Posts tagged ‘CAPEX’
Mideast War an Investor Bore as Markets Soar
If I told you at the beginning of the year that the U.S. would bomb key nuclear sites in Iran, would you have guessed that Middle East stability would follow—and that global financial markets would soar to record highs? Personally, I wouldn’t have bet on that outcome. But that’s exactly what happened last month. While geopolitical dynamics remain fluid, markets shrugged off the chaos. The S&P 500 rallied +5.0%, the Dow Jones Industrial Average climbed +4.3%, and the NASDAQ catapulted +6.6%, powered largely by artificial intelligence stocks like NVIDIA Corp., which surged +16.9% for the month to a market value of $3.9 trillion (more on AI below). This is an important reminder that trading off of news headlines is a fool’s errand.
Economy Resilient Despite Tariffs and Geopolitical Turmoil

Source: Calafia Beach Pundit
Credit Default Swaps (CDS) act as insurance contracts that protect investors against corporate debt defaults. During financial stress—like the 2008 crisis or the COVID crash in 2020—CDS prices surge as investors seek protection. Today, however, CDS prices are falling across both high-yield (junk bonds) and investment-grade (Blue Chip) debt. As seen in the chart above, the cost to insure corporate bonds has declined steadily over the past two years. This signals bond investors aren’t worried about a recession or a wave of defaults, despite tariff policy uncertainty, geopolitical risk, and modest GDP growth.
Inflation Tame as Tariffs Loom
President Trump has repeatedly criticized Fed Chair Jerome Powell for not cutting interest rates, calling him everything from a “dummy” to a “major loser” and a “stupid person” to a “numbskull”. While the name-calling is colorful, the economic pressure is real: U.S. GDP contracted -0.5% in Q1 2025. Powell, however, wants to see the full impact of upcoming tariffs before making a move. . A new tariff deadline looms on July 9th, and the market is anxiously awaiting clarity. But even if tariffs are implemented, many economists believe the inflationary impact will be temporary—what’s known as a one-time price shock.

Source: Calafia Beach Pundit
The Fed’s preferred inflation gauge—the Personal Consumption Expenditure (PCE) index—has been easing and is now near the 2% target (see chart above). With inflation cooling, Trump’s case for rate cuts gains credibility. Still, the Fed appears in no rush. It will take time to understand the lasting effects of the tariff rollout.
AI Wave Fueling Markets
For a generation, the semiconductor revolution has quietly powered innovation, guided by Moore’s Law—the principle that chip performance doubles roughly every two years (see my article The Traitorous 8). Sixty years after Gordon Moore wrote his seminal article, “Cramming More Components onto Integrated Circuits”, the power of software is catching up. NVIDIA’s Grace Blackwell GB200 chip contains an astronomical 208 billion transistors, supercharging AI software models like ChatGPT.
The AI revolution is fueling trillions in global investment and rapidly transforming industries – from data centers and self-driving cars to robotics and drug discovery. It’s important to realize that this AI arms race is not just occurring in the United States. AI investment spending extends way beyond Silicon Valley to countries like Saudi Arabia, Singapore, and China.
The AI boom is not a U.S.-only phenomenon. Countries like China, Saudi Arabia, and Singapore are pouring capital into AI, creating a global arms race in tech. In the U.S., the four biggest hyperscalers—Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and Meta—are projected to spend over $300 billion on capital expenditures in 2025 alone (see chart below).
To illustrate the scale: Amazon is forecasted to spend more than $100 billion in CapEx this year. For context, that’s 40% more than the company spent over the entire 2000–2020 period combined.

Source: The Financial Times
The Stargate Initiative: AI Infrastructure on a Galactic Scale
A prime example of the AI gold rush is the $500 billion Stargate initiative, with Phase 1 already underway in Abilene, Texas (see rendering below). The initial construction includes two buildings totaling 1,000,000 square feet. Ultimately, the full project will cove about 1,000 acres and be powered by an on-site natural gas facility generating 360 megawatts—enough to support 300,000 homes.
A huge portion of the project costs are dedicated to the budget for NVIDIA super chips. Oracle Corp. has committed $40 billion to purchase 400,000 of NVIDIA’s GB200 chips, making this project a centerpiece of the global AI infrastructure boom. Just this week, Oracle also announced a new $30 billion cloud deal, which will soak up a good chunk of the data center supply created by the database and enterprise software company.

Source: CoStar
The Big Picture: Volatility and Opportunity
There’s no shortage of risk—geopolitics, inflation, Fed uncertainty, tariffs. But the economy is showing surprising resilience. If tariff clarity improves, interest rate cuts materialize, and AI capital spending accelerates, a “boring” market could rapidly turn into a soaring one.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
This article is an excerpt from a previously released Sidoxia Capital Management complimentary newsletter (July 1, 2025). Subscribe Here to view all monthly articles.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on the IC Contact page.
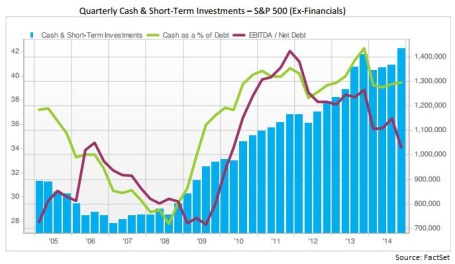
Short Arms, Deep Pockets
Companies have deep pockets flush with cash, but are plagued with short arms, unwilling to reach into their wallets to make substantive new hires. I have talked about “unemployment hypochondria” in the past but is this cautious behavior rational?
The short answer is yes, and it is very typical in light of the similar “jobless recoveries” we experienced in 1991 and 2001. After suffering the worst financial crisis in a generation, employers’ wounds are still not completely healed and the frightening memories of 2008-2009 are still fresh in their minds.
Linchpin Labor
The globalization cat is out of the bag, and technology is only accelerating the commoditization of labor. When labor can be purchased for $1 per hour in China or $.50 per hour in India , and in many instances no strategic benefit lost, then why are so many people surprised about the hemorrhaging of $25 per hour manufacturing jobs to cheaper locales? Agriculture and related industries used to account for more than 90% of our economy about 150 years ago – today agriculture makes up about 2% of our economic output. Even though this dominating sector withered away on a relative basis, the United States became the global powerhouse innovator of the 20th century.
Innovative companies understand that true value is created by those workers who make themselves indispensable – or what Seth Godin calls “Linchpins.” Apple Inc. (AAPL) understands these trends. If you don’t believe me, just flip over an iPhone and read where it clearly states, “Designed by Apple in California. Assembled in China.” (see BELOW).
We are falling further behind our global brethren in math and science, and our immigration policy is all backwards (Keys to Success). Education, creativity, ingenuity, and entrepreneurial spirit are the main ingredients necessary to climb the labor food chain. For those workers that make themselves linchpins, their services will be in demand during good times and bad times.
Jobs = Heavy Hiking Boots
Like scared hikers jettisoning heavy hiking boots to escape a pursuing grizzly bear, business owners will eventually need to purchase a new pair of boots, if they want to hike the mountain to face the next challenge. Right now, businesses are content waiting it out, more worried about the potential of a bear jumping out to devour them.
Although businesses may not be plunging into hiring a substantial number of new workers, positive leading indicators are becoming more apparent. Beyond the obvious improvement in the explicit job numbers (e.g., nine consecutive months of private job creation), other factors such as increased temporary workers, accelerating job listings, and increased capital expenditures are the precursors to sustained job hiring.
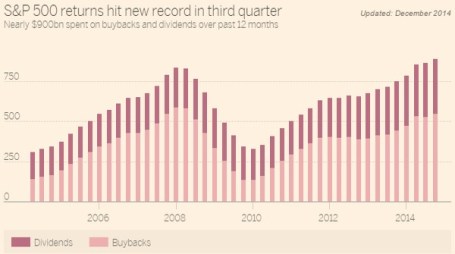
Quarterly Capital Carrots
Capital expenditures generally lead to more immediate productivity improvements and do not have a complete negative and immediate impact on the sacred EPS (earnings per share) and income statement metrics. On the other hand, hiring a new employee has an instant depressing effect on expenses, thereby dragging down the beloved EPS figure. What’s more, new employees do not typically become productive or sales generative for months. If you consider the heavy explicit wages coupled with implicit training costs, until the coast is clear and confidence overcomes fear, businesses are not going to dip their hands into their cash-filled pockets to hire workers willy-nilly.
As previously mentioned, improved business confidence is being signaled by increased capital spending. Just over the last week, investors have witnessed significantly expanded capital expenditures across a broad array of industries. Here are a few random samplings:
September 2010 – Quarterly Capital Expenditures
Q3 – 2010 Q3 – 2009 YOY%
Apple Inc. (AAPL) $760 mil vs. $459 mil +66%
Halliburton Company (HAL) $557 mil vs. $440 mil +27%
Coca Cola Company (KO) $442 mil vs. $419 mil +5%
Dominos Pizza Inc. (DPZ) $5.2 mil vs. $4.1 mil +26%
Intel Corp. (INTC) $1.4 bill vs $944 mil +44%
Although the pace of the recovery is losing steam, companies’ health persists to strengthen, as evidenced in part by the +45% growth in 2010 S&P 500 profits, swelling record cash piles, and increasing corporate confidence (rising capital expenditures). Despite these positive leading indicators, business owners are reluctant to dip their short arms into their deep cash-filled pockets to hire new employees. Given our experience over the last few decades this corporate behavior is perfectly consistent with recent jobless recoveries. Until its clear the economic bear is hibernating, businesses will continue building their cash warchests. Everyone will be happier once we are done running from bears, and instead chasing bulls.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds and AAPL, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in HAL, KO, DPZ, INTC, or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Taking Facebook and Twitter Public
Valuing high growth companies is similar to answering a typical open-ended question posed to me during business school interviews: “Wade, how many ping pong balls can you fit in an empty 747 airplane?” Obviously, the estimation process is not an exact science, but rather an artistic exercise in which various techniques and strategies may be implemented to form a more educated guess. The same estimation principles apply to the tricky challenge of valuing high growth companies like Facebook and Twitter.
Cash is King
Where does one start? Conceptually, one method used to determine a company’s value is by taking the present value of all future cash flows. For growth companies, earnings and cash flows can vary dramatically and small changes in assumptions (i.e., revenue growth rates, profit margins, discount rates, taxes, etc.) can lead to drastically different valuations. As I have mentioned in the past, cash flow analysis is a great way to value companies across a broad array of industries – excluding financial companies (see previous article on cash flow investing).
Mature companies operating in stable industries may be piling up cash because of limited revenue growth opportunities. Such companies may choose to pay out dividends, buyback stock, or possibly make acquisitions of target competitors. However, for hyper-growth companies earlier in their business life-cycles, (e.g., Facebook and Twitter), discretionary cash flow may be directly reinvested back into the company, and/or allocated towards numerous growth projects. If these growth companies are not generating a lot of excess free cash flow (cash flow from operations minus capital expenditures), then how does one value such companies? Typically, under a traditional DCF (discounted cash flow model), modest early year cash flows are forecasted until more substantial cash flows are generated in the future, at which point all cash flows are discounted back to today. This process is philosophically pure, but very imprecise and subject to the manipulation and bias of many inputs.
To combat the multi-year wiggle room of a subjective DCF, I choose to calculate what I call “adjusted free cash flow” (cash flow from operations minus depreciation and amortization). The adjusted free cash flow approach provides a perspective on how much cash a growth company theoretically can generate if it decides to not pursue incremental growth projects in excess of maintenance capital expenditures. In other words, I use depreciation and amortization as a proxy for maintenance CAPEX. I believe cash flow figures are much more reliable in valuing growth companies because such cash-based metrics are less subject to manipulation compared to traditional measures like earnings per share (EPS) and net income from the income statement.
Rationalizing Ratios
Other valuation methods to consider for growth companies*:
- PE Ratio: The price-earnings ratio indicates how expensive a stock is by comparing its share price to the company’s earnings.
- PEG Ratio (PE-to-Growth): This metric compares the PE ratio to the earnings growth rate percentage. As a rule of thumb, PEG ratios less than one are considered attractive to some investors, regardless of the absolute PE level.
- Price-to-Sales: This ratio is less precise in my mind because companies can’t pay investors dividends, buy back stock, or make acquisitions with “sales” – discretionary capital comes from earnings and cash flows.
- Price-to-Book: Compares the market capitalization (price) of the company with the book value (or equity) component on the balance sheet.
- EV/EBITDA: Enterprise value (EV) is the total value of the market capitalization plus the value of the debt, divided by EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest Taxes Depreciation and Amortization). Some investors use EBITDA as an income-based surrogate of cash flow.
- FCF Yield: One of my personal favorites – you can think of this percentage as an inverted PE ratio that substitutes free cash flow for earnings. Rather than a yield on a bond, this ratio effectively provides investors with a discretionary cash yield on a stock.
*All The ratios above should be reviewed both on an absolute basis and relative basis in conjunction with comparable companies in an industry. Faster growing industries, in general, should carry higher ratio metrics.
Taking Facebook and Twitter Public
Before we can even take a stab at some of these growth company valuations, we need to look at the historical financial statements (income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement). In the case of Facebook and Twitter, since these companies are private, there are no publically available financial statements to peruse. Private investors are generally left in the dark, limited to public news related to what other early investors have paid for ownership stakes. For example, in July, a Russian internet company paid $100 million for a stake in Facebook, implying a $6.5 billion valuation for the total company. Twitter recently obtained a $100 million investment from T. Rowe Price and Insight Venture Partners thereby valuing the total company at $1 billion.
Valuing growth companies is quite different than assessing traditional value companies. Because of the earnings and cash flow volatility in growth companies, the short-term financial results can be distorted. I choose to find market leading franchises that can sustain above average growth for longer periods of time (i.e., companies with “long runways”). For a minority of companies that can grow earnings and cash flows sustainably at above-average rates, I will take advantage of the perception surrounding current short-term “expensive” metrics, because eventually growth will convert valuation perception to “cheap.” Google Inc. (GOOG) is a perfect example – what many investors thought was ridiculously expensive, at the $85 per share Initial Public Offering (IPO) price, ended up skyrocketing to over $700 per share and continues to trade near a very respectable level of $500 per share.
The IPO market is heating up and A123 Systems Inc (AONE) is a fresh example. Often these companies are volatile growth companies that require a deep dive into the financial statements. There is no silver bullet, so different valuation metrics and techniques need to be reviewed in order to come up with more reasonable valuation estimates. Valuation measuring is no cakewalk, but I’ll take this challenge over estimating the number of ping pong balls I can fit in an airplane, any day. Valuing growth companies just requires an understanding of how the essential earnings and cash flow metrics integrate with the fundamental dynamics surrounding a particular company and industry. Now that you have graduated with a degree in Growth Company Valuation 101, you are ready to open your boutique investment bank and advise Facebook and Twitter on their IPO price (the fees can be lucrative if you are not under TARP regulations).
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management and client accounts do not have direct long positions AONE, however some Sidoxia client accounts do hold GOOG securities at the time this article was published. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.