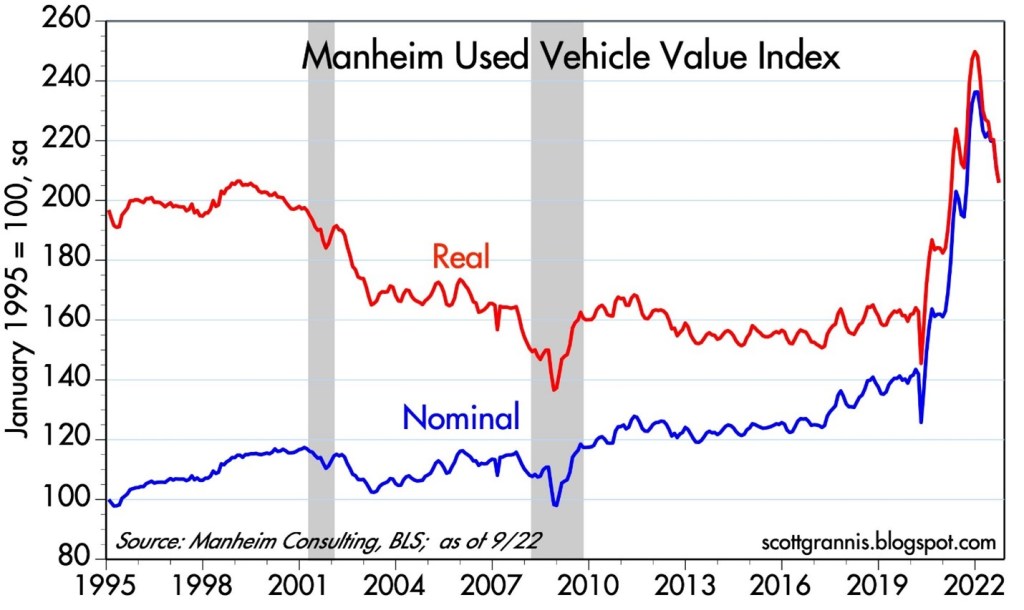
Anybody who was shopping for a car during the pandemic knows what happened to pricing – it exploded higher. But even in this area, we are seeing prices coming down (see chart below), and CarMax Inc. (KMX), the national used car retail chain confirmed the softening price trend last week.
Pain Spread Broadly
When interest rates increase at the fastest pace in 40 years, pain is felt across almost all asset classes. It’s not just U.S. stocks, which declined -9.3% last month (S&P 500), but it’s also housing -8.5% (XHB), real estate investment trusts -13.8% (VNQ), bonds -4.4% (BND), Bitcoin -3.1%, European stocks -10.1% (VGK), Chinese stocks -14.4% (FXI), and Agriculture -3.0% (DBA). The +17% increase in the value of the U.S. dollar this year against a basket of foreign currencies is substantially pressuring cross-border business for larger multi-national companies too – Microsoft Corp. (MSFT), for example, blamed U.S. dollar strength as the primary reason to cut earnings several months ago. Like Hurricane Ian, large interest rate increases have caused significant damage across a wide swath of areas.
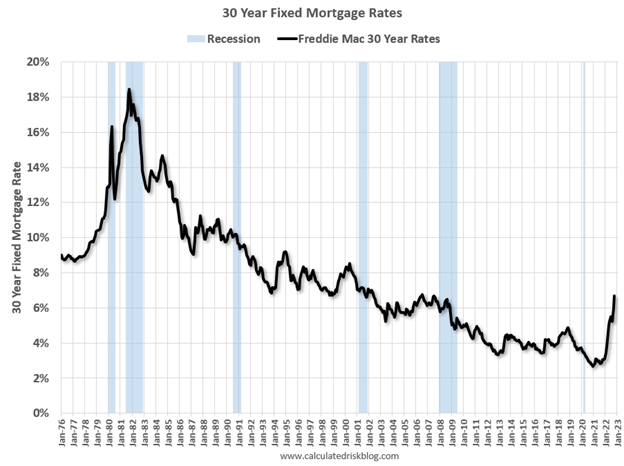
But for those following the communication of Federal Reserve Chairman, Jerome Powell, in recent months, they should not be surprised. Chairman Powell has signaled on numerous occasions, including last month at a key economic conference in Jackson Hole, Wyoming, that the Fed’s war path to curb inflation by increasing interest rates will inflict wide-ranging “pain” on Americans. Some of that pain can be seen in mortgage rates, which have more than doubled in 2022 and last week eclipsed 7.0% (see chart below), the highest level in 20 years.
Now is Not the Time to Panic
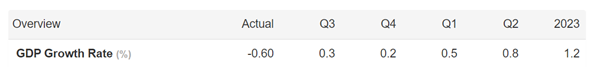
There is a lot of uncertainty out in the world currently (i.e., inflation, the Fed, Russia-Ukraine, strong dollar, elections, recession fears, etc.), but that is always the case. There is never a period when there is nothing to be concerned about. With the S&P 500 down more than -25% from its peak (and the NASDAQ down approximately -35%), now is not the right time to panic. Knee-jerk emotional decisions during stressful times are very rarely the right response. With these kind of drops, a mild-to-moderate recession is already baked into the cake, even though the economy is expected to grow for the next four quarters and for all of 2023 (see GDP forecasts below). Stated differently, it’s quite possible that even if the economy deteriorates into a recession, stock prices could rebound smartly higher because any potential future bad news has already been anticipated in the current price drops.
Worth noting, as I have pointed out previously, numerous data points are indicating inflation is peaking, if not already coming down. Inflation expectations have already dropped to about 2%, if you consider the spread between the yield on the 5-Year Note (4%) and the yield on the 5-Year TIP-Treasury Inflation Protected Note (2%). If the economy continues to slow down, and inflation has stabilized or declined, the Federal Reserve will likely pivot to decreasing interest rates, which should act like a tailwind for financial markets, unlike the headwind of rising rates this year.
Ripping off the Band-Aid can be painful in the short-run, but the long-term gains achieved during the healing process can be much more pleasurable.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in MSFT, BND and certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing had no direct position in KMX, XHB, VNQ, VGK, FXI, DBA or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.