Posts filed under ‘Fixed Income (Bonds)’
Rates Dance their Way to a Floor
The globe is awash in debt, deficits are exploding, and the Euro is about to collapse…right? Well, then why in the heck are six countries out of the G-7 seeing their 10-year sovereign debt trade at 2.5% or lower on a consistent downward long-term trajectory? What’s more, three of the six countries witnessing their rates plummet are from Europe, despite pundits continually calling for the demise of the eurozone.
Here is a snapshot of 10-year sovereign debt yields for the majority of the G-7 countries over the last few decades:
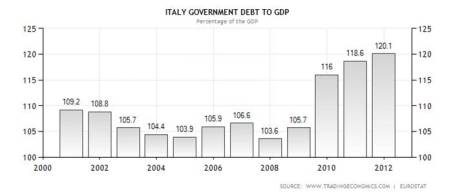
The sole G-7 member missing from the bond yield charts above? Italy. Although Italy’s deficits are not massive (Italy actually has a smaller deficit than U.S. as % of GDP: 3.9% in 2011), its Debt/GDP ratio has been large and rising (see chart below):
As the globe has plodded through the financial crisis of 2008-2009, investors have flocked to the perceived stability of these larger developed countries’ bonds, even if they are merely better homes in a bad neighborhood right now. PIMCO likes to call these popular sovereign bonds, “cleaner dirty shirts.” Buying sovereign debt from these less dirty shirt countries, without sensitivity to price or yield, has been a lucrative trade that has worked consistently for quite some time. Now, however, with sovereign bond yields rapidly approaching 0%, it becomes mathematically impossible to fall lower than the bottom rate floor that developed countries are standing on.
Bond bears have been wrong about the timing of the inevitable bond price reversal, myself included, but the bulls are skating on thinner and thinner ice as rates continue moving lower. The bears may prolong their bragging rights if interest rates continue downward, or persist at these lower levels for extended periods of time. Eventually the “buy the dips” mentality dies, as we so poignantly experienced in 2000 when the technology dips turned into outright collapse.
The Flies in the Bond Binging Ointment
As long as equities remain in a trading range, the “risk-off” bond binging arguments will continue holding water. If corporate earnings remain elevated and stock buybacks carry on, the pain of deflating real returns will eventually become too unbearable for investors. As the insidious rising prices of energy, healthcare, food, leisure, and general costs keep eating away everyone’s purchasing power, even the skeptics will become more impatient with the paltry returns they are currently earning. Earning negative real returns in Treasuries, CDs, money market accounts, and other conservative investments, is not going to help millions of Americans meet their future financial goals. Due to the laundry list of global economic concerns, large swaths of investors are still running and hiding, but this is not a sustainable strategy longer term. The danger from these so-called “safe,” low-yielding asset classes is actually riskier than the perceived risk, in my view.
With that said, I’ve consistently held there are a subset of investors, including a significant number of my Sidoxia Capital Management clients, who are in the later stage of retirement and have a rational need for capital preservation and income generating assets (albeit low yielding). For this investor segment, portfolio construction is not executed due to an opportunistic urge of chasing potential outsized rates of return, but more-so out of necessity. Shorter time horizons eliminate the prudence of additional equity exposure because of the extra associated volatility. Unfortunately, many of the 76 million Baby Boomers will statistically live another 20 – 30 years based on actuarial life expectations and under-save, so the risks of being too conservative can dramatically outweigh the risks of increasing equity exposure. This is all stated in the context of stocks paying a higher yield than long-term Treasuries – the first time in a generation.
Short-term risks and uncertainties remain high, with Greek election outcomes unknown; a U.S. Presidential election in flux; and an impending domestic fiscal cliff that needs to be addressed. But with interest rates accelerating towards 0% and investors’ fright-filled buying of pricey, low-yielding asset classes, many of these risks are already factored into current valuations. As it turns out, the pain of panic can be more detrimental than being stuck in over-priced assets, driven by rates dancing near an absolute floor.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
The Rule of 20 Can Make You Plenty
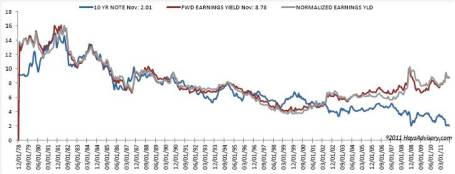
There is an endless debate over whether the equity markets are overvalued or undervalued, and at some point the discussion eventually transitions to what the market’s appropriate P/E (Price-Earnings) level should be. There are several standard definitions used for P/Es, but typically a 12-month trailing earnings, 12-month forward earnings (using earnings forecasts), and multi-year average earnings (e.g., Shiller 10-year inflation adjusted P/E – see Foggy P/E Rearview Mirror) are used in the calculations. Don Hays at Hays Advisory (www.haysadvisory.com) provides an excellent 30+ year view of the historical P/E ratio on a forward basis (see chart below).
If you listen to Peter Lynch, investor extraordinaire, his “Rule of 20” states a market equilibrium P/E ratio should equal 20 minus the inflation rate. This rule would imply an equilibrium P/E ratio of approximately 18x times earnings when the current 2011 P/E multiple implies a value slightly above 11x times earnings. The bears may claim victory if the earnings denominator collapses, but if earnings, on the contrary, continue coming in better than expected, then the sun might break through the clouds in the form of significant price appreciation.
Just because prices have been chopped in half, doesn’t mean they can’t go lower. From 1966 – 1982 the Dow Jones Industrial index traded at around 800 and P/E multiples contracted to single digits. That rubber band eventually snapped and the index catapulted 17-fold from about 800 to almost 14,000 in 25 years. Even though equities have struggled at the start of this century, a few things have changed from the market lows of 30 years ago. For starters, we have not hit an inflation rate of 13% or a Federal Funds rate of 20% (~3.5% and 0% today, respectively), so we have some headroom before the single digit P/E apocalypse descends upon us.
Fed Model Implies Equity Throttle
Hays Advisory exhibits another key valuation measurement of the equity market (the so-called “Fed Model”), which compares the Treasury yield of the 10-year Note with the earnings yield of stocks (see chart below).
Regardless of your perspective, the divergence will eventually take care of it in one of three ways:
1.) Bond prices collapse, and Treasury yields spike up to catch up with equity yields.
2.) Forward earnings collapse (e.g., global recession/depression), and equity yields plummet down to the low Treasury yield levels.
AND/OR
3.) Stock prices catapult higher (lower earnings yield) to converge.
At the end of the day, money goes where it is treated best, and at least today, bonds are expected to treat investors substantially worse than the unfaithful treatment of Demi Moore by Ashton Kutcher. The Super Committee may not have its act together, and Europe is a mess, but the significant earnings yield of the equity markets are factoring in a great deal of pessimism.
The holidays are rapidly approaching. If for some reason the auspice of gifts is looking scarce, then review the Fed Model and Rule of 20, these techniques may make you plenty.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Your Portfolio’s Silent Killer
Shhh, if you listen closely enough, you may hear the sound of your portfolio disintegrating away due to the quiet killer…inflation. Inflation is especially worrisome with what we’ve seen happening with commodity prices and the drastic fiscal challenges our country faces. Quantitative Easing (read Flying to the Moon) has only added fuel to the inflation fear flames.
Whether you’re a conspiracy theorist who believes the government inflation data is cooked, or you are a Baby Boomer just looking to secure your retirement, it doesn’t take a genius to figure out that movies, pair of jeans, a tank of gas, concert tickets, or healthcare premiums are all going up in price (See also Bacon and Oreo Future).
Companies are currently churning out quarterly results in volume and seeing the impact from commodity prices, whether you are McDonald’s Corp. (MCD) facing rising beef prices or luxury handbag maker Coach Inc. (COH) dealing with escalating leather costs, margins are getting crimped. Investors, especially those on fixed income streams, are experiencing the same pain as these corporations, but the problem is much worse. Unlike a market share leading company that can pass on price increases onto its customers, an investor with piles of cash, and low yielding CDs (Certificates of Deposit), and bonds runs the risk of getting eaten alive. Baby Boomers are beginning to reach retirement age in mass volume. Life spans are extending, and this demographic pool of individuals will become ever-large consumers of costlier and costlier healthcare services. If investments are not prudently managed, Baby Boomers will see their nest eggs evaporate, and be forced to work as Wal-Mart (WMT) greeters into their 80s…not that there’s anything wrong with that.
Every day investors are bombarded with a hundred different scary headlines on why the economy will collapse or the world will end. Most of these sensationalist scare tactics distort the truth and overstate reality. What is understated is what Charles Ellis (see Winning the Loser’s Game) calls a “corrosive power”:
“Over the long run, inflation is the major problem for investors, not the attention-getting daily or cyclical changes in securities prices that most investors fret about. The corrosive power of inflation is truly daunting: At 3 percent inflation – which most people accept as ‘normal’ – the purchasing power of your money is cut in half in 24 years. At 5 percent inflation, the purchasing power of your money is cut in half in less than 15 years – and cut in half again in 15 years to just one-quarter.”
In order to bolster his case, Ellis cites the following period:
“From 1977 to 1982, the inflation-adjusted Dow Jones Industrial Average took a five-year loss of 63 percent…In the 15 years from the late 1960s to the early 1980s the unweighted stock market, adjusted for inflation, plunged by about 80 percent. As a result, the decade of the 1970s was actually worse for investors than the decade of the 1930s.”
Solutions – How to Beat Inflation
Although the gold bugs would have you believe it, we are not resigned to live in a world with worthless money, which only has a useful purpose as toilet paper. There are ways to protect your portfolio, if you are properly invested. Here are some strategies to consider:
- TIPS (Treasury Inflation Protection Securities): These government-guaranteed tools are a useful way to protect yourself against rising inflation (see Drowning TIPS).
- Equities (including real estate): Bond issuers do not generally call up there investors and say, “You are such a great investor, so we have decided to increase your interest payments.” However, many publicly traded stocks do exactly that. Wal-Mart Stores (WMT) is an example of such a company that has increased its dividend for 37 consecutive years. As alluded to earlier, stocks are unique in that they allow inflationary pressures placed on operating profits to be relieved somewhat by the ability to pass on price increases to customers.
- Commodities: Whether you are talking about petroleum products, precious metals (those with a commercial purpose), or agricultural goods, commodities in general act as a great inflationary hedge. Another reason that commodities broadly perform better in an inflationary environment is because the U.S. dollar can often depreciate, which commonly increases the value of commodities.
- Short Duration Bonds: Rising rates are usually tied to escalating inflation, therefore investors would be best served by reducing maturity length and increasing coupon.
There are other ways of battling the inflation problem, but number one is saving and investing across a broadly diversified portfolio. If you want to secure and grow your nest egg, you need to use the silent power of compounding (see Penny Saved is Billion Earned) to combat the silent killer of inflation.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, WMT, TIP, equities, commodities, and short duration bonds, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Winning Coaches Telling Players to Quit
How would you feel if your coach told you not only are you going to lose, but you should quit and join the other team? Effectively, that is what Loomis Sayles bond legend Dan Fuss (read Fuss Making a Fuss), and fellow colleagues Margie Patel (Wells Fargo Advantage Funds), and Anthony Crescenzi (PIMCO) had to say about the chances of bonds winning at the recent Advisors’ Money Show.
This is what Fuss said regarding “statistically cheap” equities:
“I’ve never seen it this good in half a century.”
Patel went on to add:
“By any measure you want to look at, free cash flow, dividend yield, P/E ratio – stocks look relatively cheap for the level of interest rates.” Stock offer a “once-in-a-decade opportunity to buy and make some real capital appreciation.”
Crescenzi included the following comments about stocks:
“Valuations are not risky…P/E ratios have been fine for a decade, in part because of the two shocks that drove investors away from equities and compressed P/E ratios.”
Bonds Dynasty Coming to End
The bond team has been winning for three decades (see Bubblicious Bonds), but its players are getting tired and old. Crescenzi concedes the “30-year journey on rates is near its ending point” and that “we are at the end of the duration tailwind.” Even though it is fairly apparent to some that the golden bond era is coming to a close, there are ways for the bond team to draft new players to manage duration (interest rate/price sensitivity) and protect oneself against inflation (read Drowning TIPS).
Equities on the other hand have had a massive losing streak relative to bonds, especially over the last decade. The equity team had over-priced player positions that exceeded their salary cap and the old market leaders became tired and old. Nothing energizes a new team better than new blood and new talent at a much more attractive price, which leaves room in the salary cap to get the quality players to win. There is always a possibility that bonds will outperform in the short-run despite sky-high prices, and the introduction of any material, detrimental exogenous variable (large country bailout, terrorist attack, etc.) could extend bonds’ outperformance. Regardless, investors will find it difficult to dispute the relative attractiveness of equities relative to prices a decade ago (read Marathon Investing: Genesis of Cheap Stocks).
As I have repeated in the past, bonds and cash are essential in any portfolio, but excessively gorging on a buffet of bonds for breakfast, lunch, and dinner can be hazardous for your long-term financial health. Maximizing the bang for your investment buck means not neglecting volatile equity opportunities due to disproportionate conservatism and scary economic media headlines.
There are bond coaches and teams that believe the winning streak will continue despite the 30-year duration of victories. Fear, especially in this environment, is often used as a tactic to sell bonds. Conflicts of interest may cloud the advice of these bond coaches, but the successful experienced coaches like Dan Fuss, Margie Patel, Anthony Crescenzi are the ones to listen to – even if they tell you to quit their team and join a different one.
Read Full Advisor Perspectives Article
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds (including TIP), but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
QE2 Drowning TIPS Yields Below Water
The holiday season is creeping up on us, and the only question building up more anticipation than what gift kids are going to get from Santa Claus is what investors are going to get from Federal Reserve Chairman Ben Bernanke – in the form of QE2 (Quantitative Easing Part II)? The inevitable QE2 program is an effort designed by the Fed to keep interest rates low and reduce the threat of deflation. In addition, QE2 is structured to stimulate the meager 0.8% core inflation experienced over the last 12 months (Bloomberg) to a Goldilocks level – not too hot and not too cold. Some pundits suggest the Fed should target a 2% inflation rate. QE2 asset purchase estimates are all over the map, but I can safely guess somewhere between a few hundred billion and $2 trillion (very brave of me).
Treasuries Weigh Down TIPS Yields
Ever since QE1 expired in the March timeframe, speculation began about the next potential slug of Treasuries and mortgage backed securities to be purchased by the Fed. As a consequence, this speculation became a contributing factor to 10-Year Treasury yields plummeting from around 4.0% to around 2.5%. Simultaneously, 5-Year TIPS (Treasury Inflation Protection Securities) yields have moved to negative territory.
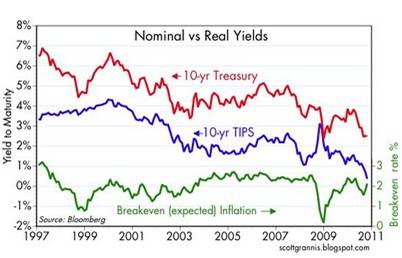
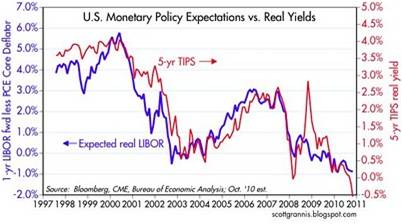
Scott Grannis at Calafia Beach Pundit has a great chart showing the relationship between nominal Treasury yields, real TIPS yields, and expected inflation for 10-year maturities. As you can see below, over the last ten years there has been a tight correlation between the 10-year Treasury bond versus TIPS, with the former 10-year declining yield acting as a weight drowning the latter TIPS yield:
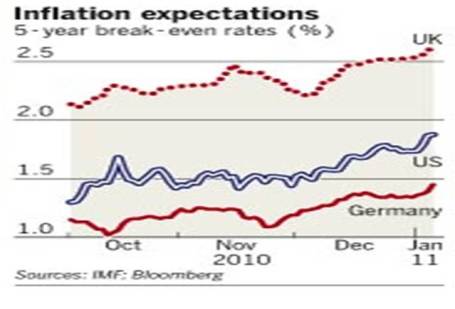
Worth noting, absent the brief period in late-2008 and early-2009, inflation expectations have been remarkably stable in that 1.5% – 2.5% range.
Negative Yields…Who Cares?!
Unprecedented times have created an unprecedented appetite for bonds (see Bubblicious Bonds), and as a result, we just witnessed a historic $10 billion TIPS auction this week producing an eye-catching negative -0.55% yield. Sensationalist commentators characterize the negative yield dynamic as a money losing proposition, whereby investors are forced to pay the government. This assertion is quite a distortion and not quite true – we will review the mechanics of TIPS later.
If we’re not back to a panic filled environment of soup kitchen lines and bank runs, then why are TIPS paying a negative yield?
- QE2: As mentioned above, investor expectations are that Uncle Sam will come to the rescue and deliver lower interest rates (higher prices) through purchases of Treasuries and mortgage-backed securities.
- Rising Inflation Expectations: As fears surrounding future inflation increase, the price of TIPS will rise, and yields will fall.
- Sluggish Economy: Lackluster growth and fear of double dips have pressured rates lower as debates still linger about whether or not the U.S. will follow Japan (see Lost Decade).
Nuts & Bolts of TIPS
TIPS maturities come in terms of 5 years, 10 years and 30 years. Per the Treasury, 5-year TIPS are auctioned in April and October; 10-year TIPS in January, March, May (beginning in 2011), July, September, and November; and 30-year TIPS in February and August.
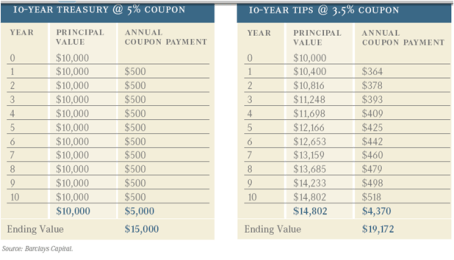
This table from Barclays Capital below does an excellent job of conceptually displaying the differences between vanilla Treasuries and TIPS.
Some Observations:
1) As you can see, the principal value of the TIPS security adjusts with inflation (Consumer Price Index). The price of the TIPS security, which we cannot see in the example, adjusts upwards (or downwards) with inflation expectations.
2) The TIPS security pays a lower coupon (3.5% vs. 5.0%), but you can see that under a 4% annual inflation assumption (principal value adjusts from $10,000 in Year 0 to $10,400 in Year 1), the ending value of the TIPS comes up significantly higher ($19,172 vs. $15,000).
3) The break-even inflation expectation rate is 1.5% (derived from 5% coupon minus 3.5% coupon). If you think inflation will average more than 1.5%, then buy the TIPS security. If you think inflation will average less than 1.5%, then buy the 10-year Treasury.
TIPS Advantages
- Inflation Protection: At the risk of stating the obvious, if you expect long-term inflation to average substantially more than about 2% (current inflation expectations), then TIPS are a great way of protecting your purchasing power.
- Deflation Protection: Perhaps TIPS should be called DIPS (Deflation Income Protection Securities)? What some investors do not realize is that even if our country were to spiral into long-term deflationary crisis, TIPS investors are guaranteed the original amount of principal. Yes, that’s right…guaranteed. Interest payments could conceivably decline to zero and the principal value could temporarily fall below par, but the government guarantees the original principal regardless of the scenario.
- No Credit or Default Risk: The advantage of the government owning its own printing press is that there is very little risk of default, so preservation of capital is not much of a risk.
TIPS Disadvantages
- Interest Rate Risk: It’s great to be indexed to inflation, but because TIPS include long-range maturities, investors face a significant amount of interest rate risk if the TIPS are not held until maturity. TIPS will likely outperform Treasuries under a rising rate scenario, but will be impacted nonetheless.
- CPI Risk: Even if you are not a conspiracy theorist who believes government CPI figures are artificially depressed, it is still quite possible your personal baskets of purchases do not perfectly align with the arbitrary CPI basket of goods.
- Negative Deflation Adjustments: Although a TIPS investor has an embedded “deflation floor” equivalent to original principal value, interest payments will be negatively impacted by declines in principal value during deflationary periods. Also, previously issued TIPS with accumulated principal values from inflationary adjustments run larger principal loss risks as compared to newly issued TIPS.
Although 5-year TIPS yields may have dunked below water into negative territory, the headline bark is much worse than the bite. There has been a massive rally in bond prices in front of the QE2 bond binge by the Fed. Nevertheless, inflation expectations have remained fairly stable and TIPS still provide defensive characteristics under both a future inflationary or deflationary scenario. If the Fed is indeed successful in manufacturing a reasonable Goldilocks range of inflation then TIPS yields should once again be able to come up for air.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds (including TIP), but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
PIMCO – The Downhill Marathon Machine
How would you like to run a marathon? How about a marathon that is prearranged all downhill? How about a downhill marathon with the wind at your back? How about a downhill marathon with the wind at your back in a wheelchair? Effectively, that is what a 30-year bull market has meant for PIMCO (Pacific Investment Management Co.) and the “New Normal” brothers (Co-Chairman Bill Gross and Mohamed El-Erian) who are commanding the bond behemoth (read also New Normal is Old Normal). Bill Gross can appreciate a thing or two about running marathons since he once ran six marathons in six consecutive days.
This perseverance also assisted Gross in co-founding PIMCO in 1971 with $12 million in assets under management. Since then, the company has managed to add five more zeroes to that figure (today assets exceed $1.2 trillion). In the first 10 years of the company’s existence, as interest rates were climbing, PIMCO managed to layer on a relatively thin amount of assets (approximately $1 billion). But with the tailwind of declining rates throughout the 1980s, PIMCO’s growth began to accelerate, thereby facilitating the addition of more than $25 billion in assets during the decade.
The PIMCO Machine
For the time-being, PIMCO can do no wrong. As the endless list of media commentators and journalists bow to kiss the feet of the immortal bond kings, the blinded reporters seem to forget the old time-tested Wall Street maxim:
“Never confuse genius with a bull market.”
The gargantuan multi-decade move in interest rates, the fuel used to drive bond prices to the moon, might have something to do with the company’s success too? PIMCO is not exactly selling ice to the Eskimos – many investors are scooping up PIMCO’s bond products as they wait in their bunkers for Armageddon to arrive. Thanks to former Federal Reserve Chairman Paul Volcker (appointed in 1979), the runaway inflation of the early 1980s was tamed by hikes he made in the key benchmark Federal Funds Rate (the targeted rate that banks lend to each other). From a peak of around 20% in 1980-1981 the Fed Funds rate has plummeted to effectively 0% today with the most recent assistance coming from current Fed Chairman Ben Bernanke.
Although these west-coast beach loving bond gurus are not the sole beneficiary in this “bond bubble” (see Bubblicious Bonds story), PIMCO has separated itself from the competition with its shrewd world-class marketing capabilities. A day can hardly go by without seeing one of the bond brothers on CNBC or Bloomberg, spouting on about interest rates, inflation, and global bond markets. As PIMCO has been stepping on fruit in the process of collecting the low-hanging fruit, the firm has not been shy about talking its own book. Subtlety is not a strength of El-Erian – here’s what he had to pimp to the USA Today a few months ago as bond prices were continuing to inflate: “Simply put, investors should own less equities, more bonds, more global investments, more cash and more dry ammunition.”
If selling a tide of fear resulted in a continual funnel of new customers into your net, wouldn’t you do the same thing? Fearing people into bonds is something El-Erian is good at: “In the New Normal you are more worried about the return of your capital, not return on your capital.” Beyond alarm, accuracy is a trivial matter, as long as you can scare people into your doomsday way of thinking. The fact Bill Gross’s infamous Dow 5,000 call never came close to fruition is not a concern – even if the forecast overlapped with the worst crisis in seven decades.
Mohamed Speak
Mohamed El-Erian is a fresher face to the PIMCO scene and will be tougher to pin down on his forecasts. He arrived at the company in early 2008 after shuffling over from Harvard’s endowment fund. El-Erian has a gift for cryptically speaking in an enigmatic language that could only make former Federal Reserve Chairman Alan Greenspan proud. Like many economists, El-Erian laces his commentary with many caveats, hedges, and generalities – concrete predictions are not a strength of his. Here are a few of my favorite El-Erian obscurities:
- “ongoing paradigm shift”
- “endogenous liquidity”
- “tail hedging”
- “deglobalization”
- “post-realignment”
- “socialization losses”
Excuse me while I grab my shovel – stuff is starting to pile up here.
Don’t get me wrong…plenty of my client portfolios hold bonds, with some senior retiree portfolios carrying upwards of 80% in fixed income securities. This positioning is more a function of necessity rather than preference, and requires much more creative hand-holding in managing interest-rate risk (duration), yield, and credit risk. At the margin, unloved equities, including high dividend paying Blue Chip stocks, provide a much better risk-adjusted return for those investors that have the risk tolerance and time-horizon threshold to absorb higher volatility.
PIMCO has traveled along a long prosperous road over the last 30 years with the benefit of a historic decline in interest rates. While PIMCO may have coasted downhill in a wheelchair for the last few decades, this behemoth may be forced to crawl uphill on its hands and knees for the next few decades, as interest rates inevitably rise. Now that is a “New Normal” scenario Bill Gross and Mohamed El-Erian have not forecasted.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds, but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in PIMCO/Allianz, or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
The Next Looming Bailout…Muni Bonds
Government politicians and voters have made it clear they do not want to bail out “fat-cat” bankers in the private sector, but what about bailing out “fat-cat” state pensioners in the public sector? States and cities across the country are increasingly under economic strain with deficits widening and debt-loads stacking up. California’s statewide budget problems have been well publicized, but you are now also hearing about more scandalous financial problems at the city level (read about the multi-million dollar malfeasance in the city of Bell).
Why Worry?
Well if a 2010 $1.3 trillion federal deficit is not enough to tickle your fancy, then how does another $137 billion in state deficits over fiscal 2011 and 2012 sound to you (National Governors Association)? Unfortunately, the states have made no meaningful structural improvements. If you layer on general economic “double dip” recession fears with excess pension liabilities, then you have a recipe for a major unresolved financial predicament.
Despite the dire financial state of the states, municipal bond prices have generally survived the 2008-2009 financial crisis unscathed. With unacceptably poor state budget risks, muni bond prices have continued to rise in 2010. The downside…new investors must accept a pitiful yield of 2.75% on 10-year municipal debt, according to Financial Advisor Magazine.
One investor who is not buying into the strength of the tax-free municipal bond market is famed investor and CEO of Berkshire Hathaway (BRKA/BRKB), Warren Buffett. Here is what he wrote about munis in his legendary annual shareholder letter last year:
“Insuring tax-exempts, therefore, has the look today of a dangerous business…Local governments are going to face far tougher fiscal problems in the future than they have to date.”
Buffett has this to say about rating muni bonds:
“I mean, if the federal government will step in to help them [municipalities], they’re triple-A. If the federal government won’t step in to help them, who knows what they are?”
Safety Net Disappears
Like a high wire artist dangling high in the air without a safety net below, the states are currently borrowing money with little to no protection from the bond insurance providers. The shakeout of the subprime debt defaults has battered the insurers from many perspectives, leaving a much smaller market in the wake of the financial crisis. In 2007 about 50% of new municipal bonds were issued with bond insurance, while today only approximately 7% carry it (UBS Wealth Management Research). With decreased insurance coverage, the silver lining for muni investors is the necessity for them to perform more comprehensive research on their bond holdings.
Defaults on the Rise
On the whole, less insurance will result in more defaults. Although defaults are expected to decline in 2010, non-payments totaled $6.9 billion in 2009, up from $526 million in 2007 (Distressed Debt Securities). Even though the numbers sounds large, the recent default rate only represents a 0.25% default rate on the hefty $2.8 trillion market. That muni default rate compares to a more intimidating corporate bond default rate of 11% in 2009.
Bigger Bark Than Bite?
James T. Colby, senior municipal strategist at Van Eck Global, understands the severity of the states’ budget crisis but he believes a lot of the doomsday headlines are bogus. Riva Atlas, writer for Financial Advisor Magazine, summarizes Colby’s thoughts:
“Even those states in the worst straits like California and Illinois have provisions in their constitutions or statutes requiring them to pay their debts. In California, the state’s constitution says bondholders come second only to the school system, so the state would have to empty its jails before it stopped paying its teachers.”
Certainly municipalities could raise taxes to compensate for any budget shortfalls, but we all know most politicians are reluctant to raise taxes, because guess what? Tax increases may result in fewer votes – the main motivator driving most politicians.
If the states decide to not raise taxes, they still have other ways to weasel out of obligations. For starters, they can just stick it to the insurance company (if coverage exists). If that option is not available, the municipalities can look to the federal government for a bailout. Irresponsible actions have their consequences, and like consumers walking away from payments on their mortgages, municipalities will effectively be preventing themselves from future access to borrowing. Either way, the bark is less than the bite for investors since the insurance company or federal government will be making them whole.
BABs and Taxes Add Fuel to the Fire
A glut of Build America Bonds (BABs) issued by municipalities, driven by demand from yield hungry pension funds, along with expected tax hikes for the wealthy have created a scarcity of tax-free munis.
In the first half of 2010 BABs accounted for more than 25% of municipal bonds issued, which was a significant contributing factor to the robust muni market. The BABs tailwinds aiding muni prices won’t last forever, as the bond issuance program is expected to expire at the end of 2010.
On the tax front, the wealthy are likely to see higher federal tax rates in the future – upwards of 36% – 40%. If you include the double tax-exempt benefits in states like New York and California, the relative attractiveness becomes even that much better. Combined, these factors have elevated muni prices.
Despite higher defaults, scarier headlines, and the lack of insurance, the municipal bond market remains robust. General interest rate declines caused by macroeconomic fears have caused investors to flock to the perceived “safe haven” status of Treasuries and Munis, but as we have all witnessed, the fickle pendulum of emotions never sits still for long.
Managing the Munis
As is evident from the municipal bond discussion, states and cities across the country have been plagued by the same deficit and debt issues as the country faces on a federal level. Tough structural expense issues, and revenue generating tax policies need to be scrutinized in order to prevent federal taxpayer bailouts of municipalities across the country.
From a municipal bond investor perspective, it’s best to focus on general obligation bonds (GOs) because those bonds are backed by the taxing authority of the municipal government. On the flip side, it’s best to stray away from revenue bonds or privately issued municipals because revenue streams from these bond channels are not guaranteed by the municipality, meaning the risk of default is larger.
While Congress sorts out financial regulatory reform with respect to banking bailouts and “too big to fail” corporations, our federal government should not lose sight of the widespread municipality problems our country faces today. If not, get ready to pull out the checkbook to pay for another taxpayer-led bailout…
Read the Complete Financial Advisor Magazine Article: The Muni Minefield
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds (including CMF), but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in BRKA/B or any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Siegel & Co. See “Bubblicious” Bonds
Siegel compares 1999 stock prices with 2010 bonds
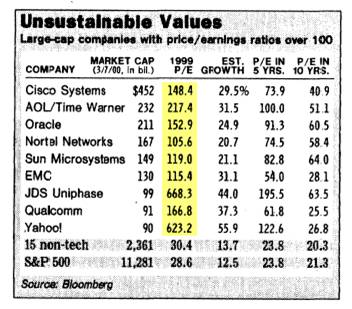
Unlike a lot of economists, Jeremy Siegel, Professor at the Wharton School of Business, is not bashful about making contrarian calls (see other Siegel article). Just days after the Nasdaq index peaked 10 years ago at a level above 5,000 (below 2,200 today), Siegel called the large capitalization technology market a “Sucker’s Bet” in a Wall Street Journal article dated March 14, 2000. Investors were smitten with large-cap technology stocks at the time, paying balloon-like P/E (Price-Earnings) ratios in excess of 100 times trailing earnings (see table above).
Bubblicious Boom
Today, Siegel has now switched his focus from overpriced tech-stock bubbles to “Bubblicious” bonds, which may burst at any moment. Bolstering his view of the current “Great American Bond Bubble” is the fact that average investors are wheelbarrowing money into bond funds. Siegel highlights recent Investment Company Institute data to make his point:
“From January 2008 through June 2010, outflows from equity funds totaled $232 billion while bond funds have seen a massive $559 billion of inflows.”
The professor goes on to make the stretch that some government bonds (i.e., 10-year Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities or TIPS) are priced so egregiously that the 1% TIPS yield (or 100 times the payout ratio) equates to the crazy tech stock valuations 10 years earlier. Conceptually the comparison of old stock and new bond bubbles may make some sense, but let’s not lose sight of the fact that tech stocks virtually had a 0% payout (no dividends). The risk of permanent investment loss is much lower with a bond as compared to a 100-plus multiple tech stock.
Making Rate History No Mystery
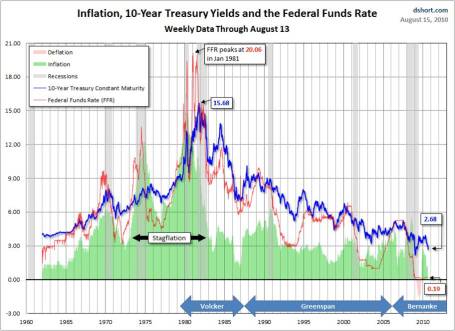
What makes Siegel so nervous about bonds? Well for one thing, take a look at what interest rates have done over the last 30 years, with the Federal Funds rate cresting over 20%+ in 1981 (View RED LINE & BLUE LINE or click to enlarge):
As I have commented before, there is only one real direction for interest rates to go, since we currently sit watching rates at a generational low. Rates have a minute amount of wiggle room, but Siegel rightfully understands there is very little wiggle room for rates to go lower. How bad could the pain be? Siegel outlines the following scenario:
“If over the next year, 10-year interest rates, which are now 2.8%, rise to 3.15%, bondholders will suffer a capital loss equal to the current yield. If rates rise to 4% as they did last spring, the capital loss will be more than three times the current yield.”
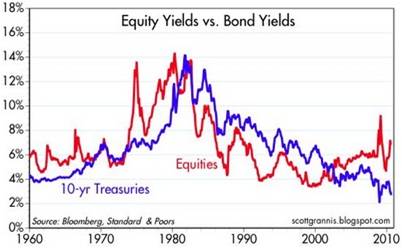
Siegel is not the only observer who sees relatively less value in bonds (especially government bonds) versus stocks. Scott Grannis, author of the Calafia Report artfully shows the comparisons of the 10-Year Treasury Note yield relative to the earnings yield on the S&P 500 index:
As you can see, rarely have there been periods over the last five decades where bonds were so poorly attractive relative to equities.
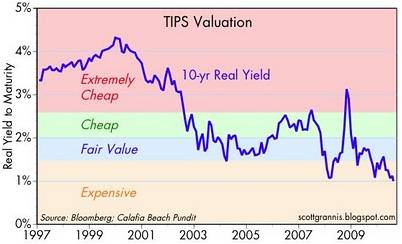
Grannis mirrors Siegel’s view on government bond prices through his chart on TIPS pricing:
Pricey Treasuries is not a new unearthed theme, however, Siegel and Grannis make compelling points to highlight bond risks. Certainly, the economy could soften further, and trying to time the bottom to a multi-decade bond bubble can be hazardous to your investing health. Having said that, effectively everyone should desire some exposure to fixed income securities, depending on their objectives and constraints (retirees obviously more). The key is managing duration and the risk of inflation in a prudent fashion. If you believe Siegel is correct about an impending bond bubble bursting, you may consider lightening your Treasury bond load. Otherwise, don’t be surprised if you do not collect on another “sucker’s bet.”
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
*DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds (including TIP and other fixed income ETFs), but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in any security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Private Equity: Hitting Maturity Cliff
Wow, those were the days when money was as cheap and available as that fragile, sandpaper-like toilet paper you find at gas stations. Private equity took advantage of this near-free, pervasive capital and used it to the greatest extent possible. The firms proceeded to lever up and gorge themselves on a never-ending list of target companies with reckless abandon (see also Private Equity Shooting Blanks). Now the glory days of abundant, ultra-cheap capital are history.
Rather than rely on low-cost bank debt, private equity firms are now turning to the fixed income markets – specifically the high yield market (a.k.a. junk bonds). As The Financial Times points out, more than $170 billion of junk bonds have been issued this year, in large part to refinance debt issued in the mid-2000s that has gone sour due to overoptimistic projections and a flailing U.S. economy. In special instances, private equity owners are fattening their own wallets by declaring special dividends for themselves.
Even though some of these over-levered, private equity portfolio companies have received a temporary reprieve from facing the harsh economic realities thanks to these refinancings, the cliff of maturing debt in 2012 is fast approaching. Some have estimated that $1 trillion in maturing debt will roll through the market in the 2012-2014 timeframe. Either the economy (or operating performance) improves enough for these companies to service their debt, or these companies will find themselves falling off these maturity cliffs into bankruptcy.
Junk is Not Risk-Free
Driving this trend of loan recycling is risk aversion to stocks and a voracious appetite for yield in a yield desert. Stuffing the money under the mattress, earning next to nothing on CDs (Certificates of Deposit) and money market accounts, will not help in meeting many investors’ long-term objectives. The “uncertain uncertainty” swirling around global equity markets has nervous investors flocking to bonds. The opening of liquidity in the high yield markets has served as a life preserver for these levered companies desperate to refinance their impending debt. This high-yield debt refinancing window is also an opportunity for companies to lower their interest expense burden because of the current, near record-low interest rates.
But as the name implies, these “junk bonds” are not risk free. For starters, embedded in these bonds is interest rate risk – with a Federal Funds rate at effectively zero, there is only one upward direction for interest rates to go (bad for bond prices). In addition, credit risk is a concern as well. In the midst of the financial crisis, many of these high-yield bonds corrected by more than -40% from their highs in 2008 until the bottom achieved in early 2009. If the economy regresses back into a double-dip recession, many of these bonds stand to get pummeled as default rates escalate (see also, bond risks).
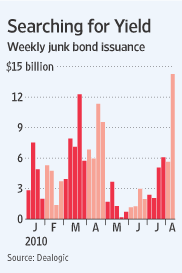
Pace Not Slowing
Does the appetite for high yield appear to be slowing? Au contraire. In the most recent week, Dealogic noted $15.4 billion in junk bonds were sold. The FT sees the pace of junk deals handily outpacing the record of $185.4 billion set in 2006.
The Wall Street Journal used the following deals to provide a flavor of how companies are using high-yield debt in the present market:
“First Data Corp. sold $510 million of 10-year notes this week, at 9.125%, to pay down bank debt due in 2014. Peabody Energy sold $650 million of 6.5%, 10-year notes to pay off the same amount of higher-priced debt due in three years. MultiPlan Inc., a health-care cost-management provider, sold $675 million of notes this week, at 9.875%, to help fund a buyout of the company. Cott Corp., a maker of store-branded soft drinks, sold $375 million of debt at 8.125% to fund its purchase of another company, Cliffstar Corp.”
The roads on the junk bond highway appear to be pothole free at the moment, however a cliff of debt is rapidly approaching over the next few years, so high-yield investors should travel carefully as conditions in the junk market potentially worsen. As we witnessed in 2008-2009, it can take a while to hit rock bottom in the riskier areas of the credit spectrum.
Read full Financial Times and Wall Street Journal articles on the high yield market.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
*DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds (including HYG and JNK), but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct position in First Data Corp., Peabody Energy (BTU), MultiPlan Inc., Cott Corp. (COT), Cliffstar Corp., or any security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.
Baseball, Hot Dogs, and Fixed Income Securities
Having just celebrated another 4th of July holiday, I reflected on the historical importance of our country’s independence finalized 234 years ago, the defining birthday of our great country that permanently marked the separation of our nation from Great Britain. In honor of this revolutionary milestone, our culture has added a few American traditions over the centuries, including watching baseball, and gorging ourselves on hot dogs, and apple pie.There is no better symbol of the importance our culture places on overindulgence than Nathan’s International Hot Dog Eating Contest, held each year on July 4th in Coney Island, Brooklyn, New York. The 95th annual contest winner was Joey Chestnut with a total of 54 HDBs (Hot Dogs & Buns) consumed, but not without some controversy thanks to the arrest of former Nathan’s champ Takeru Kobayashi, who watched from the sidelines this year due to a contract dispute with event organizers. Chestnut holds the world record set in 2009 with 68 HDBs, equivalent to about 20,000 calories. In setting the unmatched record, the winner of wiener eating contest inhaled in 10 minutes what an average human should consume in 10 days.
Bond Binge
In the financial markets, Americans have been pigging out on something else over the last few decades, and that is bonds. The craving for bonds has not changed since the end of the financial crisis either. According to Morningstar, since the end of 2008, investors have placed a net $390 billion into taxable bond funds and withdrawn -$45 billion out of U.S. stock funds. A continuation of these trends can be seen in the latest ICI (Investment Company Institute) fund flow data, in which we saw a +$6.3 billion inflow into bonds and a -$1.3 billion abandonment of stocks from the hands of jittery stock investors.
Beyond the endless checklist of worries (Europe default, China slowing, twin deficits, elections, etc.), there has been a consistent exodus of capital from money market funds due to the ridiculously low yields – the seven-day yield on taxable money-market funds, as measured by IMoneyNet, has recently held steady around 0.04%. For yield-hungry investors, bondholders are not getting a lot of bang for their buck if you consider the 10-Year Treasury Note is trading at 2.98%. Nothing in life comes for free, so in the case of Treasuries, bond investors are predominantly swapping market risk for interest rate risk. As I have repeatedly stated in the past, bonds are not evil, however fixed income exposure in a portfolio should be customized for an individual in the context of a diversified portfolio that meets investors’ objectives and risk tolerance.
Although the inflation skies are sunny now, there are clouds on the horizon and the stimulative monetary policies conducted over the last few years do not augur well for a likely climb in future interest rates.
Reversal of Fortune
In the competitive eating world, there is a so-called “reversal of fortune” that disqualifies eaters. At some point, you can only consume so much before the forces of nature take over.
I don’t know when the day of regurgitation will come for many fixed income securities, but managing your consumption of bonds, and the associated duration, becomes crucial as bond bellies continue to bulge. Takeru Kobayashi discovered this first hand at the Nathan’s 2007 championship event.
Baseball, hot dogs, and apple pie have been essential components to the unique aspects of the great American culture. In the world of investing, we have witnessed an acceleration in investors’ appetite for bonds – I just hope for the sake of overzealous bond investors, they will not suffer a reversal of fortune.
Wade W. Slome, CFA, CFP®
Plan. Invest. Prosper.
*DISCLOSURE: Sidoxia Capital Management (SCM) and some of its clients own certain exchange traded funds (including fixed income ETFs), but at the time of publishing SCM had no direct positions in any other security referenced in this article. No information accessed through the Investing Caffeine (IC) website constitutes investment, financial, legal, tax or other advice nor is to be relied on in making an investment or other decision. Please read disclosure language on IC “Contact” page.