Posts filed under ‘Themes – Trends’
Uncertainty: Love It or Hate It?
Uncertainty is like a fin you see cutting through the water – many people are uncertain whether the fin sticking out of the water is a great white shark or a dolphin? Uncertainty generates fear, and fear often produces paralysis. This financially unproductive phenomenon has also reared its ugly fin in the investment world, which has led to low-yield apathy, and desensitization to both interest rate and inflation risks.
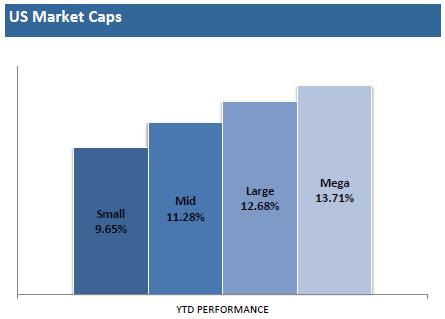
The mass exodus out of stocks into bonds worked well for the very few that timed an early 2008 exit out of equities, but since early 2009, the performance of stocks has handily trounced bonds (the S&P has outperformed the bond market (BND) by almost 100% since the beginning of March 2009, if you exclude dividends and interest). While the cozy comfort of bonds has suited investors over the last five years, a rude awakening awaits the bond-heavy masses when the uncertain economic clouds surrounding us eventually lift.
The Certainty of Uncertainty
What do we know about uncertainty? Well for starters, we know that uncertainty cannot be avoided. Or as former Secretary of the Treasury Robert Rubin stated so aptly, “Nothing is certain – except uncertainty.”
Why in the world would one of the world’s richest and most successful investors like Warren Buffett embrace uncertainty by imploring investors to “buy fear, and sell greed?” How can Buffett’s statement be valid when the mantra we continually hear spewed over the airwaves is that “investors hate uncertainty and love clarity?” The short answer is that clarity is costly (i.e., investors are forced to pay a cherry price for certainty). Dean Witter, the founder of his namesake brokerage firm in 1924, addressed the issue of certainty in these shrewd comments he made some 78 years ago, right before the end of worst bear market in history:
“Some people say they want to wait for a clearer view of the future. But when the future is again clear, the present bargains will have vanished.”
Undoubtedly, some investors hate uncertainty, but I think there needs to be a distinction between good investors and bad investors. Don Hays, the strategist at Hays Advisory, straightforwardly notes, “Good investors love uncertainty.”
When everything is clear to everyone, including the novice investing cab driver and hairdresser, like in the late 1990s technology bubble, the actual risk is in fact far greater than the perceived risk. Or as Morgan Housel from Motley Fool sarcastically points out, “Someone remind me when economic uncertainty didn’t exist. 2000? 2007?”
What’s There to Worry About?
I’ve heard financial bears argue a lot of things, but I haven’t heard any make the case there is little uncertainty currently. I’ll let you be the judge by listing these following issues I read and listen to on a daily basis:
- Fiscal cliff induced recession risks
- Syria’s potential use of chemical weapons
- Iran’s destabilizing nuclear program
- North Korean missile tests by questionable new regime
- Potential Greek debt default and exit from the eurozone
- QE3 (Quantitative Easing) and looming inflation and asset bubble(s)
- Higher taxes
- Lower entitlements
- Fear of the collapse in the U.S. dollar’s value
- Rigged Wall Street game
- Excessive Dodd-Frank financial regulation
- Obamacare
- High Frequency Trading / Flash Crash
- Unsustainably growing healthcare costs
- Exploding college tuition rates
- Global warming and superstorms
- Etc.
- Etc.
- Etc.
I could go on for another page or two, but I think you get the gist. While I freely admit there is much less uncertainty than we experienced in the 2008-2009 timeframe, investors’ still remain very cautious. The trillions of dollars hemorrhaging out of stocks into bonds helps make my case fairly clear.
As investors plan for a future entitlement-light world, nobody can confidently count on Social Security and Medicare to help fund our umbrella-drink-filled vacations and senior tour golf outings. Today, the risk of parking your life savings in low-rate wealth destroying investment vehicles should be a major concern for all long-term investors. As I continually remind Investing Caffeine readers, bonds have a place in all portfolios, especially for income dependent retirees. However, any truly diversified portfolio will have exposure to equities, as long as the allocation in the investment plan meshes with the individual’s risk tolerance and liquidity needs.
Given all the uncertain floating fins lurking in the economic background, what would I tell investors to do with their hard-earned money? I simply defer to my pal (figuratively speaking), Warren Buffett, who recently said in a Charlie Rose interview, “Overwhelmingly, for people that can invest over time, equities are the best place to put their money.” For the vast majority of investors who should have an investment time horizon of more than 10 years, that is a question I can answer with certainty.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs) including BND, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct positions in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Lily Pad Jumping & Term Paper Cramming

Article is an excerpt from previously released Sidoxia Capital Management’s complementary December 3, 2012 newsletter. Subscribe on right side of page.
Over the last year, investors’ concerns have jumped around like a frog moving from one lily pad to the next. From the debt ceiling debate to the European financial crisis, and then from the presidential election to now the “fiscal cliff.” With the election behind us (Obama winning 332 electoral votes vs 206 for Romney; and Obama 50.8% of the popular vote vs 47.5% for Romney), the frog’s bulging eyes are squarely focused on the fiscal cliff. For the uninformed frogs that have been swimming underwater, the fiscal cliff is the roughly $600 billion in automatic tax hikes and spending cuts that are scheduled to be triggered by the end of this year, if Congress cannot come to some type of agreement (for more fiscal cliff information see videos here). The mathematical consequences are clear: Congress + No Deal = Recession.
While political brinksmanship and theater are nothing new, the explosive amount of data is something new. In our mobile world of 6 billion cell phones (more than the number of toothbrushes on our planet) and trillions of text messages sent annually, nobody can escape the avalanche of global data. Google (GOOG), Facebook (FB), Twitter, and millions of blogs (including this one) didn’t exist 15 years ago, therefore fiscal boogeymen like obscure Greek debt negotiations and Chinese PMI figures wouldn’t have scared pre-internet generations underneath their beds like today’s investors. The fact of the matter is our country has triumphed over plenty of significant issues (many of them scarier than today’s headlines), including wars, assassinations, currency crises, banking crises, double digit inflation, SARS, mad cow disease, flash crashes, Ponzi schemes, and a whole lot more.
Although today’s jumpy investors may worry about the lily pads of a double-dip recession in the US, a financial meltdown in Europe, and/or a hard landing in China, fiscal frogs will undoubtedly be worried about different lily pads (concerns) twelve months from now. This may not be an insightful observation for day traders, but for the other 99% of investors, taking a longer term view of the daily news cycle may prove beneficial.
Fiscal Cliff Term Paper Due on Friday December 21st

As a college student, chugging Jolt Cola, in combination with a couple dosages of NoDoz, was part of the routine procrastination process the day before a term paper was due. Apparently Congress has also earned a PhD in procrastination, judging by the last minute conclusion of the debt ceiling negotiations last summer. There are only a few more weeks until politicians break for the Christmas holiday break, therefore I am setting an Investing Caffeine mandated fiscal cliff due date of December 21st. Could Congress turn in its term paper early? Anything is possible, but unfortunately turning in the assignment early is highly unlikely, especially when politically bashing your opponent is perceived as a better re-election tactic compared to bipartisan negotiation.
A higher probability scenario involves Americans stuck listening to Nancy Pelosi, Harry Reid, John Boehner, and Mitch McConnell on a daily basis as these politicians finger-point and call the other side obstructionists. While I’m not alone in believing a deal will ultimately get done before Christmas, how credible and substantive the announcement will be depends on whether the politicians seriously face entitlement and tax reforms. Regardless, any deal announced by Investing Caffeine’s December 21st due date will likely be received well by the market, as long as a framework for entitlement and tax reform is laid out for 2013.
Frog News Bites

Source: Photobucket
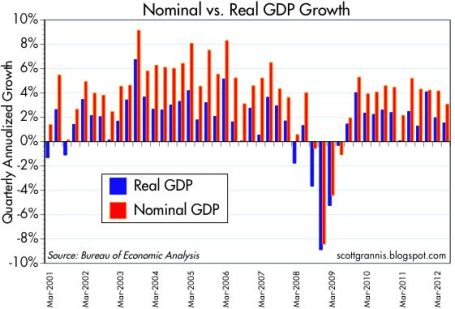
GDP Revised Higher: Despite all the gloom and uncertainties, the barometer of the economy’s health (i.e., Real Gross Domestic Product), was revised higher to 2.7% growth for the third quarter (from 2.0%). Nominal growth, a related measurement that includes inflation, reached a five-year high of 5.55%. In the wake of Superstorm Sandy, which caused upwards of $50 billion in damage, fourth quarter GDP numbers are likely to be artificially depressed. The silver lining, however, is first quarter 2013 figures may get an economic boost from reconstruction efforts.
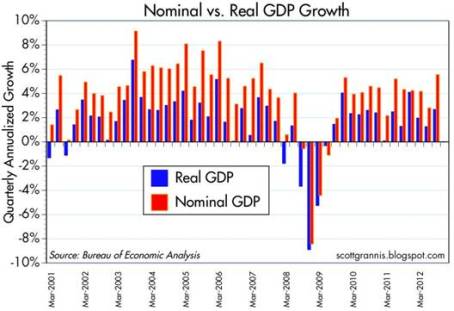
Source: Calafia Beach Pundit
Housing Recovery Continues: Buoyed by record low interest rates (30-yr fixed mortgages < 3.5%), housing sales and prices continue on an upward trajectory. New home sales came in at 368,000 in October, below expectations, but sales are still up around +20% from 2011 (Calculated Risk).
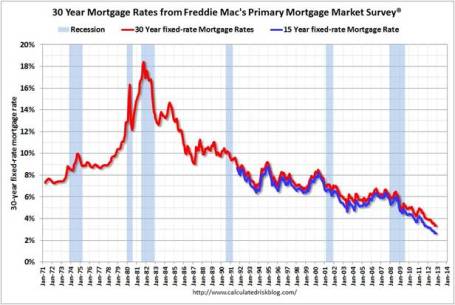
Source: Calculated Risk
Confidence Still Low but Climbing: The recently reported consumer confidence figures reached the highest level in more than four years, but as Scott Grannis highlights, this is nothing to write home about. These current confidence levels match where we were during the 1990-91 and 1980-82 recessions.
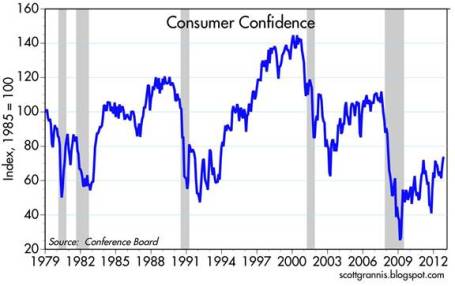
Source: Calafia Beach Pundit
Car Sales Picking Up: Fiscal cliff discussions haven’t discouraged consumers from buying cars. As you can see from the chart below, car and truck sales reached 14.3 million annualized units in October. November sales are expected to rise about +13% on a year-over-year basis, reaching approximately 15.3 million units.
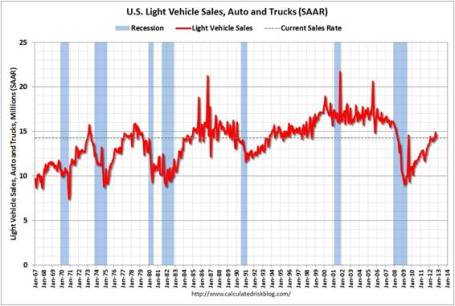
Source: Calculated Risk
CIA Chief Fired in Sex Scandal: If you didn’t get enough of the Lindsay Lohan bar brawl dirt in New York, never fear, there was plenty of salacious details emanating from Washington DC this month. A complicated web of Florida socialites, a biographer, email chains, and a bare-chested FBI agent led to the firing of CIA director David Petraeus.
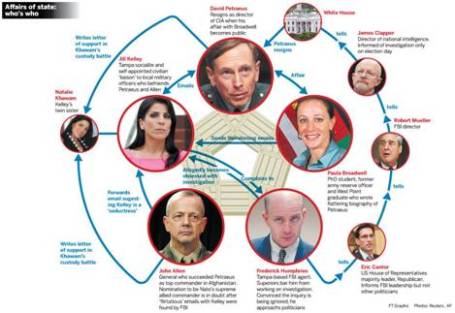
Source: The Financial Times
Death to Twinkies: After lining stomachs with golden cream-filled cakes for more than 80+ years, Hostess Brands was forced to halt production of Twinkies, Ding Dongs, and Ho Hos. Negotiations with union bakers crumbled, which led to Hostess Brands’ Chapter 7 bankruptcy and liquidation proceedings. My financial brain understands, but my sweet tooth is still grieving (see also Twinkie Investing).

Source: Photobucket
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct positions in FB, Twitter or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Twinkie Investing – Sweet but Unhealthy
It’s a sad day indeed in our history when the architect of the Twinkies masterpiece cream-filled sponge cakes (Hostess Brands) has been forced to close operations and begin bankruptcy liquidation proceedings. Food snobs may question the nutritional value of the artery-clogging delights, but there is no mistaking the instant pleasure provided to millions of stomachs over the 80+ years of the Twinkies dynasty. Most consumers understand that a healthy version of an organic Twinkie will not be found on the shelves of a local Whole Foods Market (WFM) store anytime soon. The reason people choose to consume these 150-calorie packages of baker bliss is due to the short-term ingestion joy, not the vitamin content (see Nutritional Facts below). Most people agree the sugar high gained from devouring half a box of Twinkies outweighs the long-term nourishing benefits reaped by eating a steamed serving of alfalfa sprouts.
Much like dieting, investing involves the trade-offs between short-term impulses and long-term choices. Unfortunately, the majority of investors choose to react to and consume short-term news stories, very much like the impulse Twinkie gorging, rather than objectively deciphering durable trends that can lead to outsized gains. Day trading and speculating on the headline du jour are often more exciting than investing, but these emotional decisions usually end up being costlier to investors over the long-run. Politically, we face the same challenges as Washington weighs the simple, short-term decisions of kicking the fiscal debt and deficits down the road, versus facing the more demanding, long-term path of dealing with these challenges.
With controversial subjects like the fiscal cliff, entitlement reform, taxation, defense spending, and gay marriage blasting over our airwaves and blanketing newspapers, no wonder individuals are defaulting to reactionary moves. As you can see from the chart below, the desire for a knee jerk investment response has only increased over the last 70 years. The average holding period for equity mutual funds has gone from about 5 years (20% turnover) in the mid 1960s to significantly less than 1 year (> 100% turnover) in the recent decade. Advancements in technology have lowered the damaging costs of transacting, but the increased frequency, coupled with other costs (impact, spread, emotional, etc.), have been shown to be detrimental over time, according to John Bogle at the Vanguard Group.
During volatile periods, like this post-election period, it is always helpful to turn to the advice of sage investors, who have successfully managed through all types of unpredictable periods. Rather than listening to the talking heads on TV and radio, or reading the headline of the day, investors would be better served by following the advice of great long-term investors like these:
“In the short run the market is a voting machine. In the long run it’s a weighing machine.” -Benjamin Graham (Famed value investor)
“Excessive short-termism results in permanent destruction of wealth, or at least permanent transfer of wealth.” -Jack Gray (Grantham, Mayo, Van Otterloo)
“The stock market serves as a relocation center at which money is moved from the active to the patient.” – Warren Buffett (Berkshire Hathaway)
“It was never my thinking that made big money for me. It always was my sitting.” – Jesse Livermore (Famed trader)
“The farther you can lengthen your time horizon in the investment process, the better off you will be.”- David Nelson (Legg Mason)
“The growth stock theory of investing requires patience, but is less stressful than trading, generally has less risk, and reduces brokerage commissions and income taxes.” T. Rowe Price (Famed Growth Investor)
“Time arbitrage just means exploiting the fact that most investors…tend to have very short-term time horizons.” -Bill Miller (Famed value investor)
“Long term is not a popular time-horizon for today’s hedge fund short-term mentality. Every wiggle is interpreted as a new secular trend.” -Don Hays (Hays Advisory – Investor/Strategist)
A legendary growth investor who had a major impact on how I shaped my investment philosophy is Peter Lynch. Mr. Lynch averaged a +29% return per year from 1977-1990. If you would have invested $10,000 in his Magellan fund on the first day he took the helm, you would have earned $280,000 by the day he retired 13 years later. Here’s what he has to say on the topic of long-term investing:
“Your ultimate success or failure will depend on your ability to ignore the worries of the world long enough to allow your investments to succeed.”
“Far more money has been lost by investors preparing for corrections, or trying to anticipate corrections, than has been lost in corrections themselves.”
“My best stocks performed in the 3rd year, 4th year, 5th year, not in the 3rd week or 4th week.”
“The key to making money in stocks is not to get scared out of them.”
“Worrying about the stock market 14 minutes per year is 12 minutes too many.”
It is important to remember that we have been through wars, assassinations, banking crises, currency crises, terrorist attacks, mad-cow disease, swine flu, recessions, and more. Through it all, our country and financial markets most have managed to survive in decent shape. Hostess and its iconic Twinkies brand may be gone for now, but removing these indulgent impulse items from your diet may be as beneficial as eliminating detrimental short-term investing urges.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct positions in WFM, BRKA/B, LM, TROW or any security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Sleeping Through Bubbles and Decade Long Naps
We have lived through many investment bubbles in our history, and unfortunately most investors sleep through the early wealth-creating inflation stages. Typically, the average investor wakes up later to a hot idea once every man, woman, and child has identified the clear trend…right as the bubble is about burst. Sadly, the masses do a great job of identifying financial bubbles at the end of a cycle, but have a tougher time realizing the catastrophic consequences of exiting a tired winner. Or as strategist Jim Stack states, “Bubbles, for the most part, are invisible to those trapped inside the bubble.” The challenge of recognizing bubbles explains why they are more easily classified as bubbles after a colossal collapse occurs. For those speculators chasing a precise exit point on a bubblicious investment, they may be better served by waiting for the prick of the bubble, then take a decade long nap before revisiting the fallen angel investment idea.
Even for the minority of pundits and investors who are able to accurately identify these financial bubbles in advance, a much smaller number of these professionals are actually able to pinpoint when the bubble will burst. Take for example Alan Greenspan, the ex-Federal Reserve Chairman from 1987 to 2006. He managed to correctly identify the technology bubble in late-1996 when he delivered his infamous “irrational exuberance” speech, which questioned the high valuation of the frothy, tech-driven stock market. The only problem with Greenspan’s speech was his timing was massively off. Stated differently, Greenspan was three years premature in calling out the pricking of the bubble, as the NASDAQ index subsequently proceeded to more than triple from early 1997 to early 2000 (the index exploded from about 1,300 to over 5,000).
One of the reasons bubbles are so difficult to time during their later stages is because the deflation period occurs so quickly. As renowned value investor Howard Marks fittingly notes, “The air always goes out a lot faster than it went in.”
Bubbles, Bubbles, Everywhere
Financial bubbles do not occur every day, but thanks to the psychological forces of investor greed and fear, bubbles do occur more often than one might think. As a matter of fact, famed investor Jeremy Grantham claims to have identified 28 bubbles in various global markets since 1920. Definitions vary, but Webster’s Dictionary defines a financial bubble as the following:
A state of booming economic activity (as in a stock market) that often ends in a sudden collapse.
Although there is no numerical definition of what defines a bubble or collapse, the financial crisis of 2008 – 2009, which was fueled by a housing and real estate bubble, is the freshest example in most people minds. However, bubbles go back much further in time – here are a few memorable ones:
Dutch Tulip-Mania: Fear and greed have been ubiquitous since the dawn of mankind, and those emotions even translate over to the buying and selling of tulips. Believe it or not, some 400 years ago in the 1630s, individual Dutch tulip bulbs were selling for the same prices as homes ($61,700 on an inflation adjusted basis). This bubble ended like all bubbles, as you can see from the chart below.
British Railroad Mania: In the mid-1840s, hundreds of companies applied to build railways in Britain. Like all bubbles, speculators entered the arena, and the majority of companies went under or got gobbled up by larger railway companies.
Roaring 20s: Here in the U.S., the Roaring 1920s eventually led to the great Wall Street Crash of 1929, which finally led to a nearly -90% plunge in the Dow Jones Industrial stock index over a relatively short timeframe. Leverage and speculation were contributors to this bust, which resulted in the Great Depression.
Nifty Fifty: The so-called Nifty Fifty stocks were a concentrated set of glamour stocks or “Blue Chips” that investors and traders piled into. The group of stocks included household names like Avon (AVP), McDonald’s (MCD), Polaroid, Xerox (XRX), IBM and Disney (DIS). At the time, the Nifty Fifty were considered “one-decision” stocks that investors could buy and hold forever. Regrettably, numerous of these hefty priced stocks (many above a 50 P/E) came crashing down about 90% during the1973-74 period.
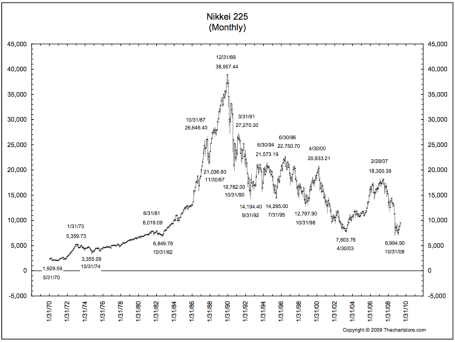
Japan’s Nikkei: The Japanese Nikkei 225 index traded at an eye popping Price-Earnings (P/E) ratio of about 60x right before the eventual collapse. The value of the Nikkei index increased over 450% in the eight years leading up to the peak in 1989 (from 6,850 in October 1982 to a peak of 38,957 in December 1989).
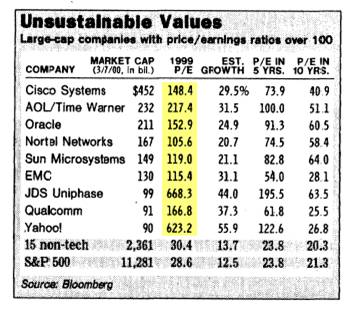
The Tech Bubble: We all know how the technology bubble of the late 1990s ended, and it wasn’t pretty. PE ratios above 100 for tech stocks was the norm (see table below), as compared to an overall PE of the S&P 500 index today of about 14x.
The Next Bubble
What is/are the next investment bubble(s)? Nobody knows for sure, but readers of Investing Caffeine know that long-term bonds are one fertile area. Given the generational low in yields and rates, and the near doubling of long-term Treasury prices over the last twelve years, it can be difficult to justify heavy allocations of inflation losing bonds for long time-horizon investors. Gold, another asset class that has increased massively in price (over 6-fold rise since about 2000) and attracted swaths of speculators, is another target area. However, as we discussed earlier, timing bubble bursts is extremely challenging. Nevertheless, the great thing about long-term investing is that probabilities and valuations ultimately do matter, and therefore a diversified portfolio skewed away from extreme valuations and speculative sectors will pay handsome dividends over the long-run.
Many traders continue to daydream as they chase performance through speculative investment bubbles, looking to squeeze the last ounce of an easily identifiable trend. As the lead investment manager at Sidoxia Capital Management, I spend less time sucking the last puff out of a cigarette, and spend more time opportunistically devoting resources to less popular growth trends. As demonstrated with historical examples, following the trend du jour eventually leads to financial ruin and nightmares. Avoiding bubbles and pursuing fairly priced growth prospects is the way to achieve investment prosperity…and provide sweet dreams.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs) and are short TLT, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct positions in AVP, MCD, XRX, IBM, DIS, or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Robotic Chain Saw Replaces Paul Bunyan
The world is rapidly changing and so is the profile of jobs. Technology is advancing at an accelerating pace, and this is having enormous impacts on the look, feel, and shape of global workforce dynamics. If lumberjack Paul Bunyan and his blue ox Babe were alive today, the giant would not be chopping down trees with a plain old steel axe, but more likely Mr. Bunyan would be using a 20 inch, 8 horse-power chain saw with side-mounted tensioner purchased from ChainSawsDirect.com.
But productivity in logging is not the only industry in which output has dramatically increased over the last generation. A recent New York Times article published by John Markoff explores how robots and automation are displacing humans across many different companies and industries around the world.
In China, manufacturers have exploited the value of cheap labor in the name of low-priced exports, but with millions of workers now moving to job-filled cities, workers are now demanding higher wages and better working conditions. Besides rising wages, higher transportation costs have eaten away labor expense advantages too. One way of getting around the issues of labor costs, labor relations, and transportations costs is to integrate robots into your workplace. A robot won’t ask for a raise; it always shows up on time; you don’t have to pay for its healthcare; it can work 24/7/365 days per year; it doesn’t belong to a union; dependable quality consistency is a given; it produces products near your customers; and it won’t sue you for discrimination or sexual harassment. The initial costs of a robot may be costlier than hiring a human being by a factor of five times an annual salary, but that hasn’t stopped companies everywhere from integrating robots into their operations.
The Orange Box on Wheels
One incredible example of robot usage (not covered by Markoff) is epitomized through Amazon.com Inc.’s (AMZN) $750 million acquisition of Kiva Systems Inc. last year. In some cases, Kiva uses hundreds of autonomous mobile robots in a warehouse to create a freeway-like effect of ecommerce fulfillment that can increase worker productivity four-fold. Amazon is a true believer of the technology as evidenced by the use of Kiva robots in two of its major websites, shoe-retailer Zappos.com and baby-products site Diapers.com, but Kiva’s robots have also been used by other major retailers including Crate & Barrel, Staples Inc (SPLS), and Gap Inc (GPS). The orange square robots on wheels, which can cost in the range of $2 – $20 million per system, travel around a warehouse tracking the desired items and bring them back to a warehouse worker, ready to then be packed and shipped to a customer. Larger warehouses can use up to 1,000 of the Kiva robots. To see how this organized chaos works, check out the video below to see the swarm of orange machines dancing around the warehouse floor.
The Next Chapter
The auto and electronics industry have historically been the heaviest users of robots and automation, but those dynamics are changing. Healthcare, food, aviation, and other general industries are jumping on the bandwagon. And these trends are not just happening in developed markets, but rather emerging markets are leading the charge – even if penetration rates are lower there than in the richer countries. The robotic usage growth is rapid in emerging markets, but the penetration of robotic density per 10,000 workers in China, Brazil and India is less than 10% of that in Japan and Germany (< 20% penetration of the U.S.), according to IFR World Robotics. As a matter of fact, IFR is forecasting that China will be the top robot market by 2014.
What does this mean for jobs? Not great news if you are a low-skilled worker. Take Foxconn, the company that manufactures and assembles those nifty Apple iPhones (AAPL) that are selling by the millions and generating billions in profits. The harsh working conditions in these so-called massive sweatshops have resulted in suicides and high profile worker backlashes. Related to these issues, Foxconn dealt with at least 17 suicides over a five year period. What is Foxconn’s response? Well, besides attempting to respond to worker grievances, Foxconn chairman Terry Gou announced plans to produce 1 million robots in three years , which will replace about 500,000 jobs….ouch!
As the New York Times points out, the “Rise of Machines” is not about to result in Terminator-like robots taking over the world anytime soon:
“Even though blue-collar jobs will be lost, more efficient manufacturing will create skilled jobs in designing, operating and servicing the assembly lines, as well as significant numbers of other kinds of jobs in the communities where factories are.”
Many companies see this trend accelerating and are investing aggressively to profit from the robotic automation and productivity benefits. In today’s day and age, Paul Bunyan would have surely taken advantage of these trends, just as I plan to through Sidoxia Capital Management’s opportunistic investments in the robotic sector.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients hold positions in certain exchange traded funds (ETFs), AMZN, and AAPL, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct positions in Foxconn/Hon Hai, Crate & Barrel, SPLS, GPS, or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC Contact page.
Equity Quicksand or Bond Cliff?
The markets are rigged, the Knight Capital Group (KCG) robots are going wild, and the cheating bankers are manipulating Libor. I guess you might as well pack it in…right? Well, maybe not. While mayhem continues, equity markets stubbornly grind higher. As we stand here today, the S&P 500 is up approximately +12% in 2012 and the NASDAQ market index has gained about +16%? Not bad when you consider 15 countries are offering negative yields on their bonds…that’s right, investors are paying to lose money by holding pieces of paper until maturity. As crazy as buying technology companies in the late 1990s for 100x’s or 200x’s earnings sounds today, just think how absurd negative yields will sound a decade from now? For heaven’s sake, buying a gun and stuffing money under the mattress is a cheaper savings proposition.
Priced In, Or Not Priced In, That is the Question?
So how can stocks be up in double digit percentage terms when we face an uncertain U.S. presidential election, a fiscal cliff, unsustainable borrowing costs in Spain, and S&P 500 earnings forecasts that are sinking like a buried hiker in quicksand (see chart below)?
I guess the answer to this question really depends on whether you believe all the negative news announced thus far is already priced into the stock market’s below average price-earnings (P/E) ratio of about 12x’s 2013 earnings. Or as investor Bill Miller so aptly puts it, “The question is not whether there are problems. There are always problems. The question is whether those problems are already fully discounted or not.”
While investors skeptically debate how much bad news is already priced into stock prices, as evidenced by Bill Gross’s provocative “The Cult of Equity is Dying” article, you hear a lot less about the nosebleed prices of bonds. It’s fairly evident, at least to me, that we are quickly approaching the bond cliff. Is it possible that we can be entering a multi-decade, near-zero, Japan-like scenario? Sure, it’s possible, and I can’t refute the possibility of this extreme bear argument. However with global printing presses and monetary stimulus programs moving full steam ahead, I find it hard to believe that inflation will not eventually rear its ugly head.
Again, if playing the odds is the name of the game, then I think equities will be a better inflation hedge than most bonds. Certainly, not all retirees and 1%-ers should go hog-wild on equities, but the bond binging over the last four years has been incredible (see bond fund flows).
While we may sink a little lower into the equity quicksand while the European financial saga continues, and trader sentiment gains complacency (Volatility Index around 15), I’ll choose this fate over the inevitable bond cliff.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in KCG or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Financial Olympics: Chasing Gold, Siver & Bronze
Article is an excerpt from previously released Sidoxia Capital Management’s complementary August 1, 2012 newsletter. Subscribe on right side of page.
As a record number of 204 nations compete at the XXX Olympic Games in London, and millions of couch-watchers root on their favorite athletes, a different simultaneous competition is occurring…the 2012 Financial Olympics. So far, both Olympics have provided memorable moments for all. While the 2012 London Olympic viewers watched James Bond and Queen Elizabeth II parachute into a stadium filled with 80,000 cheering fans, investors cheered the Dow Jones Industrial Average above the 13,000 level on the same day of the opening ceremony. We have already witnessed a wide range of emotions displayed by thousands of athletes chasing gold, silver, and bronze, and the same array of sentiments associated with glory and defeat have been observed in the 2012 Financial Olympics. There is still a way to go, but despite all the volatility, the stock market is still up a surprising +10% in 2012.
Here were some of the key Financial Olympic events last month:
Draghi Promises Gold for Euro: Some confident people promise gold medals while others promise the preservation of a currency – European Central Bank President (ECB) Mario Draghi personifies the latter. Draghi triggered the controversy with comments he made at the recent Global Investment Conference in London. In the hopes of restoring investor confidence Draghi emphatically proclaimed, “The ECB is ready to do whatever it takes to preserve the euro. And believe me, it will be enough.” To view this excerpt, click video link here.
U.S. Economy Wins Bronze: Whereas Europe has been disqualified from the Financial Olympics due to recessionary economic conditions (Markit predicts a -0.6% contraction in Q3 eurozone GDP), the U.S. posted respectable Q2 GDP results of +1.5%. This surely is an effort worthy of a bronze medal given the overall sluggish, global demand. Fears over a European financial crisis contagion; undecided U.S. Presidential election; and uncertain “fiscal cliff” (automatic tax hikes and spending cuts) are factors contributing to the modest growth. Nevertheless, the US of A has posted 12 consecutive quarters of economic growth (see chart below) and if some clarity creeps back into the picture, growth could reaccelerate.
Source (Calafia Beach Pundit)
No Podium for Spain: Spain’s recent economic achievements closely mirror those of the athletic team, which thus far has failed to secure a sporting medal of any color. Why no Spanish glory? Recently, the Bank of Spain announced the country’s economy was declining at a -1.6% annual rate. Shortly thereafter, Spain estimated its economy would contract by -0.5% in 2013 instead of expanding +0.2%, as previously expected. Adding insult to injury, Valencia (Spain’s most indebted region) said central government support would be needed to repay its debts. These factors, and others, have forced the Spanish government to adopt severe austerity measures to cut its budget deficit by $80 billion through 2015. Spanish banks have negotiated a multi-billion-euro bailout, but they will have to hand control over to European institutions as a concession. Considering these facts, combined with an unemployment rate near 25%, one can appreciate the dominant and pervading losing spirit.
Global Central Banks Inject Financial Steroids: The challenging and competitive global growth environment is not new news to central bankers around the world. As a result, finance leaders around the world are injecting financial steroids into their countries via monetary stimulus (mostly rate cuts and bond buying). Like steroids, these actions may have short-term invigorating effects, but these measures can also have longer-term negative consequences (i.e., inflation). Here are some of the latest country-specific examples (also see chart below):
- U.S. Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke has already shot a couple “Operation Twist” and “QE” (Quantitative Easing) bullets, but as global growth continues to slow, he has openly acknowledged his willingness to dig into his toolbox for additional measures under the right circumstances, including QE3.
- The PBOC (People’s Bank of China) surprised many observers by employing its second rate cut in less than a month. The PBOC lowered its one-year lending rate by 0.31% to 6%.
- The ECB (European Central Bank) lowered its key lending rate by 0.25% to an all-time low of 0.75% and also cut its overnight deposit rate (the equivalent of our Federal Funds rate) by 0.25% to 0%.
- Brazil’s central bank recently cut its benchmark Selic rate for the 8th time in a year to an all-time low of 8% from 12.5%.
- South Korea’s central bank lowered its key interest rates by 0.25% to 3%, its first such action in three years.
- The BOE (Bank of England) raised its quantitative easing goal by 50 billion pounds (~$78 billion).
 Source (Calafia Beach Pundit)
Source (Calafia Beach Pundit)
Banks Disqualified from Libor Games: As a result of the Libor (London Interbank Offered Rate) rigging scandal, Barclays CEO Robert Diamond resigned from the bank and agreed to forfeit $31 million in bonus money. Libor is a measure of what banks pay to borrow from each other and, perhaps more importantly, it acts as a measuring stick for determining rates on mortgages and other financial contracts. In an attempt to boost the perceived financial strength of their financial condition, multiple banks artificially manipulated the calculation of the Libor rate. Ironically, this scandal likely helped consumers with lower mortgage and credit card rates.
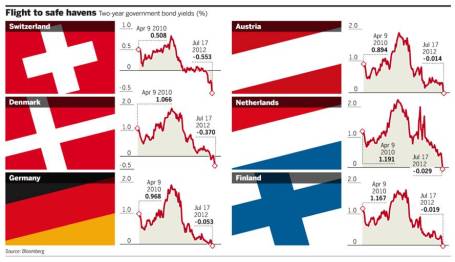
Rates Running Backwards: Sports betting on teams and events is measured by point spreads and numerical odds. In the global debt markets, betting is measured by interest rates. So while losing, debt-laden countries like Greece and Spain have seen their interest rates explode upwards, winning, fiscally responsible countries (including Switzerland, Austria, Denmark, Netherlands, Germany, and Finland) have seen their bond yields turn NEGATIVE. That’s right, investors are earning a negative return. Rather than making a bet on higher yielding bonds, many investors are flocking to the perceived safety of these interest-losing bonds (see chart below). This game cannot last forever, especially for individual and institutional investors who require income to meet liquidity and return requirements.
Source (The Financial Times)
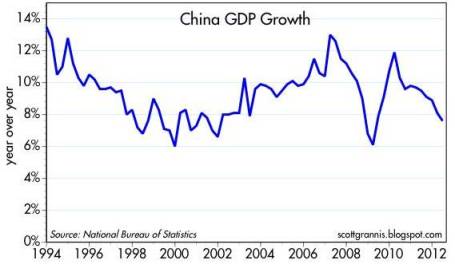
China Wins GDP Gold Medal but No World Record: China currently leads in both the Olympic Games gold medal count (China 13 vs. U.S. 9 through July 31st) and GDP competition. Given the fiscal and monetary stimulus measures the government has implemented, it appears their economy is bottoming. Despite the tremendous anxiety over China’s growth, China’s National Bureau of Statistics just announced a +7.6% Q2 GDP growth rate (see chart below), down from +8.1% in Q1. Although this is the slowest growth since the global financial crisis, Even though this was the slowest GDP growth rate in over three years, most countries would die for this level of growth. Adding evidence to the bottoming storyline, HSBC recently reported the preliminary Chinese PMI manufacturing index rose to 49.5 in July, up from 48.2 in June – the highest reading since early this year (February).
Source (Calafia Beach Pundit)
Higgs Wins God Particle Gold: Michael Phelps and Missy Franklin are not the only people to win gold medals in their fields. Peter Higgs and fellow scientists had 50-years of their physics research validated when the Large Hadron Collider discovered the long-sought Higgs boson (a.k.a., the “god particle”). The collider, located on the Franco-Swiss border, measured approximately 17 miles in length, took years to build, and cost about $8 billion to finish. Pundits are declaring the unearthing of Higgs boson as the greatest scientific discovery since the sequencing of the human genome. Higgs’s gold medal may just come in the form of a Nobel Prize in Physics.
Source (The Financial Times)
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in Barclays or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Sifting Through the Earnings Rubble
An earthquake of second quarter earnings results have rocked the markets (better than expected earnings but sluggish revenues), and now investors are left to sift through the rubble. With thousands of these earnings reports rolling in (and many more in the coming weeks), identifying the key investment trends across sectors, industries, and geographies can be a challenging responsibility. If this was an easy duty, I wouldn’t have a job! Fortunately, having a disciplined process to sort through the avalanche of quarterly results can assist you in discovering both potential threats and opportunities.
But first things first: You will need some type of reliable screening tool in order to filter find exceptional stocks. According to Reuters, there are currently more than 46,000 stocks in existence globally. Manually going through this universe one stock at a time is not physically or mentally feasible for any human to accomplish, over any reasonable amount of time. I use several paid-service screening tools, but there are plenty of adequate free services available online as well.
Investing with the 2-Sided Coin
As Warren Buffett says, “Value and growth are two sides of the same coin.” Having a disciplined screening process in place is the first step in finding those companies that reflect the optimal mix between growth and value. I am willing to pay an elevated price (i.e., higher P/E ratio) for a company with a superior growth profile, but I want a more attractive value (i.e., cheaper price) for slower growth companies. I am fairly agnostic between the mix of the growth/value weighting dynamics, as long as the risk-reward ratio is in my favor.
Since I firmly believe that stock prices follow the long-term trajectory of earnings and cash flows, I fully understand the outsized appreciation opportunities that can arise from the “earnings elite” – the cream of the crop companies that are able to sustain abnormally high earnings growth. Or put in baseball terms, you can realize plenty of singles and doubles by finding attractively priced growth companies, but as Hall of Fame manager Earl Weaver says, “You win many more games by hitting a three-run homer than you do with sacrifice bunts.” The same principles apply in stock picking. Legendary growth investor Peter Lynch (see also Inside the Brain of an Investing Genius) is famous for saying, “You don’t need a lot of good hits every day. All you need is two to three goods stocks a decade.”
Some past successful Sidoxia Capital Management examples that highlight the tradeoff between growth and value include Wal-Mart stores (WMT) and Amazon.com (AMZN). Significant returns can be achieved from slower, mature growth companies like Wal-Mart if purchased at the right prices, but multi-bagger home-run returns (i.e., more than doubling) require high octane growth from the likes of global internet platform companies. Multi-bagger returns from companies like Amazon, Apple Inc. (AAPL), and others are difficult to find and hold in a portfolio for years, but if you can find a few, these winners can cure a lot of your underperforming sins.
Defining Growth
Fancy software may allow you to isolate those companies registering superior growth in sales, earnings, and cash flows, but finding the fastest growing companies can be the most straightforward part. The analytical heavy-lifting goes into effect once an investor is forced to determine how sustainable that growth actually is, while simultaneously determining which valuation metrics are most appropriate in determining fair value. Some companies will experience short-term bursts of growth from a single large contract; from acquisitions; and/or from one-time asset sale gains. Generally speaking, this type of growth is less valuable than growth achieved by innovative products, service, and marketing.
The sustainability of growth will also be shaped by the type of industry a company operates in along with the level of financial leverage carried. For instance, in certain volatile, cyclical industries, sequential growth (e.g. the change in results over the last three months) is the more relevant metric. However for most companies that I screen, I am looking to spot the unique companies that are growing at the healthiest clip on a year-over-year basis. These recent three month results are weighed against the comparable numbers a year ago. This approach to analyzing growth removes seasonality from the equation and helps identify those unique companies capable of growing irrespective of economic cycles.
Given that we are a little more than half way through Q2 earnings results, there is still plenty of time to find those companies reporting upside fundamental earnings surprises, while also locating those quality companies unfairly punished for transitory events. Now’s the time to sift through the earnings rubble to find the remaining buried stock gems.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds and WMT, AMZN, AAPL, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Private Equity: Parasite or Pollinator?
In the wild, there exist both parasitic and symbiotic relationships. In the case of blood thirsty ticks that feed off deer, this parasitic relationship differs from the symbiotic association of nectar-sucking bees and pollen-hungry flowers. These are merely a few examples, but suffice it to say, these same intricate interactions occur in the business world as well.
Our economy is a complex jungle of relationships, spanning governments, businesses, consumers, investors, and many intermediaries, including private equity (PE) firms. With the November election rapidly approaching, more attention is being placed on how private equity firms fit into the economic food chain. Figuring out whether PE firms are more like profit-sucking parasites or constructive job creating mechanisms has moved to the forefront, especially given presidential candidate Mitt Romney’s past ties to Bain Capital, a successful private equity firm he founded in 1984.
Currently it is politically advantageous to portray PE professionals as greedy, job-cutting outsourcers – I’m still waiting for the political ad showing a PE worker clubbing a baby seal or plucking the legs off of a Daddy Long Legs spider. While I’d freely admit a PE pro can be just as gluttonous as an investment banker, hedge fund manager, or venture capitalist, simplistic characterizations like these miss the beneficial effects these firms provide to the overall economy. Capitalism is the spine that holds our economy together and has allowed us to grow into the greatest superpower on the planet. Private equity is but a small part of our capitalistic ecosystem, but plays a valuable role nonetheless.
While there are many perspectives on the role of private equity in our economy, here are my views on a few of the hot button issues:
Job Creation: Although I believe PE firms are valuable to our economy, I think it is a little disingenuous of Romney and his supporters to say Bain was a net “job creator” to the tune of 100,000+ jobs during his tenure. The fact of the matter is PE firms’ priority is to create profitable returns for its investors, and if that requires axing heads, then so be it – most PE firms have no qualms doing precisely that. Romney et al point to successes like Staples Inc. (SPLS), Dominos Pizza Inc. (DPZ) and Sports Authority, Inc., where profitability and success ultimately led to job expansion. From my viewpoint, I believe these examples are more the exception than the rule. Not surprisingly, any job losses executed in the early years of a PE deal will eventually require job additions if the company survives and thrives. Let’s face it, no company can cut its way to prosperity in perpetuity.
Competitveness: Weak, deteriorating, or bankrupt companies cannot and will not hire. Frail or mismanaged companies will sooner or later be forced to cut jobs on their own –the same protocol applied by opportunistic PE vultures swarming around. While PE firms typically focus on bloated or ineffective companies, I think the media outlets overemphasize the cost-cutting aspects of these deals. Sure, PE companies cut jobs, outsource functions, and cut benefits in the name of profits, but that alone is not a sustainable strategy. Trimming fat, by replacing complacent management teams, investing in modern software/equipment, expanding markets, and implementing accountability are all paramount factors in making these target companies more efficient and competitive in the long-run.
Financial Markets-Arbiter: At the end of the day, I think the IPO/financial markets are the final arbiters of how much value PE firms create, not only for investors, but also for the economy overall. If greedy PE firms’ sole functions were to saddle companies with massive debts, cut heads off, and then pay themselves enormous dividends, then there would never be a credible exit strategy for investors to cash out. If PE firms are correctly performing their jobs, then they will profitably create leaner more efficient durable companies that will be able to grow earnings and create jobs over the long-term. If they are unsuccessful in this broad goal, then the PE firm will never be able to profitably exit their investment via a corporate sale or public offering.
Bain Banter: Whether you agree with PE business practices or not, it is difficult to argue with the financial success of Bain Capital. According to a Wall Street Journal article, Bain Capital deals between 1984 – 1999 produced the following results:
“Bain produced about $2.5 billion in gains for its investors in the 77 deals, on about $1.1 billion invested. Overall, Bain recorded roughly 50% to 80% annual gains in this period, which experts said was among the best track records for buyout firms in that era.”
Critics are quick to point out the profits sucked up by PE firms, but they neglect to acknowledge the financial benefits that accrue to the large number of pension fund, charity, and university investors. Millions of middle-class American workers, retirees, community members, teachers, and students are participating in those same blood sucking profits that PE executives are slurping down.
Even though I believe private equity is a net-positive contributor to competiveness and economic growth in recent decades, there is no question in my mind that these firms participated in a massive bubble in the 2005-2007 timeframe. Capital was so cheap and abundant, prices on these deals escalated through the roof. What’s more, the excessive amounts of leverage used in those transactions set these deals up for imminent failure. PE firms and their investors have lost their shirts on many of those deals, and the typical 20%+ historical returns earned by this asset class have become long lost memories. Attractive returns do not come without risk.
With the presidential election rhetoric heating up, the media will continue to politicize, demonize and oversimplify the challenges surrounding this asset class. Despite its shortcomings, private equity will continue to have a positive symbiotic relationship with the economy…rather than a parasitic one.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in SPLS, DPZ, Sports authority, or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.