Posts tagged ‘Phil Fisher’
Cutting Losses with Fisher’s 3 Golden Sell Rules
Returning readers to Investing Caffeine understand this is a location to cover a wide assortment of investing topics, ranging from electric cars and professional poker to taxes and globalization. Investing Caffeine is also a location that profiles great investors and their associated investment lessons.
Today we are going to revisit investing giant Phil Fisher, but rather than rehashing his accomplishments and overall philosophy, we will dig deeper into his selling discipline. For most investors, selling securities is much more difficult than buying them. The average investor often lacks emotional self-control and is unable to be honest with himself. Since most investors hate being wrong, their egos prevent taking losses on positions, even if it is the proper, rational decision. Often the end result is an inability to sell deteriorating stocks until capitulating near price bottoms.
Selling may be more difficult for most, but Fisher actually has a simpler and crisper number of sell rules as compared to his buy rules (3 vs. 15). Here are Fisher’s three sell rules:
1) Wrong Facts: There are times after a security is purchased that the investor realizes the facts do not support the supposed rosy reasons of the original purchase. If the purchase thesis was initially built on a shaky foundation, then the shares should be sold.
2) Changing Facts: The facts of the original purchase may have been deemed correct, but facts can change negatively over the passage of time. Management deterioration and/or the exhaustion of growth opportunities are a few reasons why a security should be sold according to Fisher.
3) Scarcity of Cash: If there is a shortage of cash available, and if a unique opportunity presents itself, then Fisher advises the sale of other securities to fund the purchase.
Reasons Not to Sell
Prognostications or gut feelings about a potential market decline are not reasons to sell in Fisher’s eyes. Selling out of fear generally is a poor and costly idea. Fisher explains:
“When a bear market has come, I have not seen one time in ten when the investor actually got back into the same shares before they had gone up above his selling price.”
In Fisher’s mind, another reason not to sell stocks is solely based on valuation. Longer-term earnings power and comparable company ratios should be considered before spontaneous sales. What appears expensive today may look cheap tomorrow.
There are many reasons to buy and sell a stock, but like most good long –term investors, Fisher has managed to explain his three-point sale plan in simplistic terms the masses can understand. If you are committed to cutting investment losses, I advise you to follow investment legend Phil Fisher – cutting losses will actually help prevent your portfolio from splitting apart.

Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Playing the Field with Your Investments
For some, casually dating can be fun and exciting. The same goes for trading and speculating – the freedom to make free- wheeling, non-committal purchases can be exhilarating. Unfortunately the costs (fiscally and emotionally) of short-term dating/investing often outweigh the benefits.
Fortunately, in the investment world, you can get to know an investment pretty well through fundamental research that is widely available (e.g., 10Ks, 10Qs, press releases, analyst days, quarterly conference calls, management interviews, trade rags, research reports). Unlike dating, researching stocks can be very cheap, and you do not need to worry about being rejected.
Dating is important early in adulthood because we make many mistakes choosing whom we date, but in the process we learn from our misjudgments and discover the important qualities we value in relationships. The same goes for stocks. Nothing beats experience, and in my long investment career, I can honestly say I’ve dated/traded a lot of pigs and gained valuable lessons that have improved my investing capabilities. Now, however, I don’t just casually date my investments – I factor in a rigorous, disciplined process that requires a serious commitment. I no longer enter positions lightly.
One of my investment heroes, Peter Lynch, appropriately stated, “In stocks as in romance, ease of divorce is not a sound basis for commitment. If you’ve chosen wisely to begin with, you won’t want a divorce.”
Charles Ellis shared these thoughts on relationships with mutual funds:
“If you invest in mutual funds and make mutual funds investment changes in less than 10 years…you’re really just ‘dating.’ Investing in mutual funds should be marital – for richer, for poorer, and so on; mutual fund decisions should be entered into soberly and advisedly and for the truly long term.”
No relationship comes without wild swings, and stocks are no different. If you want to survive the volatile ups and downs of a relationship (or stock ownership), you better do your homework before blindly jumping into bed. The consequences can be punishing.
Buy and Hold is Dead…Unless Stocks Go Up
If you are serious about your investments, I believe you must be mentally willing to commit to a relationship with your stock, not for a day, not for a week, or not for a month, but rather for years. Now, I know this is blasphemy in the age when “buy-and-hold” investing is considered dead, but I refute that basic premise whole-heartedly…with a few caveats.
Sure, buy-and-hold is a stupid strategy when stocks do nothing for a decade – like they have done in the 2000s, but buying and holding was an absolutely brilliant strategy in the 1980s and 1990s. Moreover, even in the miserable 2000s, there have been many buy-and-hold investments that have made owners a fortune (see Questioning Buy & Hold ). So, the moral of the story for me is “buy-and-hold” is good for stocks that go up in price, and bad for stocks that go flat or down in price. Wow, how deeply profound!
To measure my personal commitment to an investment prospect, a bachelorette investment I am courting must pass another test…a test from another one of my investment idols, Phil Fisher, called the three-year rule. This is what the late Mr. Fisher had to say about this topic:
“While I realized thoroughly that if I were to make the kinds of profits that are made possible by [my] process … it was vital that I have some sort of quantitative check… With this in mind, I established what I called my three-year rule.” Fisher adds, “I have repeated again and again to my clients that when I purchase something for them, not to judge the results in a matter of a month or a year, but allow me a three year period.”
Certainly, there will be situations where an investment thesis is wrong, valuation explodes, or there are superior investment opportunities that will trigger a sale before the three-year minimum expires. Nonetheless, I follow Fisher’s rule in principle in hopes of setting the bar high enough to only let the best ideas into both my client and personal portfolios.
As I have written in the past, there are always reasons of why you should not invest for the long-term and instead sell your position, such as: 1) new competition; 2) cost pressures; 3) slowing growth; 4) management change; 5) valuation; 6) change in industry regulation; 7) slowing economy; 8 ) loss of market share; 9) product obsolescence; 10) etc, etc, etc. You get the idea.
Don Hays summed it up best: “Long term is not a popular time-horizon for today’s hedge fund short-term mentality. Every wiggle is interpreted as a new secular trend.”
Peter Lynch shares similar sympathies when it comes to noise in the marketplace:
“Whatever method you use to pick stocks or stock mutual funds, your ultimate success or failure will depend on your ability to ignore the worries of the world long enough to allow your investments to succeed.”
Every once in a while there is validity to some of the concerns, but more often than not, the scare campaigns are merely Chicken Little calling for the world to come to an end.
Patience is a Virtue
In the instant gratification society we live in, patience is difficult to come by, and for many people ignoring the constant chatter of fear is challenging. Pundits spend every waking hour trying to explain each blip in the market, but in the short-run, prices often move up or down irrespective of the daily headlines. Explaining this randomness, Peter Lynch said the following:
“Often, there is no correlation between the success of a company’s operations and the success of its stock over a few months or even a few years. In the long term, there is a 100% correlation between the success of a company and the success of its stock. It pays to be patient, and to own successful companies.”
Long-term investing, like long-term relationships, is not a new concept. Investment time horizons have been shortening for decades, so talking about the long-term is generally considered heresy. Rather than casually date a stock position, perhaps you should commit to a long-term relationship and divorce your field-playing habits. Now that sounds like a sweet kiss of success.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Standing on the Shoulders of a Growth Giant: Phil Fisher
Since it’s Father’s Day weekend, it seems appropriate to write about about the “Father of Growth Investing”…Phil Fisher.
It was English physicist, astronomer, philosopher, and mathematician Sir Isaac Newton who in 1675 stated, “If I have seen further it is by standing on the shoulders of giants.” Investors too can stand on the shoulders of market giants by studying the timeless financial knowledge from current and past market legends. The press, all too often, focuses on the hot managers of our time while forgetting or kicking to the curb those managers whom are temporarily out of favor. Famous and enduring value managers typically have gained the press spotlight, rightfully so in the case of current greats like Warren Buffett or past talents like Benjamin Graham, because they managed to prosper through numerous economic cycles. However, when it comes to growth legends like Phil Fisher, author of the must-read classic Common Stocks and Uncommon Profits, many people I bump into have never heard of him. Hopefully that will change over time.
The Career
Born on September 8, 1907, Mr. Fisher lived until the ripe age of 96 when he passed on March 4, 2004. Fisher was no dummy – he enrolled in college at age 15 and started graduate school at Stanford a few years later, before he dropped out and started his own investment firm in 1931. His son, Ken, currently heads his own investment firm, Fisher Investments, writes for Forbes magazine, and has authored multiple investment books. Unlike his dad, Ken has more of a natural bent towards value stocks.
Buy-And-Hold
Phil Fisher’s iconic book, Common Stocks and Uncommon Profits, was published in 1958. Mr. Fisher believed in many things and perhaps would have been thrown under the bus today for his long-term convictions in “buy-and-hold.” Or as Mr. Fisher put it, “If the job has been correctly done when a common stock is purchased, the time to sell it is – almost never.” Not every investment idea made the cut, however he is known to have bought Motorola (MOT) stock in 1955 and held it until his death in 2004 for a massive gain. Generally, he gave initial stock purchases a three-year leash before considering a change to his investment position. If the conviction to purchase a stock for such duration is not present, then the investment opportunity should be ignored.
Fisher’s concentration on growth stocks also shaped his view on dividends. Dividends were not important to Fisher – he was more focused on how the company is investing retained earnings to achieve its earnings growth. Like Fisher, Peter Lynch is another growth hero of mine that also felt there is too much focus on the Price/Earnings (PE) ratio rather than the long-term earnings potential.
“Scuttlebutt”
Another classic trademark of Fisher’s investing style was his commitment to fundamental research. He was focused on accumulating data covering a broad range of areas including, customers, suppliers, and competitors. Fisher also emphasized factors like market share, return on invested capital, margins, and the research & development budget. What Mr. Fisher called his varied approach to gathering diverse sets of information was “scuttlebutt.”
Buying & Selling Points
Although Fisher believed firmly in buy and hold, he was not scared to sell when the firm no longer met the original buying criteria or his original assessment for purchased was deemed incorrect.
When buying, Fisher preferred to buy stocks in downturns or temporary problems – contrary to your typical momentum growth manager today (read article on momentum). Fisher has this to say on the topic: “This matter of training oneself to not go with the crowd but to be able to zig when the crowd zags, in my opinion, is one of the most important fundamentals of the investment success.”
Learning from Mistakes
Like all great investors I have studied, Phil Fisher also believed in learning from your mistakes:
“I have always believed that the chief difference between a fool and a wise man is that the wise man learns from his mistakes, while the fool never does.”
He expanded on the topic by saying the following:
“Making mistakes is inherent cost of investing just like bad loans are for the finest lending institutions. Don’t blindly accept dominant opinion and don’t be contrary for the sake of being contrary.”
I could only dream of having a fraction of Mr. Fisher’s career success – he retired in 1999 at the age of 91 (not bad timing). As my investment management and financial planning firm matures (Sidoxia Capital Management, LLC), I will continue to study the legendary giants of investing (past and present) to sharpen my investing skills.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing, SCM had no direct position in MSI, BRKA/B, or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on ICContact page.
Cutting Losses with Fisher’s 3 Golden Sell Rules
Returning readers to Investing Caffeine understand this is a location to cover a wide assortment of investing topics, ranging from electric cars and professional poker to taxes and globalization. Investing Caffeine is also a location that profiles great investors and their associated investment lessons.
Today we are going to revisit investing giant Phil Fisher, but rather than rehashing his accomplishments and overall philosophy, we will dig deeper into his selling discipline. For most investors, selling securities is much more difficult than buying them. The average investor often lacks emotional self-control and is unable to be honest with himself. Since most investors hate being wrong, their egos prevent taking losses on positions, even if it is the proper, rational decision. Often the end result is an inability to sell deteriorating stocks until capitulating near price bottoms.
Selling may be more difficult for most, but Fisher actually has a simpler and crisper number of sell rules as compared to his buy rules (3 vs. 15). Here are Fisher’s three sell rules:
1) Wrong Facts: There are times after a security is purchased that the investor realizes the facts do not support the supposed rosy reasons of the original purchase. If the purchase thesis was initially built on a shaky foundation, then the shares should be sold.
2) Changing Facts: The facts of the original purchase may have been deemed correct, but facts can change negatively over the passage of time. Management deterioration and/or the exhaustion of growth opportunities are a few reasons why a security should be sold according to Fisher.
3) Scarcity of Cash: If there is a shortage of cash available, and if a unique opportunity presents itself, then Fisher advises the sale of other securities to fund the purchase.
Reasons Not to Sell
Prognostications or gut feelings about a potential market decline are not reasons to sell in Fisher’s eyes. Selling out of fear generally is a poor and costly idea. Fisher explains:
“When a bear market has come, I have not seen one time in ten when the investor actually got back into the same shares before they had gone up above his selling price.”
In Fisher’s mind, another reason not to sell stocks is solely based on valuation. Longer-term earnings power and comparable company ratios should be considered before spontaneous sales. What appears expensive today may look cheap tomorrow.
There are many reasons to buy and sell a stock, but like most good long –term investors, Fisher has managed to explain his three-point sale plan in simplistic terms the masses can understand. If you are committed to cutting investment losses, I advise you to follow investment legend Phil Fisher – cutting losses will actually help prevent your portfolio from splitting apart.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
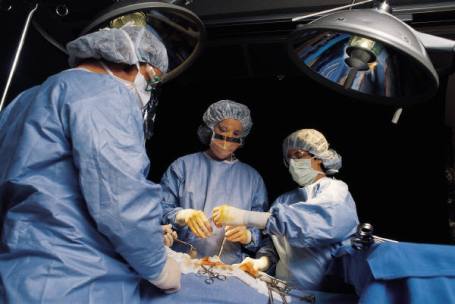
Killing Patients to Investment Prosperity
All investors are optimistic, every time they open up a position, but just like surgeons, sometimes the outcome doesn’t turn out as well as initially anticipated. When it comes to investing, I think this old Hindu proverb puts things into perspective:
“No physician is really good before he has killed one or two patients.”
So too, an investor does not become really good until he kills off some investment positions. But like surgeons, investors also have to understand the most important aspect of tragic events is learning from them. In many cases, unexpected outcomes are out of our control and cannot be prevented. This conclusion, in and of itself, can provide valuable insights. But on many occasions, there are procedures, processes, and facts that were missed or botched, and learning from those mistakes can prove invaluable when it comes to refining the process in the future – in order to further minimize the probability of a tragic outcome.
My Personal Killers
Professionally, I have killed some stocks in my career too, or they have killed me, depending on how you look at the situation. How did these heartrending incidents occur? There are several categories that my slaughtered stocks fell under:
- Roll-Up, Throw-Up: Several of my investment mistakes have been tied to roll-up or acquisition-reliant growth stories, where the allure of rapid growth shielded the underlying weak fundamentals of the core businesses. Buying growth is easier to create versus organically producing growth. Those companies addicted to growth by acquisition eventually experience the consequences firsthand when the game ends (i.e., the quality of deals usually deteriorates and/or the prices paid for the acquisitions become excessive).
- Technology Kool-Aid: Another example is the Kool-Aid I drank, during the technology bubble days, related to a “story” stock – Webvan, a grocery delivery concept. How could mixing Domino’s pizza delivery (DZP) with Wal-Mart’s (WMT) low-priced goods not work? I’m just lazy enough to demand a service like that. Well, after spending hundreds of millions of dollars and never reaching the scale necessary to cover the razor thin profit margins, Webvan folded up shop and went bankrupt. But don’t give up hope yet, Amazon (AMZN) is refocusing its attention on the grocery space (mostly non-perishables now) and could become the dominant food delivery retailer.
- Penny Stocks = Dollars Lost: Almost every seasoned investor carries at least one “penny stock” horror story. Unfortunately for me, my biotech miracle stock, Saliva Diagnostics (SALV), did not take off to the moon and provide an early retirement opportunity as planned. On the surface it sounded brilliant. Spit in a cup and Saliva Diagnostic’s proprietary test would determine whether patients were infected with the HIV virus. With millions of HIV/AIDS patients spread around the world, the profit potential behind ‘Saliva’ seemed virtually limitless. The technology unfortunately did not quite pan out, and spit turned into tears.
The Misfortune Silver Lining
These stock tragedies are no fun, but I am not alone. Fortunately for me, and other professionals, there is a nine-lives feline element to investing. One does not need to be right all the time to outperform the indices. “If you’re terrific in this business you’re right 6 times out of 10 – I’ve had stocks go from $11 to 7 cents (American Intl Airways),” admitted investment guru Peter Lynch. Growth stock investing expert, Phil Fisher, added: “Fortunately the long-range profits earned from really good common stocks should more than balance the losses from a normal percentage of such mistakes.”
Warren Buffett takes a more light-hearted approach when he describes investment mistakes: “If you were a golfer and you had a hole in one on every hole, the game wouldn’t be any fun. At least that’s my explanation of why I keep hitting them in the rough.”
Some investors purposely forget traumatic investment experiences, but explicitly sweeping the event under the rug will do more harm than good. So the next time you suffer a horrendous stock price decline, do your best to log the event and learn from the situation. That way, when the patient (stock) has been killed (destroyed), you will become a better, more prosperous doctor (investor).
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, WMT, and AMZN but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in DZP, Webvan, Saliva Diagnostics, American intl Airways, or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Playing the Field with Your Investments
For some, casually dating can be fun and exciting. The same goes for trading and speculating – the freedom to make free- wheeling, non-committal purchases can be exhilarating. Unfortunately the costs (fiscally and emotionally) of short-term dating/investing often outweigh the benefits.
Fortunately, in the investment world, you can get to know an investment pretty well through fundamental research that is widely available (e.g., 10Ks, 10Qs, press releases, analyst days, quarterly conference calls, management interviews, trade rags, research reports). Unlike dating, researching stocks can be very cheap, and you do not need to worry about being rejected.
Dating is important early in adulthood because we make many mistakes choosing whom we date, but in the process we learn from our misjudgments and discover the important qualities we value in relationships. The same goes for stocks. Nothing beats experience, and in my long investment career, I can honestly say I’ve dated/traded a lot of pigs and gained valuable lessons that have improved my investing capabilities. Now, however, I don’t just casually date my investments – I factor in a rigorous, disciplined process that requires a serious commitment. I no longer enter positions lightly.
One of my investment heroes, Peter Lynch, appropriately stated, “In stocks as in romance, ease of divorce is not a sound basis for commitment. If you’ve chosen wisely to begin with, you won’t want a divorce.”
Charles Ellis shared these thoughts on relationships with mutual funds:
“If you invest in mutual funds and make mutual funds investment changes in less than 10 years…you’re really just ‘dating.’ Investing in mutual funds should be marital – for richer, for poorer, and so on; mutual fund decisions should be entered into soberly and advisedly and for the truly long term.”
No relationship comes without wild swings, and stocks are no different. If you want to survive the volatile ups and downs of a relationship (or stock ownership), you better do your homework before blindly jumping into bed. The consequences can be punishing.
Buy and Hold is Dead…Unless Stocks Go Up
If you are serious about your investments, I believe you must be mentally willing to commit to a relationship with your stock, not for a day, not for a week, or not for a month, but rather for years. Now, I know this is blasphemy in the age when “buy-and-hold” investing is considered dead, but I refute that basic premise whole-heartedly…with a few caveats.
Sure, buy-and-hold is a stupid strategy when stocks do nothing for a decade – like they have done in the 2000s, but buying and holding was an absolutely brilliant strategy in the 1980s and 1990s. Moreover, even in the miserable 2000s, there have been many buy-and-hold investments that have made owners a fortune (see Questioning Buy & Hold ). So, the moral of the story for me is “buy-and-hold” is good for stocks that go up in price, and bad for stocks that go flat or down in price. Wow, how deeply profound!
To measure my personal commitment to an investment prospect, a bachelorette investment I am courting must pass another test…a test from another one of my investment idols, Phil Fisher, called the three-year rule. This is what the late Mr. Fisher had to say about this topic:
“While I realized thoroughly that if I were to make the kinds of profits that are made possible by [my] process … it was vital that I have some sort of quantitative check… With this in mind, I established what I called my three-year rule.” Fisher adds, “I have repeated again and again to my clients that when I purchase something for them, not to judge the results in a matter of a month or a year, but allow me a three year period.”
Certainly, there will be situations where an investment thesis is wrong, valuation explodes, or there are superior investment opportunities that will trigger a sale before the three-year minimum expires. Nonetheless, I follow Fisher’s rule in principle in hopes of setting the bar high enough to only let the best ideas into both my client and personal portfolios.
As I have written in the past, there are always reasons of why you should not invest for the long-term and instead sell your position, such as: 1) new competition; 2) cost pressures; 3) slowing growth; 4) management change; 5) valuation; 6) change in industry regulation; 7) slowing economy; 8 ) loss of market share; 9) product obsolescence; 10) etc, etc, etc. You get the idea.
Don Hays summed it up best: “Long term is not a popular time-horizon for today’s hedge fund short-term mentality. Every wiggle is interpreted as a new secular trend.”
Peter Lynch shares similar sympathies when it comes to noise in the marketplace:
“Whatever method you use to pick stocks or stock mutual funds, your ultimate success or failure will depend on your ability to ignore the worries of the world long enough to allow your investments to succeed.”
Every once in a while there is validity to some of the concerns, but more often than not, the scare campaigns are merely Chicken Little calling for the world to come to an end.
Patience is a Virtue
In the instant gratification society we live in, patience is difficult to come by, and for many people ignoring the constant chatter of fear is challenging. Pundits spend every waking hour trying to explain each blip in the market, but in the short-run, prices often move up or down irrespective of the daily headlines. Explaining this randomness, Peter Lynch said the following:
“Often, there is no correlation between the success of a company’s operations and the success of its stock over a few months or even a few years. In the long term, there is a 100% correlation between the success of a company and the success of its stock. It pays to be patient, and to own successful companies.”
Long-term investing, like long-term relationships, is not a new concept. Investment time horizons have been shortening for decades, so talking about the long-term is generally considered heresy. Rather than casually date a stock position, perhaps you should commit to a long-term relationship and divorce your field-playing habits. Now that sounds like a sweet kiss of success.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Shanking Your Way to Success: Tiger Woods & Roger McNamee
Spring has sprung and that means golf is back in full swing with the Masters golf tournament kicking off next week in Augusta, Georgia. Next week also marks the return of Tiger Woods in his first competition since news of Tiger’s sex scandal and car crash originally broke. As an avid golf fan (and occasional frustrated player), I must admit I do find a devilish sense of guilty pleasure every time I see a pro golfer shank a ball into the thick of the woods or plop one in the middle of the drink. I mean, how many hundreds of balls have I donated to golf courses across this great nation? Let’s face it, no matter how small, people derive some satisfaction from seeing others commit similar mistakes…misery loves company. Even the world’s elite, including Tiger Woods, slip up periodically.
For quite possibly the worst, nightmarish, meltdown classic of all-time, you may recall Frenchman John van de Velde’s 18th hole collapse at the 1999 British Open in Carnoustie, Scotland.
Investment Pros Shank Too
Investment legend Peter Lynch (see Investment Caffeine profile on Lynch), who trounced the market with a +29% annual return average from 1977-1990, correctly identified the extreme competitiveness of the stock-picking world when he stated, “If you’re terrific in this business you’re right six times out of ten.” Even with his indelible record, Lynch had many disastrous stocks, including American International Airways, which went from $11 per share down to $0.07 per share. Famous early 20th Century trader Jesse Livermore puts investment blundering into context by adding, “If a man didn’t make mistakes he’d own the world in a month.”
Mistakes, plain and simply, are a price of playing the investment game. Or as the father of growth investing Phil Fisher noted (see Investment Caffeine profile on Fisher), “Making mistakes is an inherent cost of investing just like bad loans are for the finest lending institutions.”
McNamee’s Marvelous Misfortune
Since the investment greats operate under the spotlight, many of their poor decisions cannot be swept under the rug. Take Roger McNamee, successful technology investor and co-founder of Elevation Partners (venture capital) and Silver Lake Partners (private equity). His personal purchase of 2.3 million shares ($37 million) in smartphone and handheld computer manufacturer Palm Inc. (PALM) has declined by more than a whopping -75% since his personal purchase just six months ago at $16.25 share price (see also The Reformed Broker). McNamee is doing his best to recoup some of his mojo with his hippy-esque band Moonalice – keep an eye out for tour dates and locations.
Lessons Learned
More important than making repeated mistakes is what you do with those mistakes. “Insanity is doing the same thing over and over again, and expecting different results,” observed Albert Einstein. Learning from your mistakes is the most important lesson in hopes of mitigating the same mistakes in the future. Phil Fisher adds, “I have always believed that the chief difference between a fool and a wise man is that the wise man learns from his mistakes, while the fool never does.” As part of my investment process, I always review my errors. By explicitly shaming myself and documenting my bad trades, I expect to further reduce the number of poor investment decisions I make in the future.
With the Masters just around the corner, I must admit I eagerly wait to see how Tiger Woods will perform under extreme pressure at one of the grandest golf events of the year. I will definitely be rooting for Tiger, although you may see a smirk on my face if he shanks one into the trees.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
*DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at the time of publishing had no direct positions in PALM or any security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Standing on the Shoulders of a Growth Giant: Phil Fisher
It was English physicist, astronomer, philosopher, and mathematician Sir Isaac Newton who in 1675 stated, “If I have seen further it is by standing on the shoulders of giants.” Investors too can stand on the shoulders of market giants by studying the timeless financial knowledge from current and past market legends. The press, all too often, focuses on the hot managers of our time while forgetting or kicking to the curb those managers whom are temporarily out of favor. Famous and enduring value managers typically have gained the press spotlight, rightfully so in the case of current greats like Warren Buffett or past talents like Benjamin Graham, because they managed to prosper through numerous economic cycles. However, when it comes to growth legends like Phil Fisher, author of the must-read classic Common Stocks and Uncommon Profits, many people I bump into have never heard of him. Hopefully that will change over time.
The Past
Born on September 8, 1907, Mr. Fisher lived until the ripe age of 96 when he passed on March 4, 2004. Fisher was no dummy – he enrolled in college at age 15 and started graduate school at Stanford a few years later, before he dropped out and started his own investment firm in 1931. His son, Ken, currently heads his own investment firm, Fisher Investments, writes for Forbes magazine, and has authored multiple investment books. Unlike his dad, Ken has more of a natural bent towards value stocks.
Buy-And-Hold
Phil Fisher’s iconic book, Common Stocks and Uncommon Profits, was published in 1958. Mr. Fisher believed in many things and perhaps would have been thrown under the bus today for his long-term convictions in “buy-and-hold.” Or as Mr. Fisher put it, “If the job has been correctly done when a common stock is purchased, the time to sell it is – almost never.” Not every investment idea made the cut, however he is known to have bought Motorola (MOT) stock in 1955 and held it until his death in 2004 for a massive gain. Generally, he gave initial stock purchases a three-year leash before considering a change to his investment position. If the conviction to purchase a stock for such duration is not present, then the investment opportunity should be ignored.
Fisher’s concentration on growth stocks also shaped his view on dividends. Dividends were not important to Fisher – he was more focused on how the company is investing retained earnings to achieve its earnings growth. Like Fisher, Peter Lynch is another growth hero of mine that also felt there is too much focus on the Price/Earnings (PE) ratio rather than the long-term earnings potential.
“Scuttlebutt”
Another classic trademark of Fisher’s investing style was his commitment to fundamental research. He was focused on accumulating data covering a broad range of areas including, customers, suppliers, and competitors. Fisher also emphasized factors like market share, return on invested capital, margins, and the research & development budget. What Mr. Fisher called his varied approach to gathering diverse sets of information was “scuttlebutt.”
Buying & Selling Points
Although Fisher believed firmly in buy and hold, he was not scared to sell when the firm no longer met the original buying criteria or his original assessment for purchased was deemed incorrect.
When buying, Fisher preferred to buy stocks in downturns or temporary problems – contrary to your typical momentum growth manager today (read article on momentum). Fisher has this to say on the topic: “This matter of training oneself to not go with the crowd but to be able to zig when the crowd zags, in my opinion, is one of the most important fundamentals of the investment success.”
Learning from Mistakes
Like all great investors I have studied, Phil Fisher also believed in learning from your mistakes:
“I have always believed that the chief difference between a fool and a wise man is that the wise man learns from his mistakes, while the fool never does.”
He expanded on the topic by saying the following:
“Making mistakes is inherent cost of investing just like bad loans are for the finest lending institutions. Don’t blindly accept dominant opinion and don’t be contrary for the sake of being contrary.”
I could only dream of having a fraction of Mr. Fisher’s career success – he retired in 1999 at the age of 91 (not bad timing). As I continue on my investment journey with my investment firm (Sidoxia Capital Management, LLC), I will continue to study the legendary giants of investing (past and present) to sharpen my investment skills.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) or its clients owns certain exchange traded funds, but currently has no direct position in MOT or BRKA/B. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.